A wedge in a molecule indicates what? Dash?
wedge: a bond going forward out of the page
Dash: bond going backward behind the page
In the acid base reaction below, which players act as an acid, base, conjugate acid, conjugate base?
H2SO4 + Cl- ->HCl + HSO4-
H2SO4: acid
Cl-: base
HCl: conjugate acid
HSO4-: Conjugate Base
What is the name of the following functional group?

epoxide
How do you determine HDI?
ring/ double bond= 1
triple bond= 2
OR
HDI= (#H in saturated molecule- # H present)/2
What are the rules (steps) of nomenclature?
1. ID the parent chain as the longest C chain
2. number the chain so the 1st substituent group gets the lowest number
3. name and locate each substituent
4. if a substituent appears more than once, use di, tri, tetra, etc. to indicate the number of times it occurs
5. alphabetize the substituents but not on the di, tri, etc.
Which elements must follow the octet rule
Elements in the 2nd row of the periodic table must have exactly 8 e-. They can be below. Carbon can be an exception with 6 e- as a carbocation intermediate.
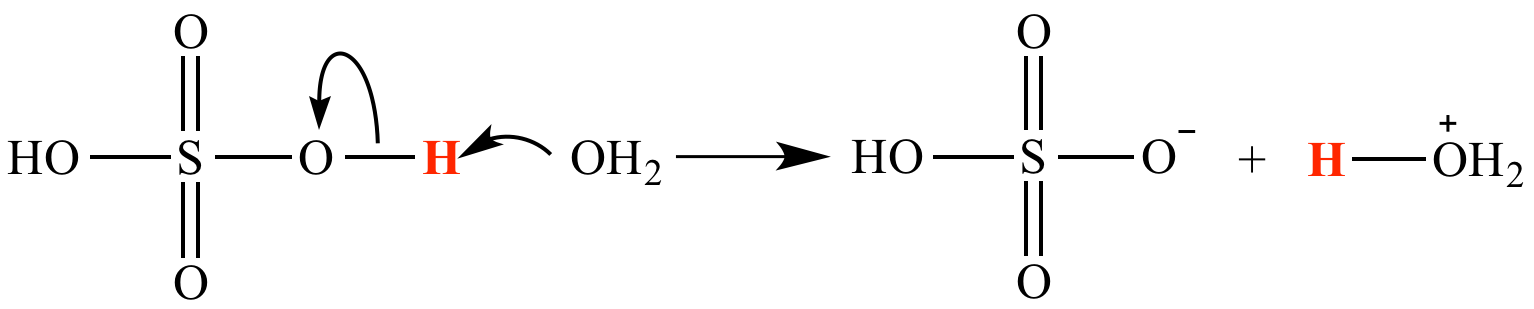
draw the arrows of the proton transfer reaction below.
H2SO4 + OH2- -> HSO4- + H3O+
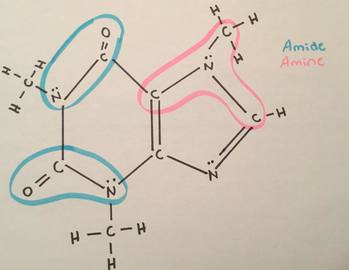
What is the difference between the amine and amide functional groups?
amide has a carbon double bonded to an oxygen and single bonded to a nitrogen and one other R group.
Amine has a carbon single bonded to a nitrogen and 3 other R groups
What are the solvents that appear in 13C NMR and what are their peaks?
TMS- 0 ppm
CDCl3- triple peaked at 77 ppm
What is the difference between a primary, secondary, tertiary, and a quaternary carbon?
primary- directly bonded to 1 other carbon atom
secondary- directly bonded to 2 other carbon atoms
tertiary- directly bonded to 3 other carbon atoms
quaternary- directly bonded to 4 other carbon atoms
Draw the lewis structure of CCl4
Label the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base in the following reaction.
HNO2 + H20 <-> NO2- + H3O+

What functional groups are present in the following molecule?

ester and carboxylic acid
What is the chemical shift of a ketone compared to that of a carboxylic acid? alcohol?
ketone= ~200 ppm
carboxylic acid= ~170-180 ppm
alcohol= ~50-70 ppm
Alcohol is most upfield and shielded
ketone is most downfield and deshielded
Draw the compound 5-methyl-2-heptanol.
What is the condensed structure of the following molecule?

CH3CH2OH
Draw the constitutional isomers of C5H12.
(Hint: there are at least 3)
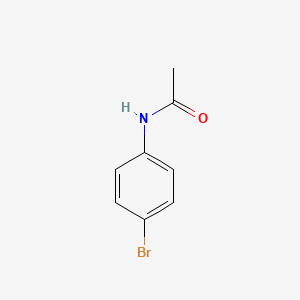
Which functional groups are present in the following molecule?
How many distinct carbon signals are in the molecule below?
BONUS: Name the compound.

BOUNS: 3,5-Dimethylphenol
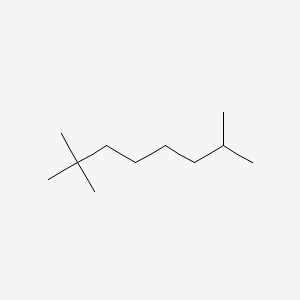
What is the correct IUPAC name for the following compound?
2,2,7-trimethyloctane
Draw the molecule CH3CH2CH2NH2.

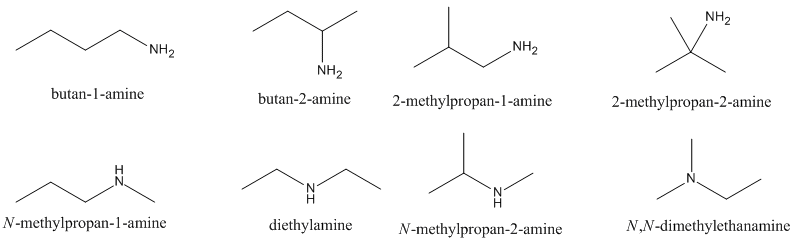
Draw the constitutional isomers of C4H11N.
(Hint: there are at least 8)
Draw an aldehyde with the formula C6H8O.
or
How many distinct carbon signals are in the molecule below?
BONUS: which carbon will appear the most downfield? What is the approximate chemical shift?
6
BONUS: the carbon double bonded to the oxygen at ~170 ppm (The N does have an influence and pulls it slightly upfield)
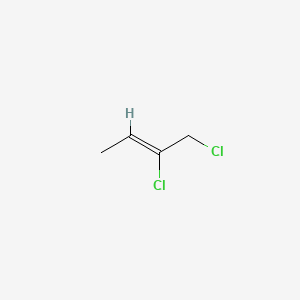
Draw the compound 1,2-dichloro-2-butene.