a related organism from a previous generation
Ancestor
What do we call group of organisms of the same type that do not reproduce with any other groups?
species
Where do species inherit their body structures from?
their ancestor populations
How are species organized on an evolutionary tree?
They are organized by similarities.
Organisms on the same branch have similar traits / body structures.
True or false: life has been very diverse for all of Earth's history.
Explain your answer.
False. For most of Earth's history life either didn't exist or was very simple, like single-celled organisms.
paleontologist:
a scientist who studies fossils in order to understand the ancient history of life on Earth
What is the cause of speciation?
Changes in the environment
When do body structures stay stable?
When the environment stays the same
If a species splits and starts living in two different environments what is likely to happen?
The two species are likely to evolve differently. potentially into two different species
How does Natural Selection work as a driving force for evolutionary change?
The environment will weed out the less well-adapted individuals and only those best adapted to survive will be able to pass their genes to the next generation.
WILD SQUARE -- What will you get???
Not this (evolutionary) time! Pick another question worth 300 or less.
WILD SQUARE - What will you get???
Your species branches off into two different environments! Choose one of the following options:
1. Your team gets a second turn after this one.
2. Your team can steal ONE TIME and answer another group's question.
Which of the following changes in traits would take the longest time. Why?
a) A population of tortoises evolves longer necks due to higher location of food sources.
b) A population of fish develop lungs and limbs to survive on land.
c) A population of birds keeps its wings but loses the ability to fly because of little predation.
b) Developing lungs and limbs require very big changes to body structures. The larger the structure change, the longer amount time it takes.
In class we put these events in order for a Warm-up. Explain what this is saying in your own words.
2) A single population gets separated into different environments
3) Two very similar descendant populations have small differences in their structures
1) A single population is living in a stable environment
4) Two descendant populations look very different, though they have many similar structures
Answers will vary.
Members of a single population living in the same environment will stay the same as each other. Something might happen to separate some of the individuals off into an environment that is different. Over long periods of time, small differences will develop in the populations based on the differences in their environments. Over very long time periods, the two populations will become different species which will look and behave vert differently although they still share some structures from a common ancestor population.
WILD SQUARE - What will you get??
Congratulations - your species branches off with an advantageous trait!
Pick another question worth 300 or less. It is now worth double.
Give an example of an adaptive trait
any example that helps an organism survive
Give an example of a non-adaptive trait
Any trait that won't help an organism survive in their environment (Brown fur in a snowy enviroment)
How does an ancestor population evolve into descendant species with differences in their shared structures?
They split into different environments and evolve different adaptive traits to survive in the new environments
Pelvises (hipbones) are a body structure that is important for carrying the weight of animals that walk on land. Whales live in water, but still have pelvises. Finding this body part in animals that don’t walk on land is best explained how?
Whales have an ancestor that walked on land. As whales were separated into a new environment, they inherited the hipbone body structure from their ancestor population but adapted different traits (lost legs - gained tails for swimming) that helped them survive in the aquatic environment.
What information does the structural similarities tell you about the 3 different organisms?

They all have the one, two, many shared structure. They must have inherited this from a common ancestor population.
Give an example of two species that have a shared structure and what is the structure?
Any two animals that share a skull, backbone, teeth, front limb structure, tail ...
Describe the process of speciation. Give 2 examples of speciation that we discussed in class.
A population is divided into different environments and evolves separately into 2 different species.
Ex: Tortoises on Galapagos. Polar Bears. Ducks on Hawaiian Islands.
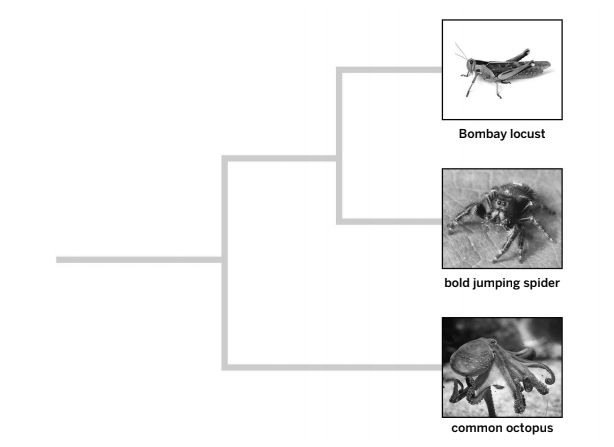
Explain the diagram
All three organisms have a common ancestor. However the top two organisms are more closely related
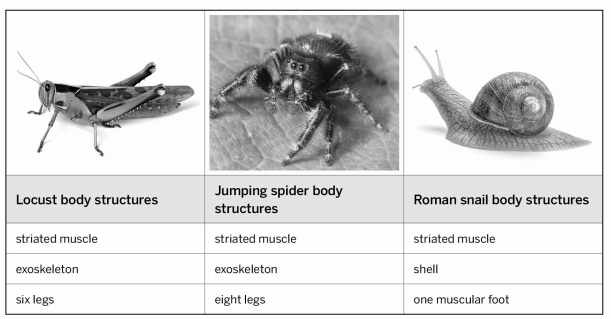
Explain the significance of the table
All three organisms have a common ancestor that had striated muscle. The Locust and Jumping spider are more closely related because they both have an exoskeleton
A tortoise and an eel both have jaws that help them grab food, but they have different jaw structures.
The tortoise has a bony beak that helps it bite plants. The moray eel has sharp teeth that help it eat fish.
What most likely explains why both have jaws and why the jaws are different?
They both have jaws because they inherited them from a common ancestor population that also had jaws.
The jaws are different because they separated into different environments that favored different traits. Over millions of years, small changes to the jaws build up and the structures become very different.