The irreversible disappearance of a species is called
Extinction
A relationship in which one organism kills and eats another organism.
Example: a lion hunts and kills a zebra
Predation
All the biotic and abiotic factors in a certain area.
Ecosystem
How an organism responds to its environment
Behavioral Adaptation
The change in genetic characteristics of populations over many generations
Evolution
The main cause of species extinction is
habitat loss
A relationship in which one organism benefits and one is harmed.
Example: a tick on a dog
Parasitism
One individual living thing
Desert animals have a considerably more efficient excretory system, leading to less excretion of water through the kidneys. This is an example of a
Functional Adaptation
An inherited trait that helps an organism survive in a certain environment is called
Adaptation
The introduction of harmful levels of chemicals or waste into the environment is called
Pollution
When two or more organisms attempt to use the same limited resource.
Example: a squirrel and a bird both eat seeds from a tree
Competition
All the populations of organisms living in an area and interacting.
Community
An external modification on an organisms body
Physical or Structural Adaptation
The process in which organisms with more desirable characteristics survive longer and are more likely to reproduce is called
Natural Selection
When resources are consumed faster than they can be renewed it is called
Resource Depletion
A cooperative relationship between two species in which both benefit.
Example: a bee and a flower
Mutualism
All life on Earth
Biosphere
Wolves traveling in packs is an example of a
When two or more species evolve in response to each other it is called
Coevolution
Exposure to environmental toxins can cause a variety of adverse health effects. This is an example of
Pollution
A relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed.
Example: a bird builds its nest in a tree
Commensalism
A group of the same species living in a certain area.
Population
An internal process that helps an organism survive
Functional Adaptation
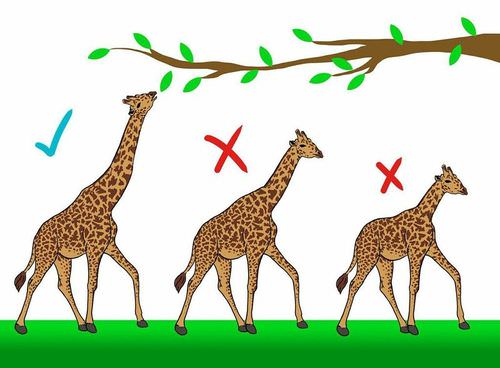
This image shows
Natural Selection
Desertification, overfishing, and overconsumption are examples of
Resource Depletion
Parasitism
Mutualism
Commensalism
A group of similar organisms that can breed to produce fertile offspring is called a
species
A giant anteater's tongue is 2 feet long and can flick in and out of its mouth 150 times per minute. This is an example of a
Physical or Structural Adaptation
The evolution of a new species due to geographic isolation is called
Speciation