True/False: Evolution only occurs slowly and gradually
FALSE
Small population size, short generation time, and big shifts in the environment can lead to rapid evolution
What is the definition of evolution?
Change in gene frequencies over time
Reproductive isolation, in the absence of geographical isolation, can result in what?
Sympatric Speciation
Mutations
Evolution occurs at the ___________ level and natural selection occurs at the __________ level.
Evolution = Population Level
Natural Selection = Individual Level
T/F
Adaptations are changes to the genes that increase survivorship and arise through demand
False. They do not arise through demand.
True/False: The bottleneck effect takes place when a few individuals become isolated from a larger population.
False
Founder Effect = a few individuals become ISOLATED from a larger population
Bottleneck Effect = a sudden REDUCTION in population size due to environmental change
What is the key evolutionary unit?
Species
What type of isolation is the most important for the biological species concept?
Reproductive Isolation
Geographical isolation is generally (intrinsic/extrinsic).
Extrinsic
Occurs outside of the population/organism
What are the 2 requirements a trait must have in order to be able to evolve?
1. The trait must be heritable
2. There must be variation in the traits
Draw a graph for each of the 3 patterns of natural selection (write which is which).
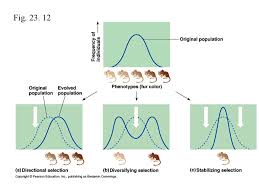
What types of speciation takes place when a portion of the population is separated?
Peripatric Speciation
What type of isolation occurs when species occupy different habitats.
Ecological Isolation
Allopatric is caused by ______ factors
Extrinsic. Think of a barrier arising and permanently separating two populations.
Define a scientific theory.
A hypothesis with LOTS of support
What is the difference between "p," "p^2," & "2pq"?
p = frequency of the dominant ALLELE in the population
p^2 = percentage of homozygous dominant INDIVIDUALS
2pq = percentage of heterozygous INDIVIDUALS
Define divergent evolution.
Organisms with a recent common ancestor evolve to look different due to different environmental pressures.
One of the driving forces of ___________ __________ is habitat heterogeneity.
What is artificial selection?
Manually controlling which traits are selected for and passed down to future generations
List 1 of Darwin's observations and 1 of Darwin's inferences. (Hint: you learned 2 of each)
Observations
1. Individuals in a population vary in their heritable characteristics
2. Organisms produce more offspring than the environment can support
Inferences
1. Individuals that are well suited to their environment tend to leave more offspring than other individuals
2. Over time, favorable traits accumulate in the population
List the 5 assumptions of Hardy Weinberg.
1. No natural selection
2. Random mating
3. No mutations
4. No migration
5. Infinite population
List the 5 types of pre-zygotic isolation.
1. Ecological
2. Temporal
3. Behavioral
4. Mechanical
5. Gametic
List the 5 mechanisms of evolution.
1. Natural Selection
2. Sexual Selection
3. Mutations
4. Genetic Drift
5. Gene Flow
What is convergent evolution?
When unrelated/distantly related species begin to adapt for the similar traits over time.