Name the three domains of life and what kind of organisms are found in each
Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. Prokaryotic organisms belong either to the domain Archaea or the domain Bacteria; organisms with eukaryotic cells belong to the domain Eukarya
Explain what pH is
pH is a measure of how acidic/basic water is. The range goes from 0 - 14, with 7 being neutral. pHs of less than 7 indicate acidity, whereas a pH of greater than 7 indicates a base. pH is really a measure of the relative amount of free hydrogen and hydroxyl ions in the water.
Describe the differences between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids
Saturated fatty acids have hydrocarbon chains connected by single bonds only. Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds.
Explain the role of peroxisomes in eukaryotic cells
Peroxisomes contain enzymes that oxidize certain molecules normally found in the cell, notably fatty acids and amino acids. Those oxidation reactions produce hydrogen peroxide, which is the basis of the name peroxisome.
Identify both of these molecules: 
The left is DNA and the right is RNA
The unified cell theory states that all living things are composed of one or more cells; that the cell is the basic unit of life; and that new cells arise from existing cells.
Describe the formation of a hydrogen bond and explain how it differs from covalent & ionic
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules, between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as a N, O, or F atom and another very electronegative atom.
Describe the monomers that make up proteins, carbohydrates and nucleic acids
Amino acids are the monomers that makeup proteins, Monomers of carbohydrates are simple sugars (monosaccharides), nucleic acid monomers are called nucleotides.
List the components of the endomembrane system
the endomembrane system includes the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes.
State 4 elements essential to life that make up 96% of living matter
oxygen, carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen
Distinguish between a hypothesis and a theory
In scientific reasoning, a hypothesis is an assumption made before any research has been completed for the sake of testing. A theory on the other hand is a principle set to explain phenomena already supported by data.
Define and distinguish among atomic number, mass number, atomic weight and valence.
The atomic number is the number of protons in an element, while the mass number is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. Valence is the property of an element that determines the number of other atoms with which an atom of the element can combine. The atomic mass is the mass of an atom.
Explain what determines protein conformation and what is meant by the 4 levels of protein structure
Protein conformation may be defined as the arrangement in space of its constituent atoms which determine the overall shape of the molecule. The conformation of the protein arises from the bonding arrangements within its structure
Secondary: Backbone, Tertiary: R groups (functional)
Name the 3 components of the cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton of a cell is made up of microtubules, actin filaments, and intermediate filaments.
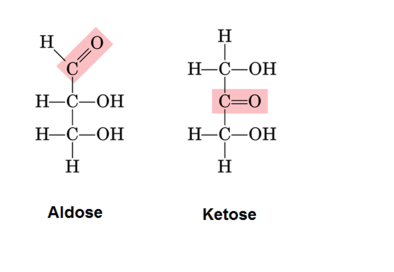
What's the difference between a ketose and an aldose?
Distinguish between archaea and protists
Explain the octet rule
The octet rule refers to the tendency of atoms to prefer to have eight electrons in the valence shell.
How do you number a glucose molecule? 
Where can you find ribosomes within the cell?
Ribosomes are found 'free' in the cell cytoplasm and also attached to rough endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes receive information from the cell nucleus and construction materials from the cytoplasm. Ribosomes translate information encoded in messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA).
What are the chemical properties of this function group in red (Just the molecule on the left): 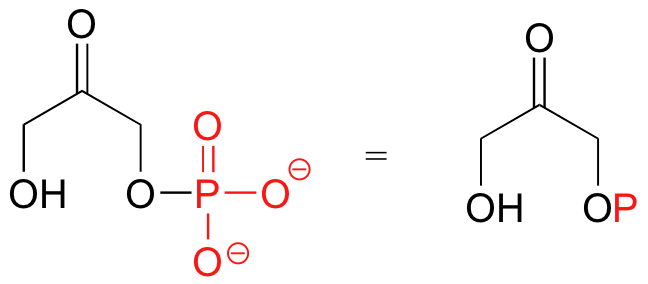
The oxygen atoms are more electronegative than the phosphorous atom, therefore these oxygen atoms are able to form hydrogen bonds with nearby hydrogen atoms that also have a δ+(hydrogen atoms bound to another electronegative atom). Phosphate groups also contain a negative charge and can participate in ionic bonds.
What is a positive control group and how does that differ from a negative control group?
Positive control is an experimental treatment which is performed with a known factor to get the desired effect of the treatment. Negative control is an experimental treatment which does not result in the desired outcome of the experiment.
Name the 7 function groups
What bonds each macromolecule type together?
Protein: Peptide
Lipid: Ester
Carbohydrate: Glycosidic
Amino Acid: Phosphodiester
Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
the biggest distinction between them is that eukaryotic cells have a distinct nucleus containing the cell's genetic material, while prokaryotic cells don't have a nucleus and have free-floating genetic material instead.
What would dissolve easier in water? A compound with a lot of methyl groups or a compound with a lot of carbonyl groups?
Carbonyl Groups
