Define: Theory
- a well-supported testable explanation of phenomena thathas occurred in the natural world
Differentiate between a polar covalent bond and a nonpolar covalent bond. Using the words:
• electronegativity
• unequally and equally
• sharing/shared/share
- polar covalent bond: two atoms; one with a higher ELECTRONEGATIVITY; resulting in UNEQUAL SHARING of electrons between the two
- nonpolar covalent bond: two atoms; fairly equal ELECTRONEGATIVITY; resulting in EQUAL SHARING of electrons between the two
Contrast inter vs intra-molecular interactions.
INTERmolecular bonds:
- Hydrogen bonds
- Van Der Waal's interactions
- Hydrophobic effect
INTRAmolecular bonds:
- Covalent bonds
- Ionic bonds
Define:
H+
OH-
[ ]
Acid
Base
Buffer
- Hydrogen ion/proton
- Hydroxide ion
- Concentration of
- a substance that donates H+ (protons)
- a substance that accepts H+ (protons)
- a substance that resists the change of pH (consisting of weak acid-base pairs)
Why is carbon the most significant element in regards to forming large and complex molecules?
- carbon can form four bonds (tetravalent)
- carbon forms covalent bonds
Differentiate artificial selection and natural selection.
AS- humans choose what survives.
NS- nature chooses what survives.
Distinguish between ionic and covalent chemical bonds.
Ionic bond: TRANSFER electrons (cation; anion)
Covalent bond: SHARING electrons (polar; nonpolar)
How do the number of H-bonds between water molecules determine the state of water?
- 0 bonds = gas
- 1,2,3 bonds = liquid
- 4 bonds = solid
How can we recognize acids and bases in chemical reactions?
Acid formulas start with an H, forms H+ ions
Base formulas end with an OH, forms OH- ions
Contrast saturated vs. unsaturated hydrocarbon chains.
Saturated hydrocarbon chains contain the maximum number of hydrogens (NO double bonds between carbon).
Unsaturated hydrocarbon chains do not have the maximum number of hydrogen (DO have double bonds between carbon).
How is natural selection the driving force of evolution?
Species show evidence of “descent with modification” from common ancestors.
What role do electrons/valence shells play in chemical bonds?
- electrons dictate an atoms reactivity (whether it will look for an interaction)
What makes a molecule have polarity?
- having partial opposite charges due to higher electronegativity from one atom
Explain how this (very significant) buffer works.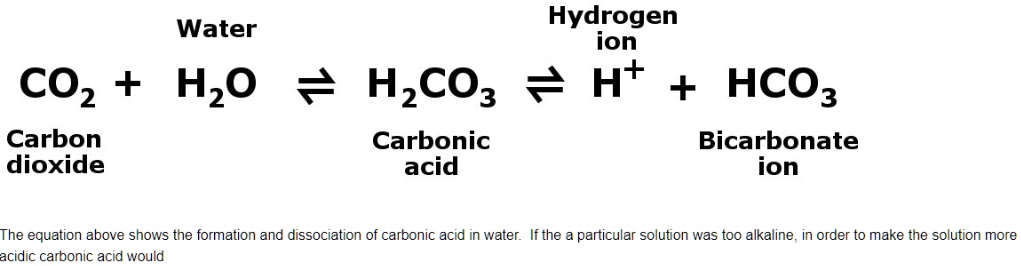
What are the 4 ways that carbon "skeletons" can vary?
1. Length
2. Double bond positioning
3. Branching
4. Presence of rings
What are the THREE domains of life?
1. Eukarya
2. Bacteria
3. Archaea
Identify the [6] major elements found in living organisms.
1. Sulfur
2. Phosphorus
3. Oxygen
4. Nitrogen
5. Carbon
6. Hydrogen
List and explain the four properties of water due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds.
1. High specific heat
2. Cohesion/adhesion
3. Universal solvent
4. Expansion upon freezing
Compare the pH of 11 to a pH of 10. Which is more acidic and by how much more?
- 10 is more acidic
- 10x more acidic
What is an isomer; identify the three types of isomers.
- molecules that share the same MOLECULAR formula but have different STRUCTURAL orientation
1. Geometric - organic molecule has double bonds between carbons which do not allow for rotations ("cis" and "trans")
2. Optical - asymmetric carbon -> chircal structure ("enantiomers" = mirror images)
3. Structural - same formula; different structural orientation
Name and classify the SIX kingdoms of life.
1. Bacteria
2. Archaea
3. Protists
4. Plantae
5. Fungi
6. Anamalia
Distinguish between the following pairs of terms: neutron, electron, proton, atomic number, atomic mass/weight.
- neutron: subatomic particle with a neutral charge
- electron: subatomic particle with a negative charge
- proton: subatomic particle with a positive charge
- atomic number: # of protons
- atomic mass/weight: # of protons +# of neutrons
Distinguish: hydrophobic and hydrophilic substances; a solute, a solvent, and a solution.
- hydrophobic: water-fearing (substances that are neutral/nonpolar)
-hydrophilic: water-loving (substances with partial opposite charges/polar)
-solute: substance that is being dissolved
-solvent: dissolving agent
-solution: 2 or more substances mixed together
If the [OH-] = 1 x 10-2 M, then:
[H+] =
pH =
If the [H+] = 1 x 10-10 M, then:
[OH-] =
pH =
1.
[H+] = 1 x 10-12
pH =12
2.
[OH-] = 1 x 10-4
pH = 10
What are the 7 different functional groups; describe their properties.
1. Hydroxyl Group (polar; hydrophilic)
2. Carbonyl Group (polar; hydrophilic)
3. Carboxyl Group (polar; hydrophilic)
4. Amino Group (polar; hydrophilic)
5. Phosphate Group (polar; hydrophilic)
6. Sulfhydryl Group (polar; hydrophilic)
7. Methyl Group (nonpolar; hydrophobic)