This type of trait can become more common in a population because the organism is more likely to survive long enough in its environment to reproduce.
What is an adaptive trait?
This is a group of organisms of the same kind (in one or more populations) that do not reproduce with organisms from any other group.
What is a species?
This is a body structure in two or more species that features the same parts (for example, the same bones)
What is a shared structure?
This is a more recent species that evolved from an ancestor population.
What is a descendant species?
These body structures can be seen in the mystery fossil.

What is the body structures for skull, teeth, , neck bones, front limb structure (arms), rib bones, backbone, hip bone (pelvis), back limbs (legs), and tail?
This type of trait can become lesson common in a population because the organism is less likely to survive long enough in its environment to reproduce.
What is a non-adaptive trait?
This is a part of an organism (for example, one or more bones).
What is a body structure?
This is the process by which species adapt to environmental changes over a very long time
What is evolution?
This is an older population from which two or more newer species descended
What is a common ancestor population?
These body structures are shared structures between the mystery fossil and the whale.

What is the body structures for skull, teeth, , neck bones, front limb structure (arms), rib bones, backbone, hip bone (pelvis), and tail?
This is why the traits of an offspring are almost identical to the traits of their mom and their dad.
What is parents pass their traits to their offspring (genetic inheritance of traits)?
These body structures are labeled on the body diagram for the Dire Wolf.

What is the body structures nostril, pelvis, radius, ulna, and distal bones?
These are traits seen on the evolutionary tree below are from the common ancestor population for Whales and Humans.
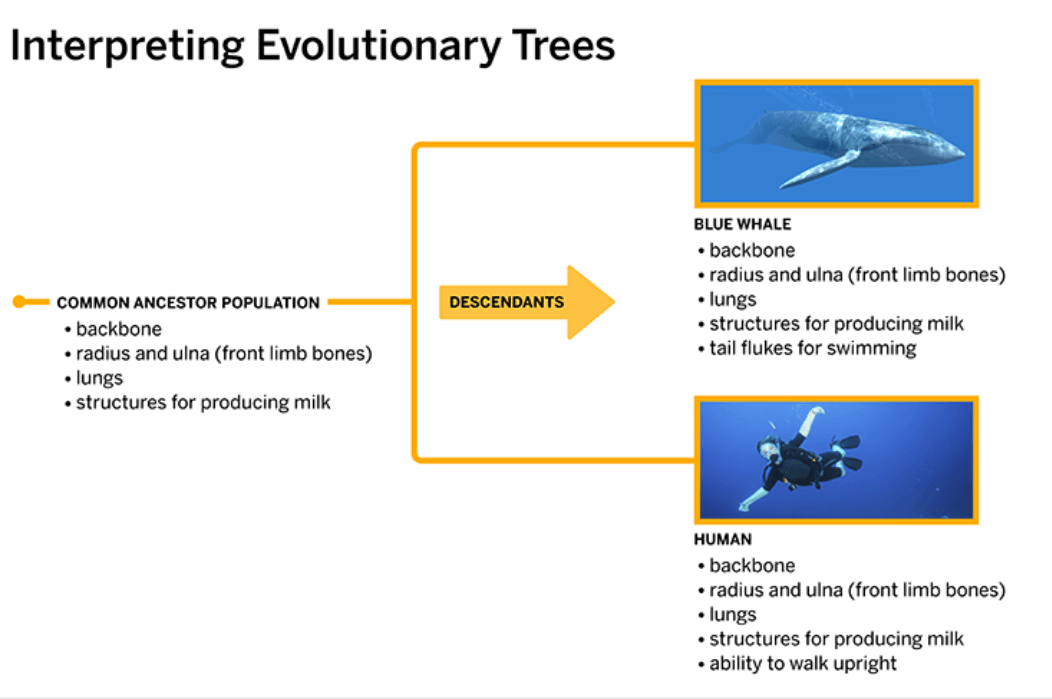
What is a back bone, a radius and ulna (front limb bones), lungs, and structures for producing milk?
This is the common ancestor population on the evolutionary tree in the image below.
What are reptiles?
These body structures are shared structures between the mystery fossil and the wolf.

What is the body structures for skull, teeth, , neck bones, front limb structure (arms), rib bones, backbone, hip bone (pelvis), back limbs (legs), and tail?
This is how new traits can appear in a population.
What is a mutated trait?
This object is used to show scale (relative size of) the size of body structures in a fruit bat. This object is used because the fruit bat is bigger, but similar in size.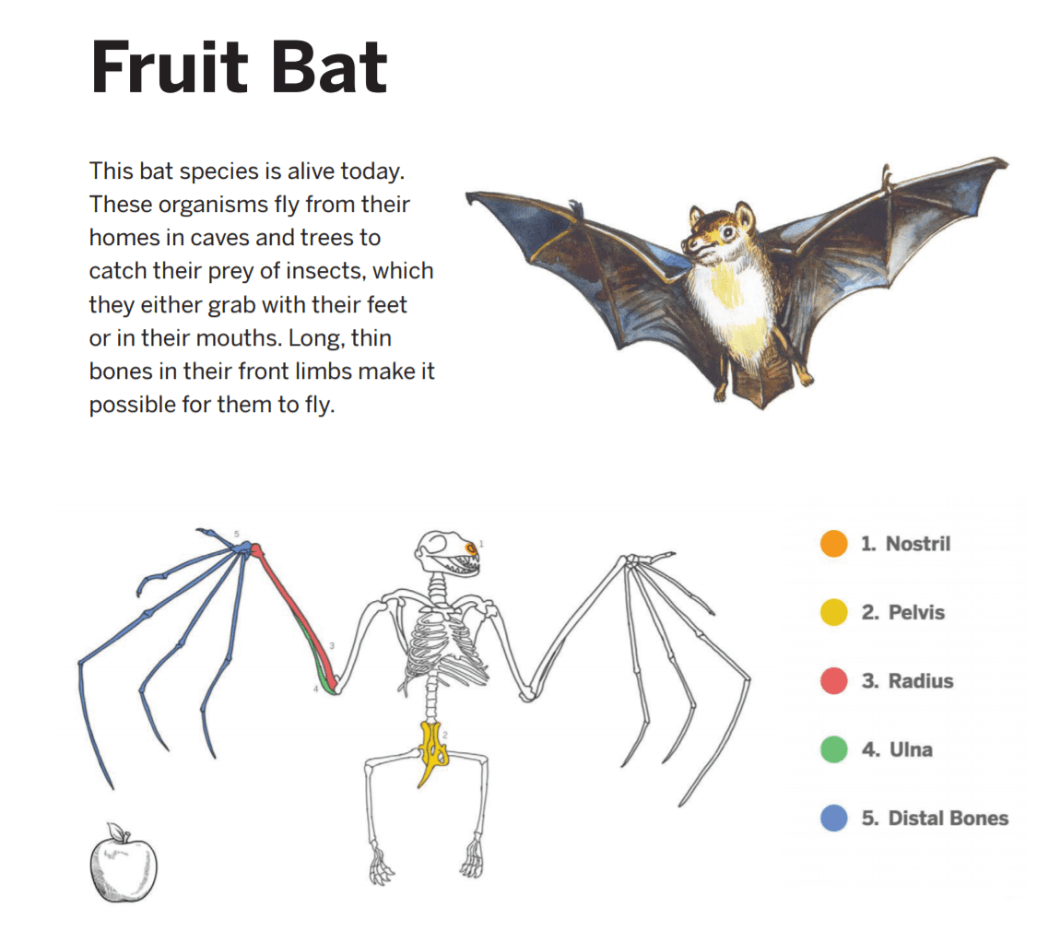 ctures in
ctures in
What is an apple?
This structure is unique to the whale. The structure is not seen in the common ancestor population or humans.
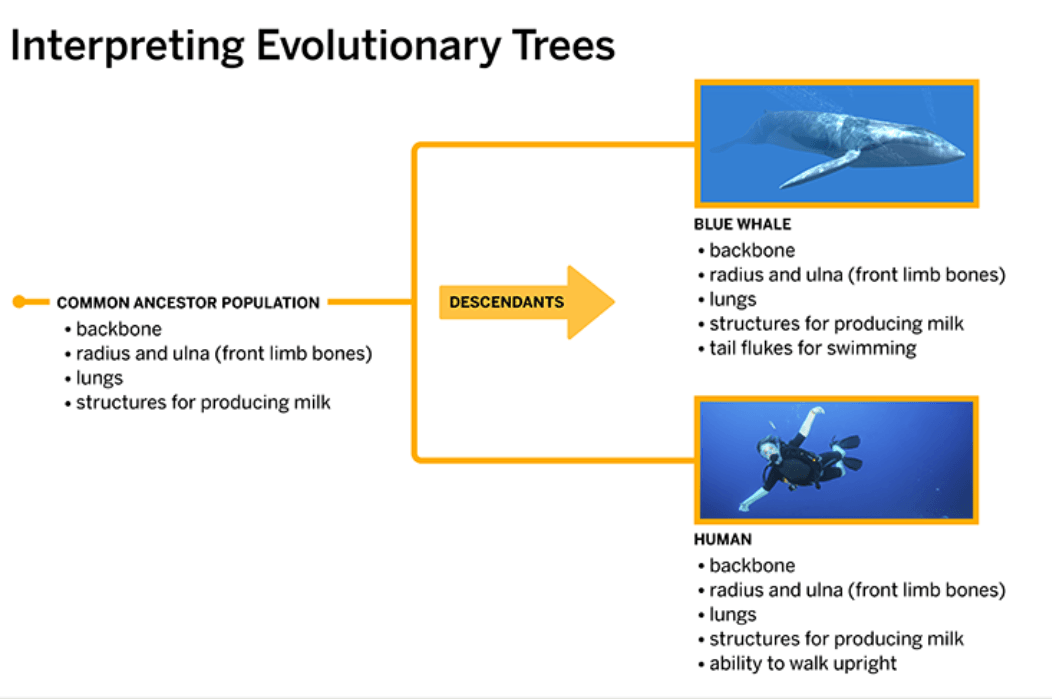
What is tail flukes for swimming?
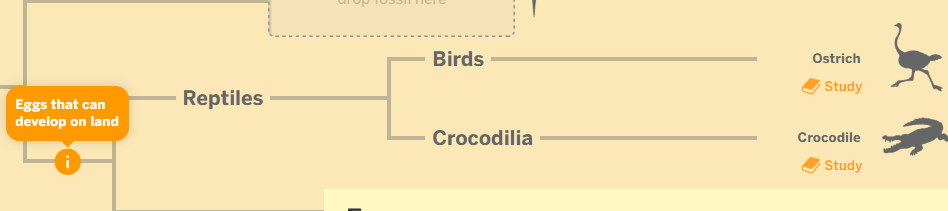
These are the descendant species on the evolutionary tree in the image below.

What are birds and crocodila?
This explains why descendant species share structures with their ancestor populations. (Key Concept 1)
What is species inherit their body structures from their ancestor populations.

This population has a larger variation of traits.
What is the population in Venezuela?
These body structures are shared between Titanotylopus and the Camel
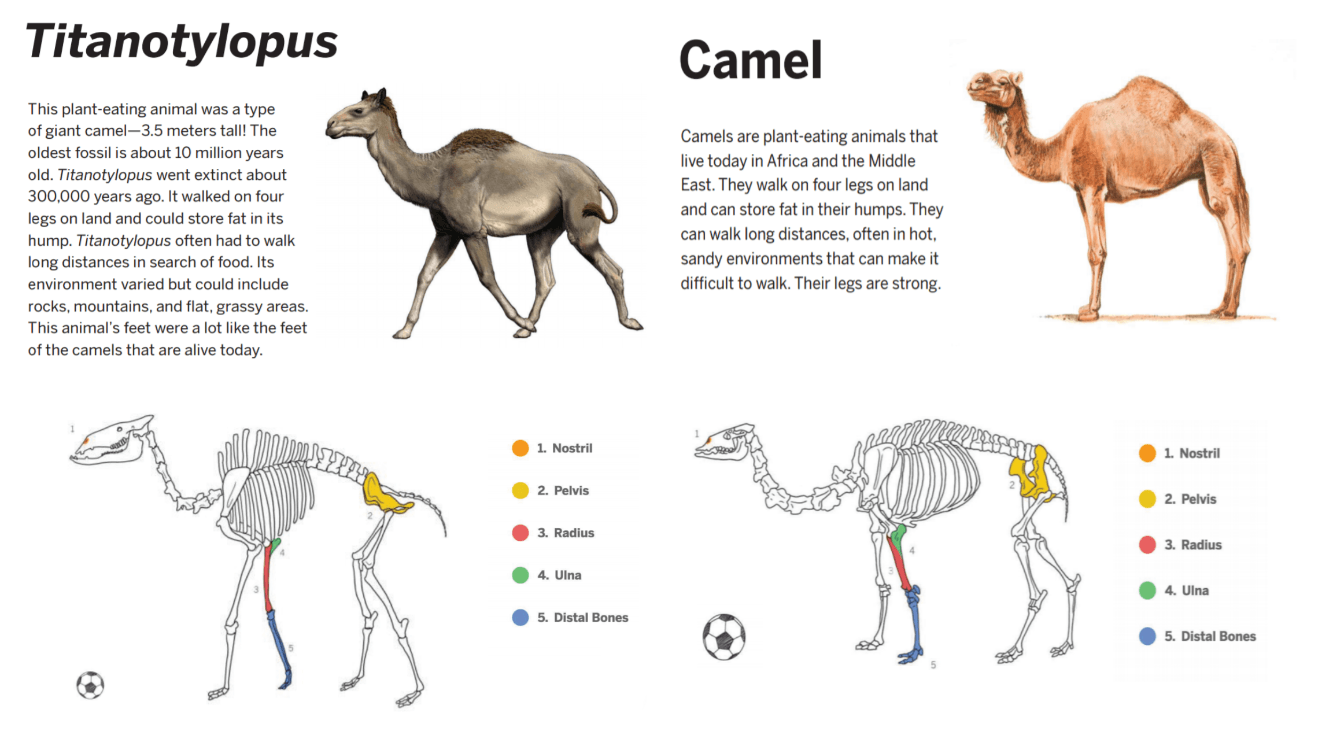
What is the body structures nostril, pelvis, radius, ulna, and distal bones?
This ability is unique to humans. The ability is not seen in the common ancestor population or whales.

What is the ability to walk upright?
This trait shared by the ancestor population and the descendant species. The split point of the branches (nodes) shows that all organisms after that point have this trait.

What is the trait of eggs that can develop on land?
This explains how shared structures are used as evidence for ancestor populations. (Key Concept 2)
What is body structures that are shared between two species are evidence that these two species inherited the shared structures from a common ancestor population?