How many lobes does each lung have?
Right Lung: 3 lobes
Left Lung: 2 Lobes
What is the normal rate of breath for an adult?
16-20 breaths
Where is the Apical pulse located?
At the apex of the heart, 5th intercostal space
Which one has unoxygenated blood and which has oxygenated blood?
Right atrium and ventricle have unoxygenated blood
Left atrium and left ventricle have oxygenated blood
How do accessory muscles help identify labored breathing?
Hypertrophy causes the muscles to become more pronounced, leading to more work to gain oxygen
Where does pulmonary circulation return oxygen to?
Where does bronchial circulation return oxygen to?
(Hint: everything needs oxygen to function)
Pulmonary: to the body
Bronchial: to the lungs
What is S1 and S2?
S1= Systole
S2= Diastole
What is preload and afterload?
Preload: load on the heart and amount of blood pumped per beat
Afterload: work required after contraction to move blood into aorta
If a patient tells you they are coughing, what would be the most appropriate question to ask first?
(Hint: sputum)
Are you coughing up anything?
Why?
Lower than
Lungs would collapse if they were higher than. If pressure were equal, lungs would not be able expand at all
What does S1 sound like and where is it the loudest?
What does S2 sound like and where is it the loudest?
S1= "lub" sound heard loudest at the apex
S2= "dub" sound heard loudest at base
What contains more blood at any give time: veins or arteries?
Veins
A patient tells you they smoke 2 packs of cigarette a day and have been smoking for 10 years, what is their pack year?
Pack year= 20
What can be factors effecting lung compliance (elastic properties of the lung and surface tension of the alveoli)?
Trauma or disease
What is the proper order of auscultation of the heart?
Aortic, Pulmonic, Erb's point, Tricuspid, and Mitral
What is Blood Pressure?
What are the perimeters that equal Blood pressure?
Def: the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels
Blood pressure= cardiac output x peripheral vascular resistance
If a patient is unable to sit up, what is the proper way to examine their lungs?
Roll patient to one side and examine posterior thorax and lungs
What is the purpose of surfactant?
Helps lower surface tension and allows for easier expansion of lungs
What is the SA Node commonly referred to as?
What is the order of conduction for the heart?
The Pacemaker
SA Node > AV Node > Bundle of His
What regulates Blood Pressure?
Baroreceptors and chemoreceptors
When auscultating the lungs, how would you move the diaphragm?
From side to side to compare both lungs
What is the difference between perfusion and ventilation?
Perfusion: blood flowing to places in the lungs where gas exchange can occur
Ventilation: getting gas into the lungs and all of the structures
What are the vessels of the neck?
What can be seen if it is distended?
Carotid arteries and Jugular Veins
The external jugular vein can be visible when distended, noted as JVD
Def: Hardening of the arterial wall due to fat accumulation in arteries
Obj: tissue disfunction distal to occlusion, hypertension
What positions of the bed allows for maximum chest expansion?
Semi-Fowler's or high Fowler's
What is the normal pH range for blood gases?
What happens if it gets too high?
Too low?
Normal: pH 7.35-7.45
Too low: acidosis
Too high: alkaline
What is the common heart rate at birth?
Are murmurs a worry at this stage?
120-160 bpms
No, they are usually harmless and will be outgrown
What is an Aneurysm and the outcome?
Def: An outpouching of the wall of a blood vessel
Outcome: Most commonly death if in a major artery
What is the highest pulmonary risk for a bedrest patient and what prevention would help mitigate this?
Risk: pneumonia
Promote lung exercises
What is the most common strain of Influenza?
Influenza A
What are the nonmodifiable and modifiable risk factors for CAD?
Nonmodifiable: Age, Gender, Race, and heredity
Modifiable: Smoking, Hypertension, Diabetes, Obesity, Sedentary, Cholesterol, Oral contraceptives
What is varicose veins and the Objective data?
Def: Dilated veins in the lower body that result from incompetent valves or blockage
Obj: Appearance of veins that are dilated and superficial, edema which is elevated
What is the normal range for pulse oximetry?
Would this be consistent for a patient with COPD?
Normal Range: 97%-100%
No, they would have a much lower resting Pulse ox sat
What is the pneumonia and the objective data?
Def: Inflammation of the alveoli and the bronchioles of the lungs- causing to fluid in the alveolar spaces
Obj data: SOB, diminished and adventitious breath sounds, hypoxia, fever, productive cough, chest pain, tachycardia, and tachypnea
What culture has the highest rate of hypertension?
What culture has the lowest rate?
Highest: African-American
Lowest: Asian
What is hypertension defined as?
What is the difference between primary and seconday?
Def: sustained elevation of blood pressure; systolic greater than 130 and diastolic greater than 80
Secondary hypertension only occurs with the presence of disease
How would you properly document "normal" respiration sounds?
Bilateral lung fields clear to auscultation
No signs of respiratory distress
No adventitious breathing
What is COPD and the objective data?
Def: Disorders that result in chronic and recurrent obstruction of airflow in pulmonary airways-third leading cause of death
Obj data: cough (productive or non-productive), cyanosis, barrel chest, tripod breathing, altered blood gas reading, hypoxemia, and hypercapnea
What is Sinus arrhythmia and is it dangerous?
Def: HR slightly increases with breathing
No, this is quite common and has no adverse effects.
What is a hypertensive emergency?
Def: BP greater than 180 systolic or 120 diastolic
What is Asthma and the objective data?
Def: chronic inflammatory disease of the airway that leads to airway obstruction
Obj: wheezing, dyspnea, decreased O2 sat, coughing
What is a murmur?
What is the difference between a systolic murmur and a diastolic murmur?
A systolic murmur is usually not a worry whereas a diastolic murmur always means heart disease
What is the grading for systolic murmurs?
I- Lowest intensity, hard to hear
II- Low intensity, but can be heard
III- medium intensity, much easier to hear but without palpable thrill
IV- Medium intensity with palpable thrill
V- Loud intensity with palpable thrill, audible even with just the edge of the stethoscope
VI- Loudest intensity, can often be heard with the stethoscope hovering above chest
When measuring pulses, do you measure one at a time or both bilaterally?
Both bilaterally to feel for any differences
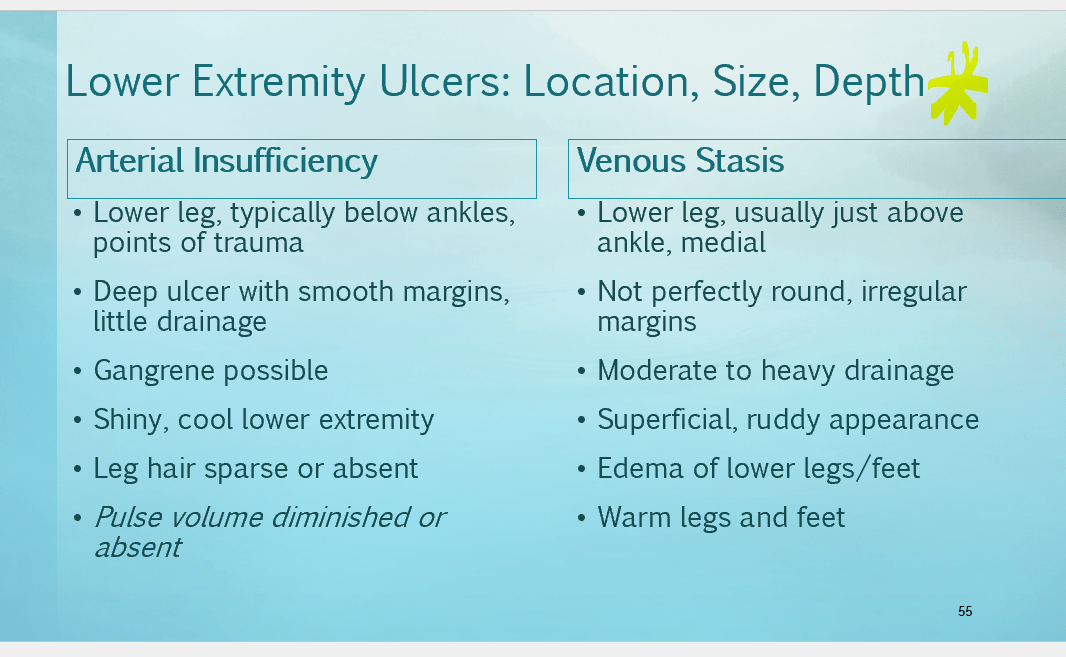
What is the data for arterial insufficiency and venous stasis?