This is why a descendant species looks similar to its ancestor population.
What is species inherit their body structures from their ancestor populations.
This is the process by which one population evolves into two or more different species
What is speciation?
This word describes when two species share a common ancestor population
What is related?
This is how differences in body structures can be used as evidence for how closely two species are related.
What is when two species share a structure that is not shared with a third species, this can be evidence that the first two species are more closely related to each other than to the third species?
This is why diagnostic structures are used by paleontologists.

What is the name for the structures used to determine relatedness of species?
This is the evidence used to know if two species share a common ancestor.
What is body structures that are shared between two species are evidence that these two species inherited the shared structures from a common ancestor population ?
This explains why body structures may or may not change due to environment.
What is when the environment is mostly the same over time, body structures stay stable. When the environment changes over time, body structures may change due to natural selection?
This describes how paleontologists know when can know that two species are more closely related to each other than another species.
What is among any three species, the two species that separated most recently are the most closely related to each other
These structures would be seen in Dorudon, but later changed for the Orca and the Blue Whale.
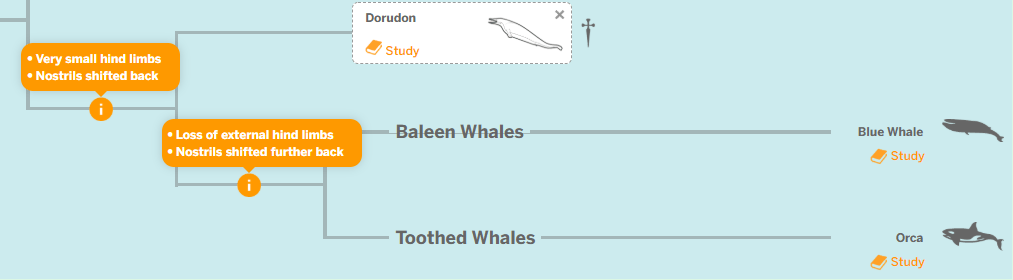
What are very small hind limbs and nostrils shifted back?
Theses structures are shared by the Whale and the Wolf.


What is the radius, ulna, distal bones, nostril, and pelvis?
According to the evolutionary tree, these traits are shared by both the Blue Whale and the Orca.

What is the loss of external hind limbs and nostrils shifted further back?
This is the method we studied to explain what happens when a population gets separated into two environments.
What is in populations separated into different environments, natural selection causes different changes to happen to each population. This causes their descendant species to end up with differences in their shared structures?
This is a reasonable prediction for the structure for population F based on what we see in the descendant population.
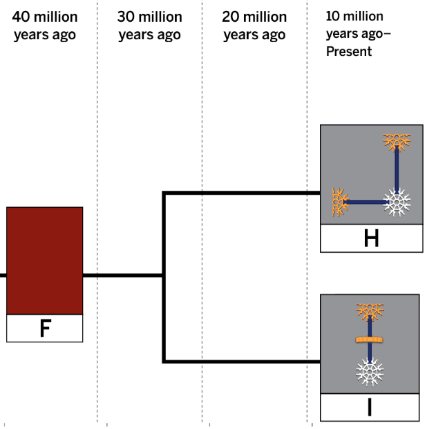
What is
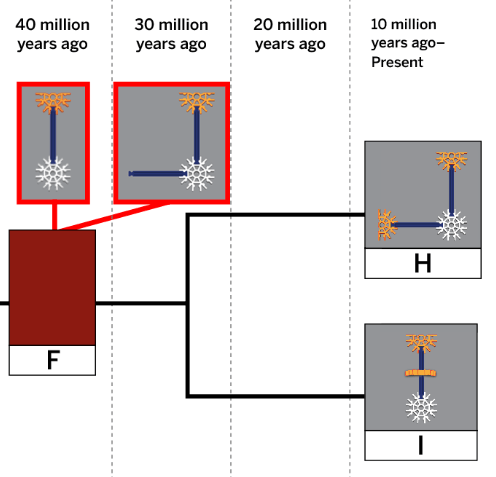
This is where Species C belongs based on the structures seen in its ancestor and the structures seen in the other descendant species.

What is space 2 on the evolutionary tree?
This structure is not shared by the Whale and the Wolf.


What is the back limb?
These are examples of how paleontologists make observations when examining organisms.
What is the Paleontologists' Observation Guidelines?

This calendar is an analogy that scientist use to explain when major events happened in evolution.

What is the calendar for evolutionary time?
This shape represents a shared structure from the ancestor population that is seen in all descendants.

What is the blue pentagon?
This explains how can you tell which species are more closely related than others.
What is in evolution, all species are related, so all species will have some shared structures. On an evolutionary tree, descendant species have shared structures with their common ancestor population, and paleontologists look at shared structures to understand how different species on the tree are related. To decide which species are more closely related to one another, paleontologists look for shared structures between the different species they compare. If two species have more shared structures in common, then those two species are more closely related; if two species have a diagnostic shared structure that another species does not have, this is evidence that these two species are more closely related.
This structure is shared between the Whale and the Wolf, but its location on the skull is different because the Whale lives in the ocean and the wolf lives on land.


What is the nostril?
This is why the fossil turtle and the hawk in the image below both share a bone structure called the atlas bone.

What is the turtle and hawk both share the same ancestor population that had an atlas bone and they inherited this structure from the ancestor population?
This explains why a mallard duck and a moose both have a foot bone called a metatarsal even though their feet look different.

What is the mallard duck and moose both inherited metatarsals from a shared ancestor population, but this population separated into different environments. In each environment, different types of feet with metatarsals evolved, which helped the populations survive?
This structure explains how the ctenophore, sea cucumber, and cuttlefish all share a common ancestor.

What is the structure for neuron cells?
This structure is evidence for the Capuchin and Bottlenose dolphin being more closely related to each other than to the Echidna.

What is lacking cervical ribs?
This explains how closely related the Roman snail, the Cuttlefish, and the Mussel are.

What is all three species share an ancestor population because they all have the structure for a mantle. The Roman snails and cuttlefish share a more recent ancestor population because they both have a radula structure.