British naturalist and father of evolutionary theory.
Charles Darwin
A model of evolution in which gradual change over a long period of time leads to diversity.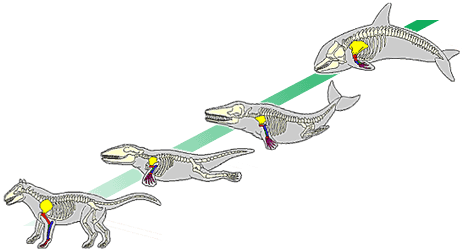
Gradualism
The human practice of breeding animals or plants that have certain desired traits.
Artificial selection
Each generation has more offspring that can be supported by the environment.
Overproduction
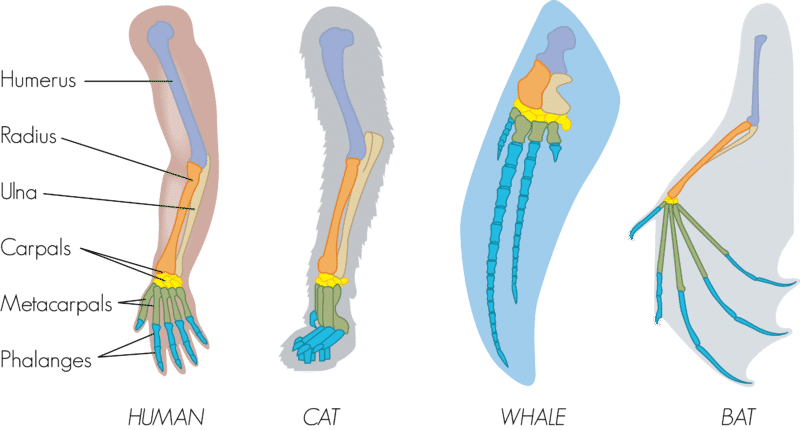
Body parts that are similar in structure to different organisms but perform different functions.
Homologous Structure
The process by which living organisms change over time through changes in the genome
Evolution
The study of fossils or extinct organisms.
paleontology
The ability of a trait to be passed from one generation to the next.
Heritability
The idea that species change over time, gives rise to new Species.
Descent with Modification
Body part that is similar in function as a body part of another organism but is structurally different.
Analogous Structure
A group of organisms that are closely related and can mate to produce fertile offspring.
Species
The idea that evolution occurs in spurts instead of following the slow, but steady path that Darwin suggested.
Punctuated equilibrium
The process by which individuals that are better adapted to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully than less well adapted individuals.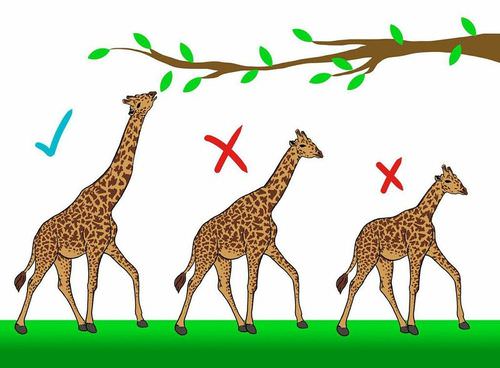
Natural selection
A group of organisms of the same species that live in a specific geographical area.
Population
Remnants of an organ or structure that functioned in an earlier ancestor, no longer functions today.
Vestigial Structure
The trace or remains of an organism that lived long ago, most commonly preserved in sedimentary rock.
Fossil
Essential principle in geology where older rocks and rock layers are formed first and are beneath younger rocks and rock layers.
Law of Superposition
The process of becoming adapted to an environment; an anatomical, physiological, or behavioral change that improves a population's ability to survive.
Adaptation
The measure of an organism's ability to survive and produce offspring relative to other members of a population.
Fitness
The study of the similarities and differences in the embryos of different species.
Embryological Evidence
type of natural selection that favors one extreme phenotype over other phenotypes
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/directionalselection.svg-56a2b38e5f9b58b7d0cd8859.png)
Directional selection
type of natural selection that favors individuals with extreme traits over those
Disruptive selection
Differences in physical traits of an individual from the group to which it belongs.
Variation
The study of the geographical distribution of living organisms and fossils on Earth.
Biogeography
The study of molecules and DNA found in living things to understand their evolutionary history.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/3-D_DNA-56a09ae45f9b58eba4b20266.jpg)
Molecular Evidence
Genetic Sequencing