A group of organisms of the same type that do not produce fertile descendants if mating with any other groups.
What is a species?
Paleontologists compare __________ to find similarities between species (both living and dead)
What are body structures?
The most distant relative of the chimpanzee.
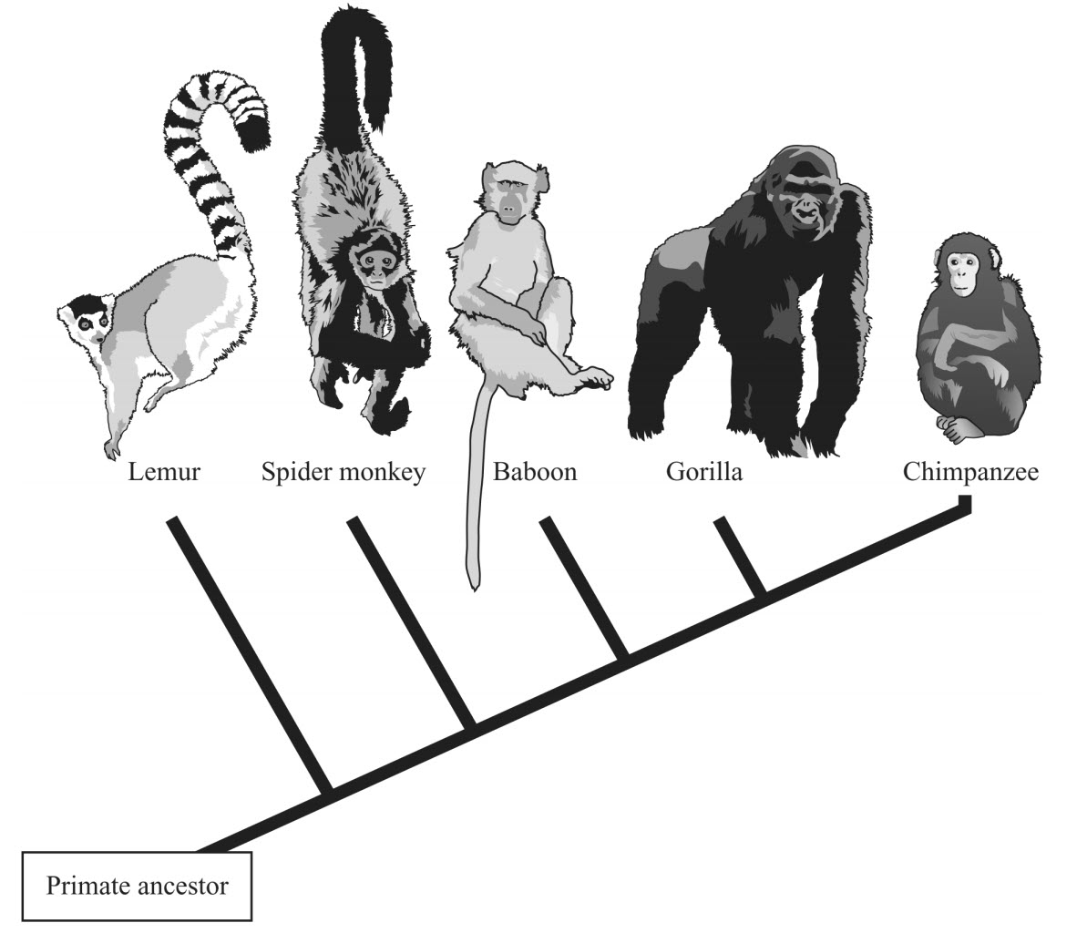
What is the lemur (who likes to move it move it)?
True or False: Multicellular life has been present for the entirety of Earth's history.
False. For most of Earth's history (3.5 billion years) life either didn't exist or consisted of single celled organisms.
Number of the most recent layer/event.
What is 3?
a) What is a common ancestor population?
b) What is a descendant species?
a) An older species from which 2 or more different species evolved.
b) A newer species that evolved from an ancestor population
How are a human arm and a cat front limb similar? What does this tell you?

They both share a "one-two-many" bone structure. They share a common ancestor.
This is a direct descendant of the oldest common ancestor.

What is the shark?
This is the most common division of time used to describe events on Earth - Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic are used with this word. Also, Taylor Swift uses it all the time.
What is an era?
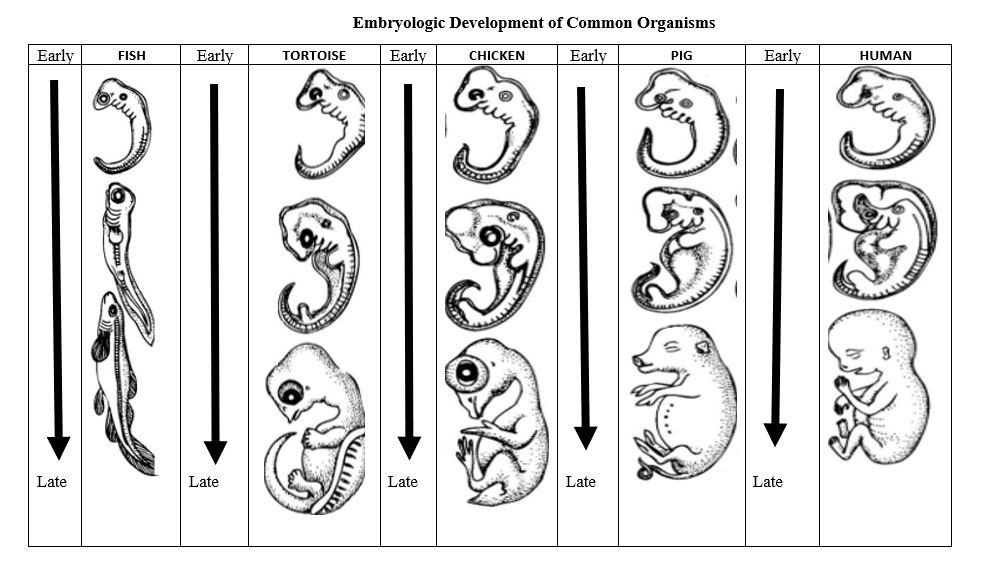
Because embryos have structures that are not present in the fully formed animals, which can show relationships that are not apparent by comparing fully developed structures.

Why do scientists compare the embryos of different species in addition to fully formed organisms of those species?
Similarities in the body structures of species is possible evidence that the species are ___________.
What is related?
Where do organisms get their body structures from? Where do species get their body structures from?
They inherit them (like all traits) from their parents. Species inherit body structures from ancestor populations.
There are 7 of these on this cladogram.
How many traits are there?
Which of the following changes in traits would take the longest time. Why?
a) A population of tortoises evolves longer necks due to higher location of food sources.
b) A population of fish develop lungs and limbs to survive on land.
c) A population of birds keeps its wings but loses the ability to fly because of little predation.
b) Developing lungs and limbs require very big changes to body structures. The larger the structure change, the longer amount time it takes.
This organism lived for a long time, and now its fossil is found in both the oldest and the youngest layers.

What is D?
Describe the process of speciation. Give 2 examples of speciation that we discussed in class.

A population is divided into different environments and evolves separately into 2 different species.
Ex: Tortoises on Galapagos. Polar Bears. Ducks on Hawaiian Islands. Apple flies and Hawthorn flies. Squirrels on the Grand Canyon. Spotted owls.
A trait shared by the platypus, kangaroo, and elephant.
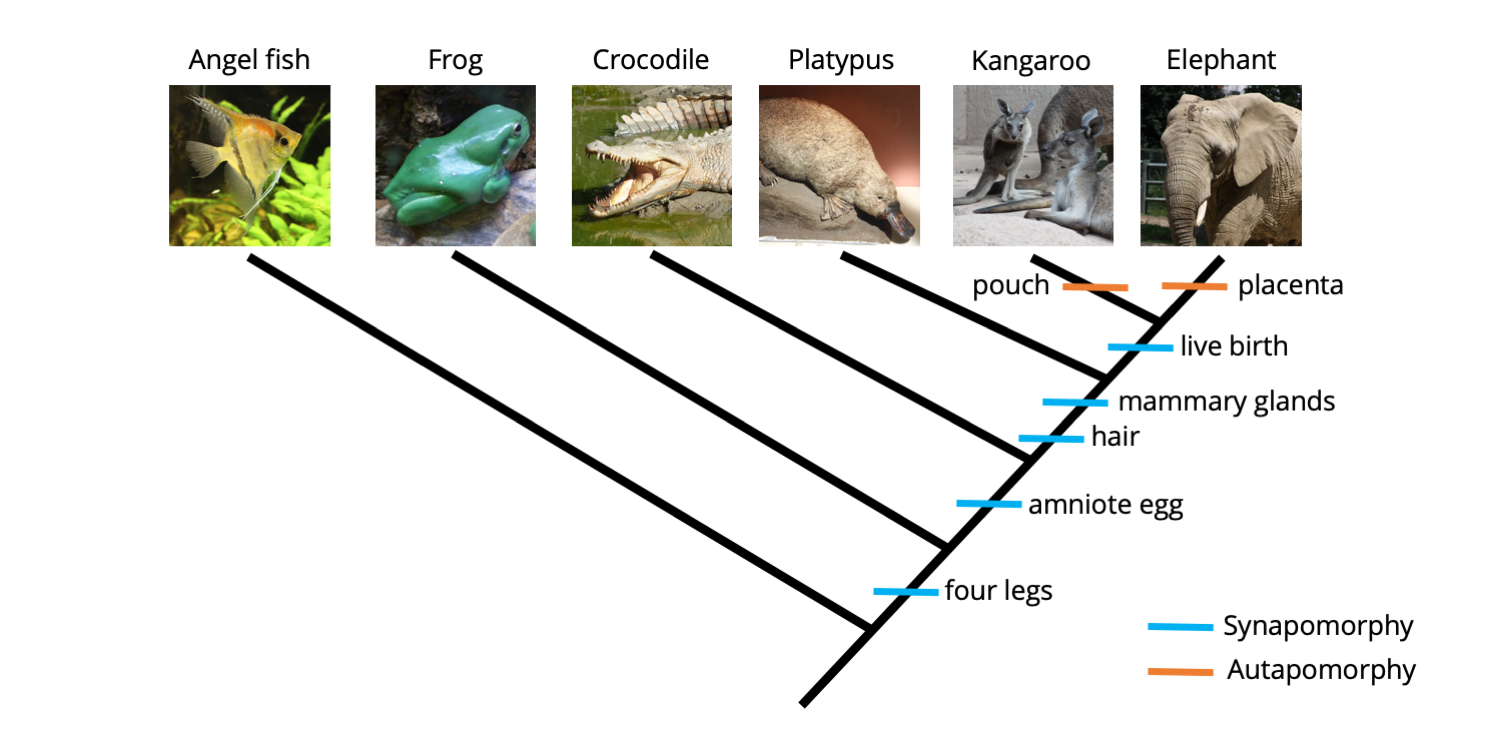
What is:
- Mammary glands?
- Hair?
These are animals that share a recent common ancestor.
What are:
- Mammal-like reptiles and mammals?
- Non-avian dinosaurs and birds?
- Snakes and lizards?
Put the following events in the correct order to show changes over evolutionary time:
1) A single population gets separated into different environments
2) Two very similar descendant populations have small differences in their structures
3) A single population is living in a stable environment
4) Two descendant populations look very different, though they have many similar structures
3, 1, 2, 4
At the first stage, these embryos all share this structure.
What are:
- Gill slits?
- Eyes?
- Notochord?
- Tail?