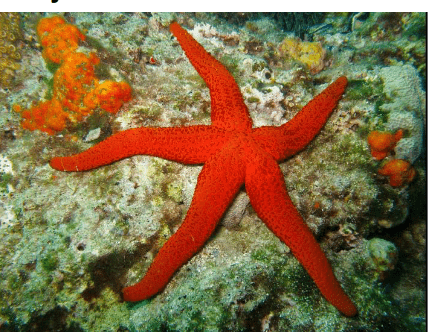
The relatively uncommon sea star preys on mussels, a dominant competitor for space. When sea stars are removed from the community, species richness rapidly declined due to mussels overpopulating and using a disproportionate amount of resources. In the example, sea stars represent
a. Ecosystem engineers
b. Dominant species
c. Invasive species
d. Keystone species
d. Keystone species
A species that is not necessarily abundant in a community yet exerts strong control on community structure by the nature of its ecological role or niche.
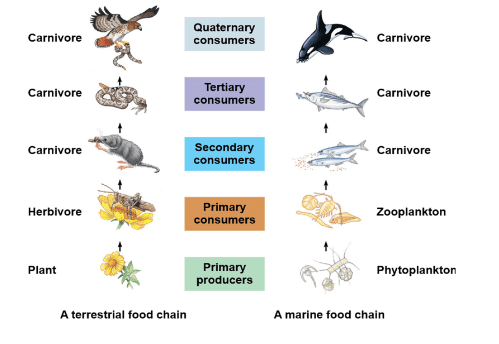
Ecosystem engineers: An organism that influences community structure by causing physical changes in the environment

Dominant species: A species that exerts strong effects on the community due to its large size, high abundance. They become competitively dominant by exploiting key resources.

An ecologist is studying the interactions between different species and how these
interactions affect the structure and organization of this specific group of species. Which
level of ecology is the ecologist working at?
a. Organismal
b. Population
c. Ecosystem
d. Community
d. Community
Of the following choices, which is best characterizes as a primary producer?
a. Fungi
b. Grasshoppers
c. Gram negative bacteria
d. Phytoplankton
d. Phytoplankton
In a given community, there are three different types of species: 7 butterflies, 10 moths, and 4 lizards. Which of the following values represents the species richness of the community?
a. 7
b. 3
c. 4
d. 10
e. None of the above
b. 3

Which of the following statements is consistent with the principle of competitive
exclusion
a. Bird species generally do not compete for nesting sites.
b. The random distribution of one competing species will have a positive impact on the
population growth of the other competing species
c. Two species with the same fundamental niche will exclude other competing species.
d. Even a slight reproductive advantage will eventually lead to the elimination of the less
well, adapted of two competing.
d. Even a slight reproductive advantage will eventually lead to the elimination of the less
well, adapted of two competing.
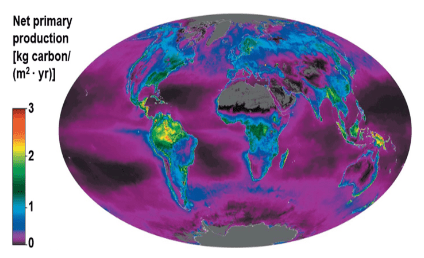
Given that the ocean has a relatively low net primary production, which answer best explains how it contributes significantly to the global net primary production?
a. The ocean recycles energy efficiently
b. The ocean is located at multiple different latitudes thus receiving a spectrum of solar energy
c. The ocean conserves a lot of heat
d. The ocean covers vast areas of the Earth's surface
d. The ocean covers vast areas of the Earth's surface
Which of the following is an example of cryptic coloration?
a. Bands on a coral snack
b. Brown or gray color of tree bark
c. Markings of a viceroy butterfly’s wings
d. Colors of an insect-pollinated flower’s petals
e. A “walking stick” insect that resembles a twig
e. A “walking stick” insect that resembles a twig
On the cliffs beneath Hogwarts castle, a new breed of tree is growing. The Shimming
Willow is an aggressively musical tree. Whenever the castle bells toll, the willow begins
to dance. As it dances, it spreads a shower of glucose on the ground around it. Unicorns
from the Forbidden Forest come to consume the glucose. How would you describe this
relationship?
a. Herbivory
b. Commensalism
c. Mutualism
d. Parasitism
b. Commensalism
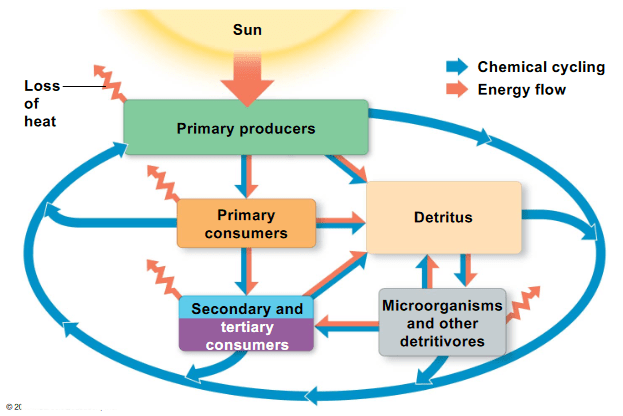
The Earth needs a constant supply of sunlight because the energy provided
a. warms the Earth and allows tropical plants to flourish
b. is converted into chemical energy by primary producers and recycled by fungi
c. moves through the ecosystem and is lost as heat
d. is used by primary consumers to create ATP.
c. moves through the ecosystem and is lost as heat
The snakehead fish, native to Africa and Asia, has been accidentally relocated to
Crofton, Maryland, where it has decimated the local fish population. Which of the
following best describes this species?
a. Invasive species
b. Dominant species
c. Keystone species
d. Ecosystem engineer
a. Invasive species
The difference between net primary production and gross primary production is
the amount of energy producers burn when they metabolize
Net primary production:
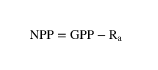
GPP= gross primary production (total amount of energy from light converted to chemical energy)
Ra= energy used by primary producers for cellular respiration (autotrophs)
A caterpillar consumes a leaf containing 200 J of energy. The caterpillar uses 33 J for growth and 67 J for cellular respiration. The final 100 J are released as feces. What is the production efficiency of the caterpillar?
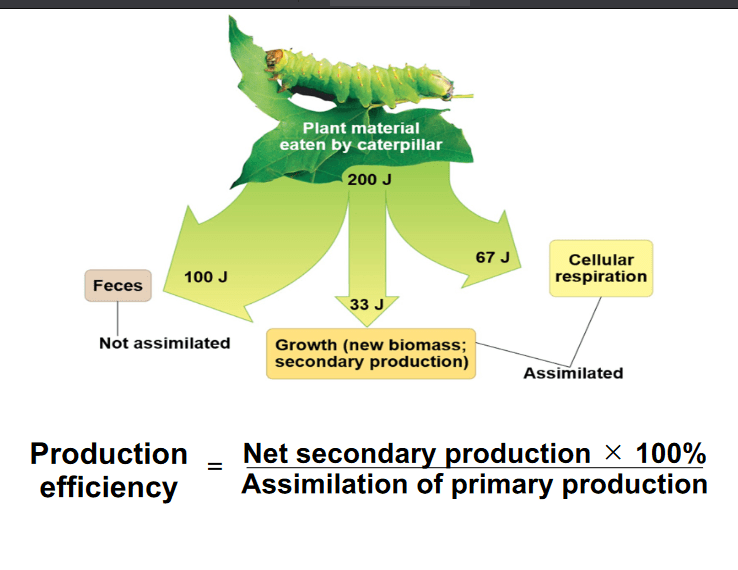
Assimilation consists of the total amount of energy an organism has consumed and used for growth, reproduction, and respiration
Net secondary production is the amount of energy used for growth and reproduction
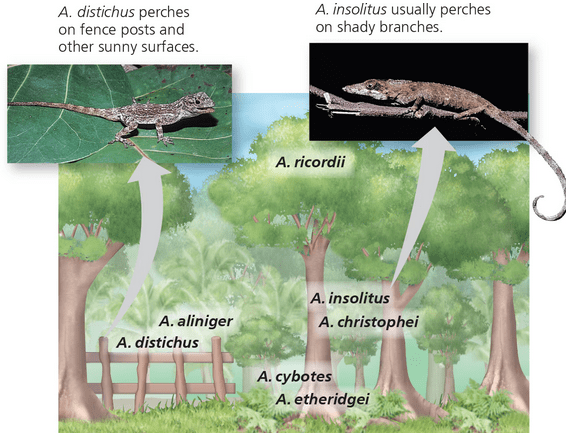
Seven species of Anolis lizards live in close proximity, and all feed on insects and other small arthropods. However, competition for food is reduced because each lizard species has a different preferred perch, thus occupying a distinct niche. This is an example of?
Resource partitioning:the differentiation of niches that enables similar species to coexist in a community (eliminate competition between species).
The monarch butterfly, characterized by bright colors, carries a toxin poisonous to
lizards and other predators. From fear of the monarch’s poison, lizards won’t eat them
or the similar looking Viceroy butterfly. which is harmless.
Which defense mechanisms are demonstrated in the example above?
Aposematic coloration
Batesian mimicry
How much biomass of primary producers would be needed to support eight 25 kg hyenas that feed on herbivores.(Assume 10% efficiency energy transfer)
Secondary consumers (Hyenas)
25 kg*8= 200 kg needed to support hyenas
Primary consumers (herbivores)
200 kg= .10 * x
x= 2,000 kg
Primary producers
2,000 kg= .1 * x
x= 20,000 kg