How many bones are in our body?
206
What is the heart's function?
Carries oxygen and nutrients to the cells of the body
Carries carbon dioxide and other waste away from the cells of the body
911 calls are for _________ only.
Emergencies
This is a break in the bone. S/S include deformity, limited ROM, pain/tenderness, swelling, and discoloration. Can be open or closed.
Fracture
List the 3 types of burns and which layers of the skin they affect
Superficial: Epidermis
Partial-Thickness: Epidermis and Dermis
Full-Thickness: Epidermis, Dermis, Hypodermis
A blockage in the heart caused by fat buildup or blood clot, causes restricted blood flow to a part of the heart.
Myocardial Infarction
List 3 functions of the skeletal system
Support of the body
Protection of soft organs
Movement due to attached skeletal muscles
Storage of minerals and fats
Blood cell formation
What are the layers of the wall of the heart from superficial to deep?
Epicardium
Myocardium
Endocardium
List 3 reasons you should call 911 for.
You should only dial 9-1-1 if someone is hurt, in danger, or if you are in need of police, fire, or emergency medical assistance.
This is an injury to tissues including ligaments surrounding a joint.
Sprain
A person was burned on their head, anterior trunk, and anterior right leg. What % of TBSA is burned?
36%
List 3 S/S of an MI
Pressure, tightness, pain, or a squeezing or aching sensation in your chest or arms that may spread to your neck, jaw or back
Nausea, indigestion, heartburn or abdominal pain
Shortness of breath
Cold sweat
Fatigue
Lightheadedness or sudden dizziness
What are the 4 bone classifications?
Long, Short, Irregular, Flat
List what each wave represents in cardiac conductivity?
- P Wave
- QRS
- T Wave
- P: Depolarization of atria
- QRS: depolarization of ventricle fibers
- T: Repolarization of ventricles
True/False: To be a 911 operator you need a high school education.
True
A strain is overstretching of a tendon holding a muscle to the bone. It is caused by overexertion or lifting. What are the 3 main S/S of a strain?
Sudden Pain
Swelling
Bruising
This is a cut or injury caused by a sharp object such as a knife or razor. The edges of this wound are smooth and regular.
Incision
This is as an irregularly fast or erratic heartbeat (arrhythmia) that affects the heart's upper chambers. Heart can beat 150-220x per min
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
What are the 3 types of muscle, where are they found, and are they voluntary or involuntary?
Smooth (involuntary, found in places like stomach and intestines)
Skeletal (voluntary, attached to bones, allows you to move)
Cardiac (involuntary, found in walls of the heart)
This is the pacemaker of the heart (no abbreviations)
Sinoatrial Node
About how much does a firefighters gear weigh?
60lbs
This is when the end of the bone is displaced from a joint or moved out of it's normal position within a joint.
Dislocation
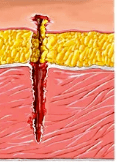 What type of wound is this?
What type of wound is this?
Puncture
List 5 risk factors for SVT
Heart disease
Heart failure
Other heart conditions, such as Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
Chronic lung disease
A lot of caffeine
Drinking too much alcohol
Drug misuse, including cocaine and methamphetamine
Pregnancy
Smoking
Thyroid disease
Certain medications, including asthma medications and cold and allergy drugs
What are the layers of the skin from superficial to deep?
Epidermis
Dermis
Hypodermis
This causes ventricular contraction
Purkinje Fibers
All firefighters are also licensed _______ _______ ________.
Emergency Medical Technicians
With a neck or spinal injury the most important thing to remember with a patient is to keep them ___________ or they can become _________.
Immobilized
Paralyzed
This occurs when a body part is removed or separated from the body. Bleeding is usually extensive and heavy.
Amputation
What is A-Fib so dangerous?
The prevention of blood flow from atria to ventricles can cause blood clots.
List 3 functions of the integumentary system:
Protection
Cushions and insulates and is waterproof
Protects from chemicals, heat, cold, bacteria
Screens UV
Synthesizes vitamin D with UV
Regulates body heat
Prevents unnecessary water loss
Sensory reception (nerve endings)
List the 14 steps of blood flow through the heart
Blood reaches heart through superior vena cava and inferior vena cava
To right atrium
Tor tricuspid valve
To right ventricle
To pulmonary valve
To main pulmonary artery
To left pulmonary artery and right pulmonary artery
To lungs-blood receives O2
From lungs to pulmonary veins
To left atrium
To bicuspid valve
To left ventricle
To aortic valve
To aorta (largest artery in the body)
Blood with oxygen then goes to all cells of the body
List 5 other non-emergent duties of a firefighter besides putting out fires.
Fire and Life Safety Presentations
Day Care Visits
Community Service
Station Tours
Special Appearances
Hydrant Flow Tests
Pre-Fire Plans
Physical Training
Monthly Training
Skills Improvement Training
Hazmat Training
Professional Development
Outside Training Opportunities
Basic EMT Refresher Course
Medical Refresher Training
Apparatus Maintenance
Upkeep of Station
List the 6 different types of fractures.
Comminuted
Compression
Depressed
Impacted
Spiral
Greenstick
What kind of integumentary injury is this?
Laceration
List 3 S/S A-Fib
Sensations of a fast, fluttering or pounding heartbeat (palpitations)
Chest pain
Dizziness
Fatigue
Lightheadedness
Reduced ability to exercise
Shortness of breath
Weakness