This inhaler combination, is recommended over LABA/ICS for most COPD patients without frequent exacerbations.
LABA/LAMA or dual bronchodilator therapy
The NOTT and the MRC trial the 1980s showed survival benefit with this treatment in COPD with hypoxemia
Oxygen therapy
NOTT and the MRC trial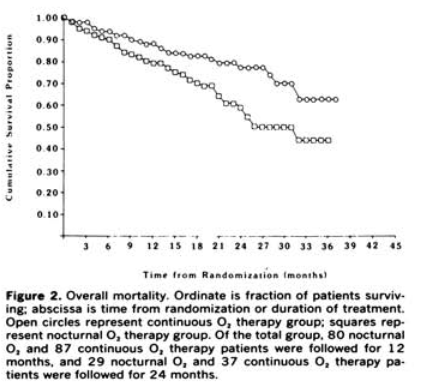

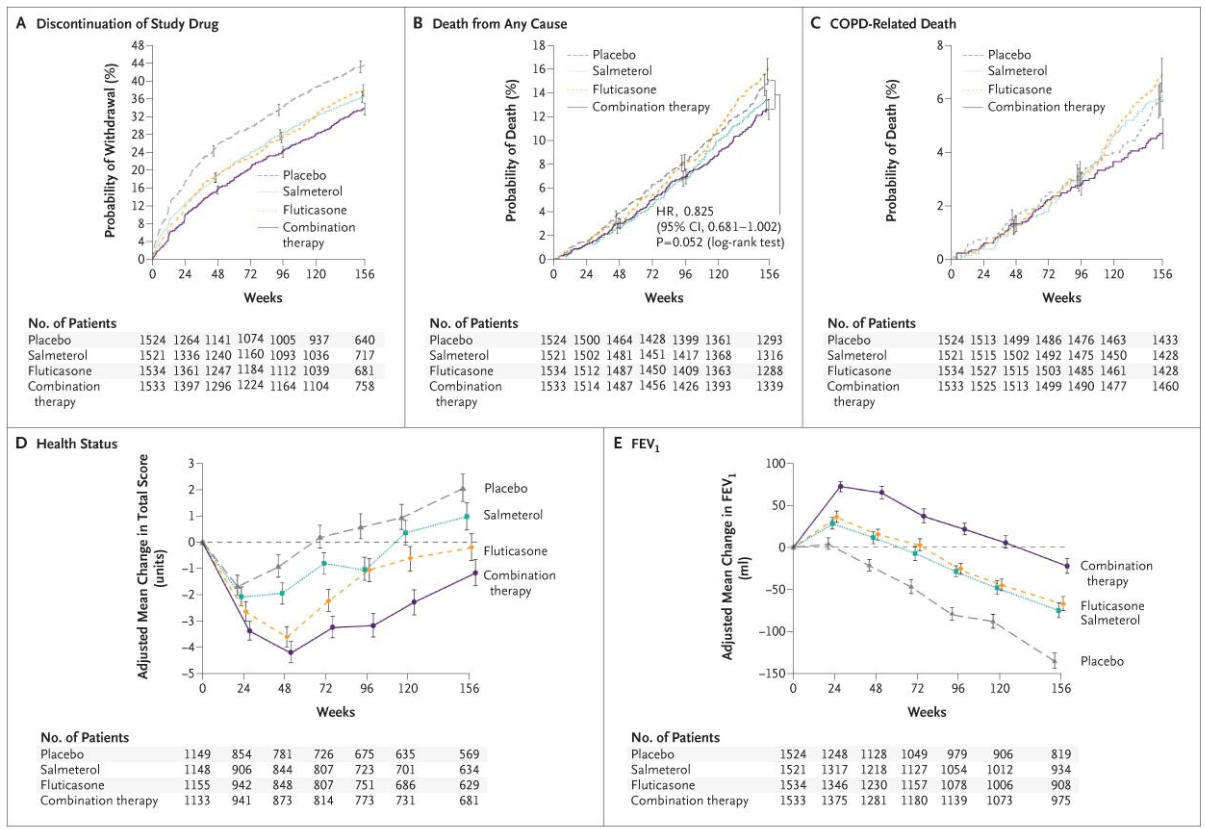
TORCH- A large and influential 2007 trial, compared the combination inhaler fluticasone/salmeterol (FP/SAL) with its individual components and placebo. While the combination reduced exacerbation rates, it did not achieve a statistically significant reduction in this common study metric, the study's primary endpoint
Hint: Its very patient centric
-ALL Cause Mortality
TORCH - Towards a Revolution in COPD Health (TORCH) study

Before inhalers, this methylxanthine class was mainstay therapy
theophyllines
This oxygen trial in moderate resting or exercise-induced desaturation found no mortality or hospitalization benefit.
Hint: Biblical figure who's wife turned into a pillar of salt
LOTT
"In patients with stable COPD and resting or exercise-induced moderate desaturation, the prescription of long-term supplemental oxygen did not result in a longer time to death or first hospitalization than no long-term supplemental oxygen, nor did it provide sustained benefit with regard to any of the other measured outcomes. "

This anti–IL-5 monoclonal antibody, used in asthma and initially rejected by the FDA for COPD, significantly reduced exacerbations in most COPD patients with high eosinophils in phase 3 trials.
Mepolizumab
Mepolizumab (FDA Advisory Committee Vote, 2018): In 2018, an FDA advisory committee voted against approving mepolizumab (Nucala) for COPD, concluding that the data did not sufficiently support its use for reducing exacerbations.
However, In May 2025:
Approval based on the positive MATINEE and METREX phase III trials
MATINEE data included reduction of exacerbations leading to hospitalisation and/or emergency department visits
Nearly 70% of patients in the US who are inadequately controlled on inhaled triple therapy have a BEC ≥150 cells/μL

This PDE-4 inhibitor reduces exacerbations in chronic bronchitis with severe COPD, especially after hospitalization.
Roflumilast
The MACRO and COLUMBUS trials showed that chronic therapy with this oral medication reduced acute exacerbations in COPD patients
Azithromycin
MACRO
COLUMBUS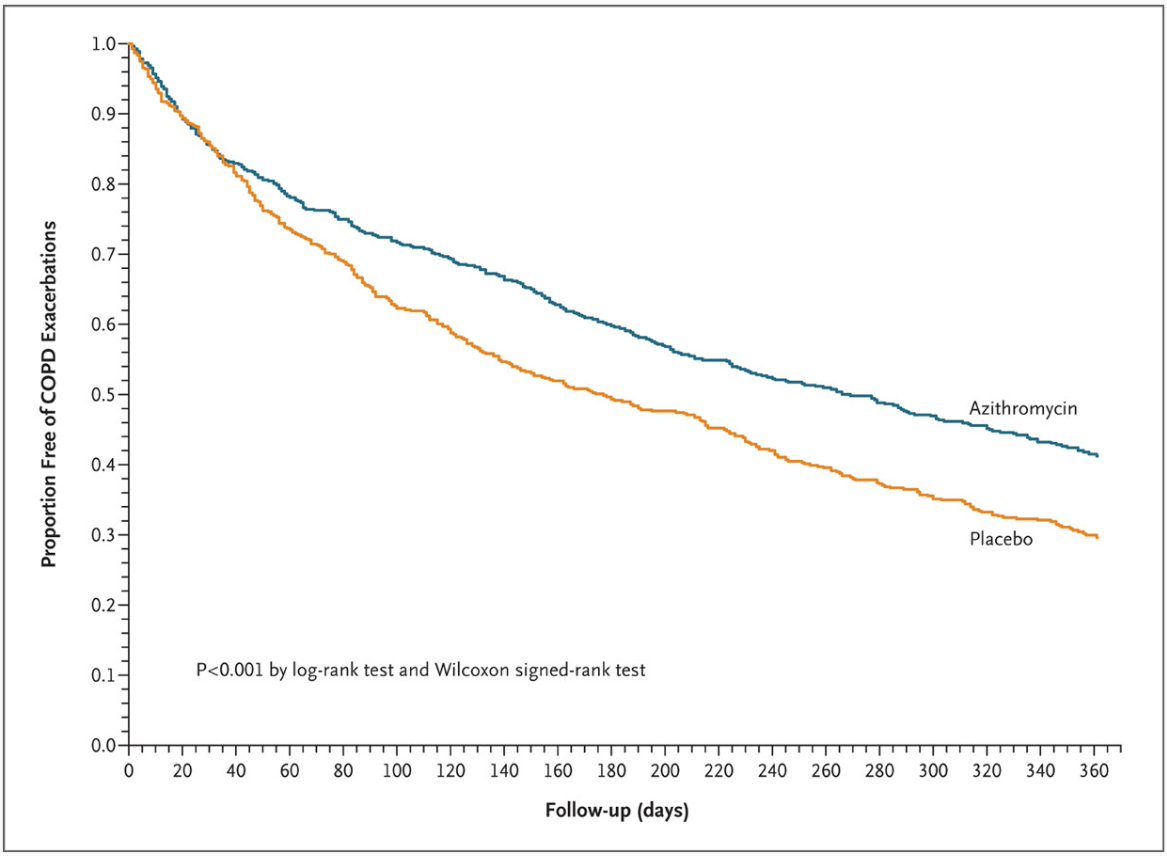


STATCOPE - This trial demonstrated that this commonly prescribed medication (not related in any way to the lungs) did not reduce COPD exacerbations in patients
Hint: blocks enzyme involved in cholesterol synthesis
STATCOPE - (Simvastatin Therapy for Moderate and Severe COPD)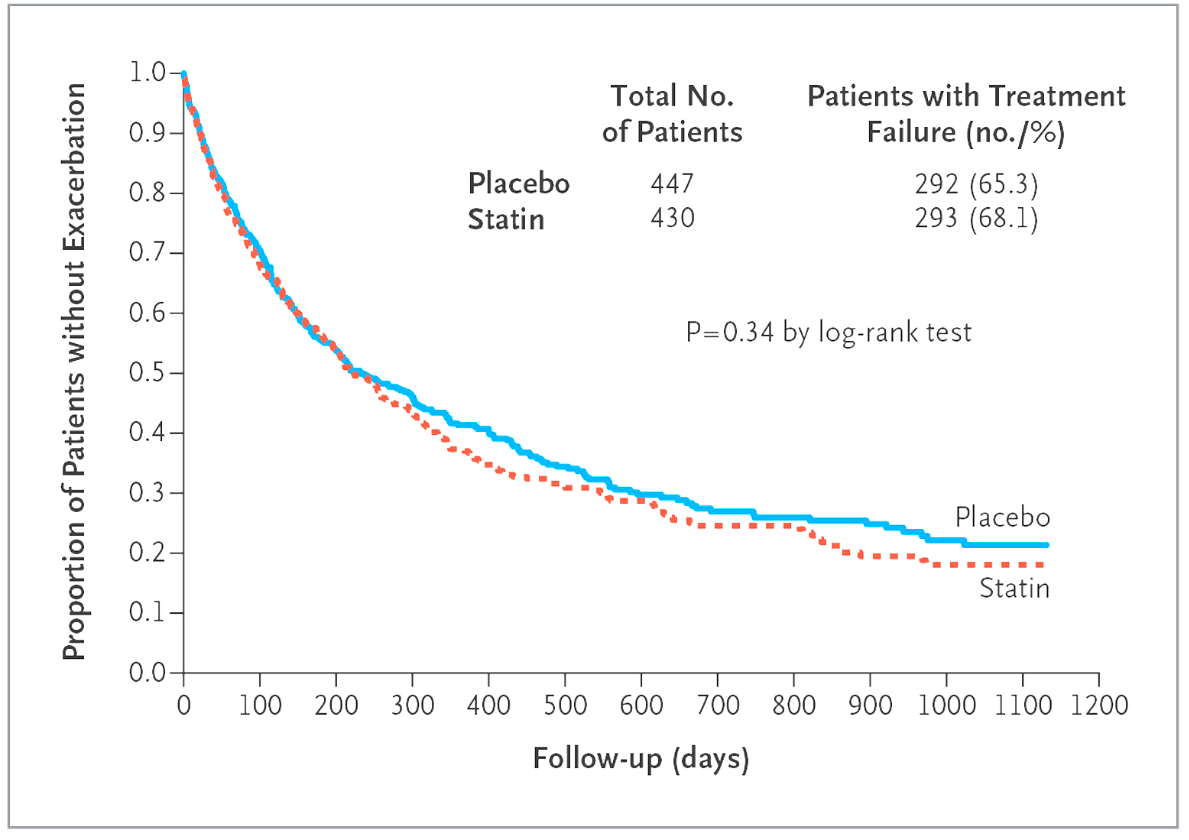

In the 1970s–80s, this was the main oxygen source for home therapy
compressed gas cylinders
This trial showed safe ICS withdrawal in stable COPD on triple therapy if bronchodilators were optimized.
Hint: Biblical King Solomon was famous for his...
WISDOM
"In patients with severe COPD receiving tiotropium plus salmeterol, the risk of moderate or severe exacerbations was similar among those who discontinued inhaled glucocorticoids and those who continued glucocorticoid therapy. "

This anti–IL-5 receptor antibody showed a modest reduction in COPD exacerbations in eosinophilic patients but missed its primary endpoint in broader populations.
Benralizumab
GALATHEA and TERRANOVA (2019): These trials investigated the biologic drug benralizumab, which targets interleukin-5 to reduce eosinophilic inflammation. Despite success in treating severe asthma, the studies found that adding benralizumab to standard COPD therapy did not significantly reduce the rate of COPD exacerbations compared to placebo, even in patients with high blood eosinophil counts.
GOLD guidelines recommend this blood test to guide ICS use in COPD
blood eosinophil count
The GOLD COPD Guidelines use blood eosinophil counts (BEC) to guide the use of inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), recommending ICS for patients with high eosinophil counts (≥300 cells/μL) and for patients with at least one COPD exacerbation and a BEC of ≥100 cells/μL, or more specifically, ≥300 cells/μL for new treatment escalation. Patients with BEC <100 cells/μL are less likely to benefit from ICS and have a higher risk of pneumonia and chronic bacterial infection, while ICS may provide benefit in the 100–300 cells/μL range, especially for those with frequent exacerbations.
UPLIFT, a 4-year trial of this LAMA showed improved lung function, QoL, and reduced exacerbations.
Tiotropium
UPLIFT - Understanding Potential Long-Term Impacts on Function with Tiotropium (UPLIFT)

BRONCUS - This study found that high-dose N-acetylcysteine did not significantly reduce this key COPD metric in Western COPD cohorts.
- Exacerbation rates
BRONCUS - Bronchitis Randomized on NAC Cost-Utility Study
The BRONCUS trial was a multi-center, randomized, placebo-controlled study that investigated the effectiveness of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The trial aimed to determine if NAC could slow the rate of decline in lung function (FEV1) and reduce the yearly rate of COPD exacerbations, with cost-utility also being a consideration. Key findings from the original BRONCUS trial and related analyses indicated that while NAC did not significantly reduce the overall rate of lung function decline or the number of exacerbations, a subgroup analysis suggested potential benefits in patients not receiving inhaled corticosteroids.
This obsolete surgical procedure for emphysema involved removing chest wall portions.
thoracoplasty
POET-COPD - This trial showed tiotropium reduced exacerbations more than this commonly used LABA
Salmeterol
POET-COPD - "results show that, in patients with moderate-to-very-severe COPD, tiotropium is more effective than salmeterol in preventing exacerbations."

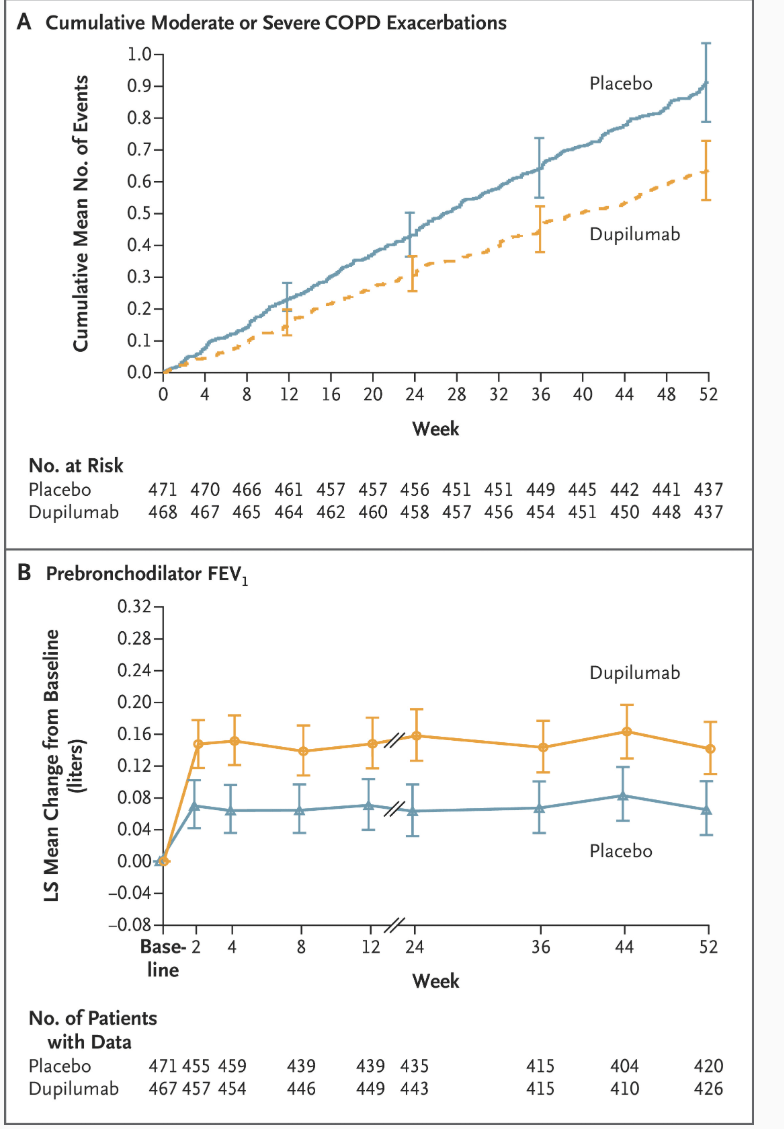
This anti–IL-4/IL-13 agent, approved for asthma and COPD with eosinophillic subtype, significantly improve lung function and reduced exacerbations in COPD patients in phase 3 trials.
dupilumab
Dupixent (dupilumab) was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in September 2024 for the add-on maintenance treatment of adults with inadequately controlled chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and an eosinophilic phenotype
In severe emphysema, this therapy targets air trapping/hyperinflation directly to improve symptoms
Endobronchial valves
VENT Trial-"found that unilobar placement of endobronchial valves has a modest positive effect on expiratory flow rates and distance on the 6-minute walk test. This improvement comes at a cost of more frequent hemoptysis and COPD exacerbations in the few months after valve implantation in patients with advanced, hyperinflated emphysema. Overall, there were modest improvements in quality of life, dyspnea, incremental exercise response, and supplemental oxygen use. "
STELVIO trial- "Endobronchial-valve treatment significantly improved pulmonary function and exercise capacity in patients with severe emphysema characterized by an absence of interlobar collateral ventilation. "


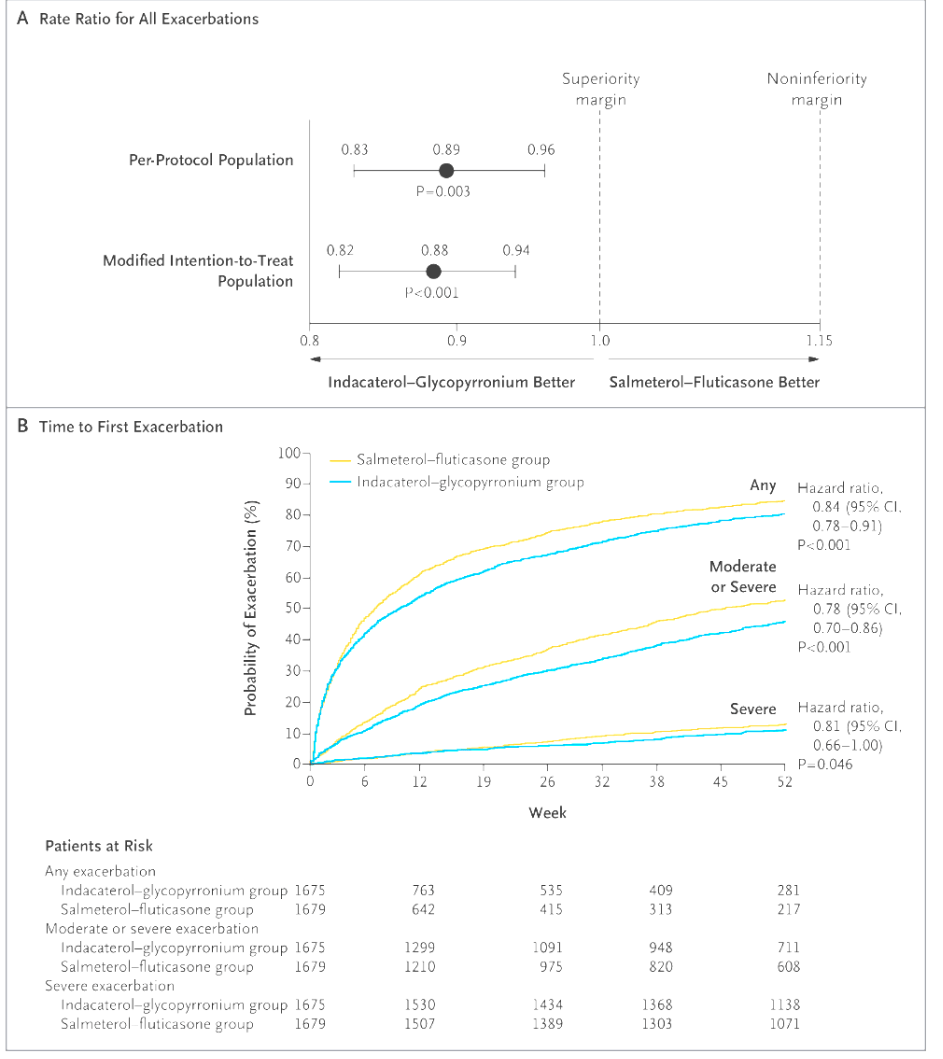
FLAME - Indacaterol–glycopyrronium outperformed this common ICS-LABA in reducing exacerbations.
Fluticasone-Salmeterol
FLAME

ViDiCO-This large study found that daily supplementation with this failed to reduce moderate-to-severe COPD exacerbations in the overall trial population.
Hint: an abbreviation that makes sense
Vitamin D3
ViDiCO
This drug, once used in COPD, caused pulmonary hypertension and was withdrawn in the 1990s.
Hint: One component of a infamous weight loss drug also introduced in the 90's.
fenfluramine
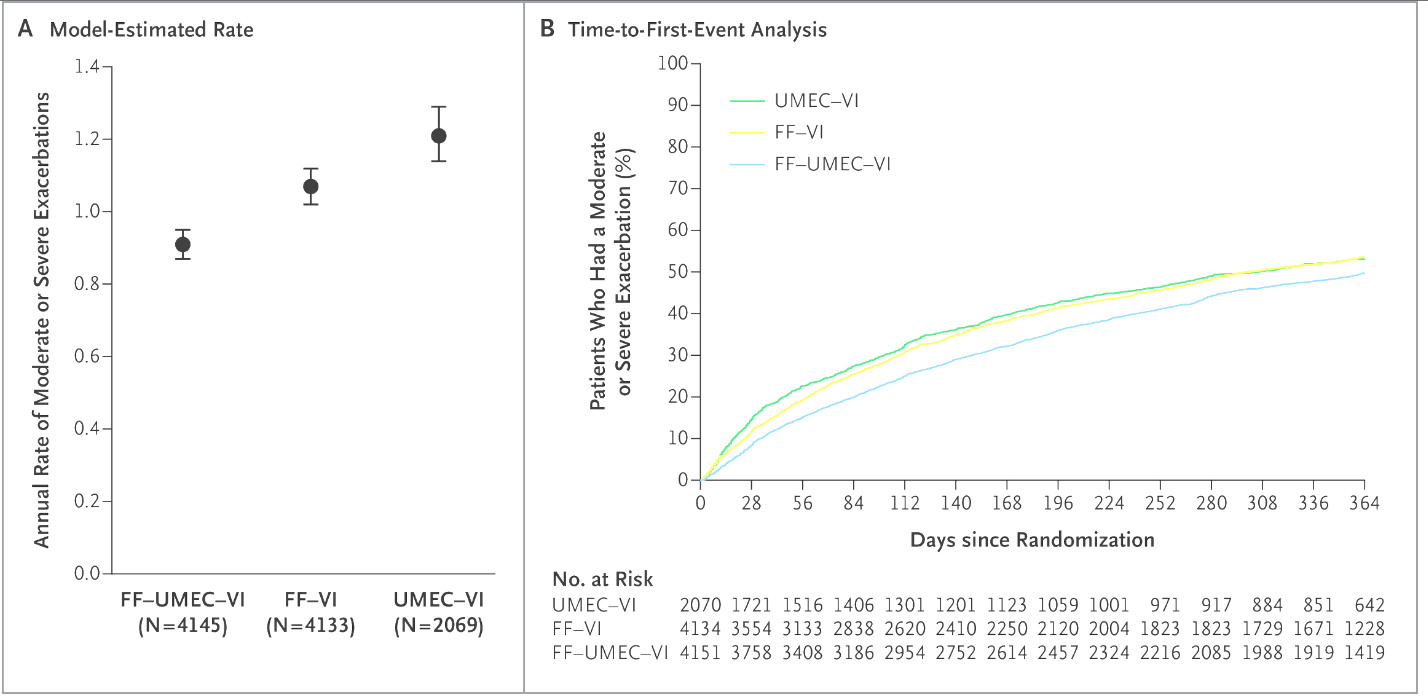
This triple therapy trial (fluticasone furoate/umeclidinium/vilanterol) reduced exacerbations compared with dual therapy.
Hint: Acronym means to have a big effect or influence
IMPACT
This anti–TNF-α biologic, widely used in autoimmune diseases, failed to improve symptoms or outcomes in COPD and raised infection risk
infliximab
Clinical trials have shown that infliximab is not an effective treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and may increase the risk of serious side effects, including cancer and infections. Infliximab is an anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) antibody, and while TNF-α is involved in the inflammatory process of COPD, blocking it has not been successful.
Key findings from infliximab trials in COPD
- Lack of efficacy: A phase 2 dose-finding study involving patients with moderate to severe COPD found no clinical benefit from infliximab. There were no improvements in the primary endpoint (Chronic Respiratory Questionnaire score) or secondary measures like lung function (FEV1) and exercise capacity. Similar findings of no clinical benefit were observed in a study of patients with mild COPD.
- Increased risks of side effects:
- Malignancies: The phase 2 trial initially observed a higher rate of cancer diagnoses in infliximab-treated subjects compared to placebo (5.7% vs. 1.3%). A long-term follow-up study (RESULTS COPD) was conducted to further track malignancy and mortality risk.
- Pneumonia: The incidence of pneumonia was also higher in patients who received infliximab.
This oral drug, once common for COPD exacerbations, is discouraged due to toxicity and no mortality benefit.
theophylline
"Trials on theophylline for COPD show limited benefit for exacerbation prevention (like the TWICS trial, which found no difference when added to inhaled corticosteroids) but may offer some improvement in lung function and reduction in hospitalizations when used as an add-on to inhaled therapy, according to meta-analyses. While higher doses are largely replaced by inhaled drugs, low-dose theophylline has been investigated for its potential anti-inflammatory and respiratory-muscle-strengthening effects, though it comes with a significant risk of adverse drug reactions "
Name this trial:
Triple therapy(budesonide/glycopyrrolate/formoterol) reduced exacerbations and signaled mortality benefit compared to glycopyrrolate–formoterol or budesonide–formoterol.
Hint: Shares a name with one of Aristotle’s rhetorical appeals or the word for the characteristic spirit of a culture, era, or community
ETHOS
Half points for IMPACT, TRILOGY, TRIBUTE or KRONOS as well
BLESS - This trial found that long-term prophylaxis with this antibiotic did not improve QoL in non CF bronchiectasis patients
Erythromycin

Before triple therapy, this combo of oral drug and nebulized epinephrine was used in acute COPD.
aminophylline + racemic epinephrine
NETT - This surgical trial showed survival benefit for select emphysema patients undergoing this procedure
Lung volume reduction
NETT - National Emphysema Treatment Trial - "Overall, lung-volume–reduction surgery increases the chance of improved exercise capacity but does not confer a survival advantage over medical therapy. It does yield a survival advantage for patients with both predominantly upper-lobe emphysema and low base-line exercise capacity. Patients previously reported to be at high risk and those with non–upper-lobe emphysema and high base-line exercise capacity are poor candidates for lung-volume–reduction surgery, because of increased mortality and negligible functional gain. "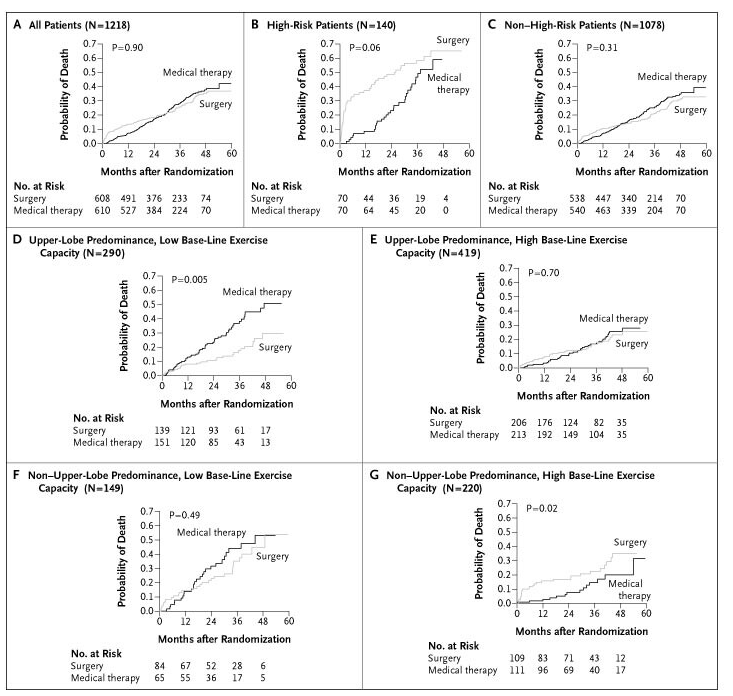
This anti–IL-1β antibody, studied for COPD after cardiovascular benefits in the CANTOS trial, showed no reduction in COPD exacerbations.
Canakinumab