What are some risk factors for Stroke?
HTN (Hypertension), Smoking, Diabetes, High cholesterol, Obesity, Physical inactivity, Atrial fibrillation, Age (risk increases with age), and Family history of stroke
What are some signs and symptoms of retinal detachment?
Sudden increase in floaters
Flashes of light
Curtain-like shadow in peripheral vision
Sudden vision loss
You prioritze increasing fluid intake for your pat, what are some tasks you can delegate to your UAP to help to reach this goal?
- Offer fluids regularly
- Record fluid intake
- Report any refusals or concerns to the nurse
A weber test is used to see if there is any conductive hearing loss, What would be an abnormal result?
If the patient can only hear on one side
SBAR is used for communication amongst healthcare staff during handoff, what does SBAR stand for?
Situation, Background, Assessment, and Recommendation
What is the pathology of Parkinson's Disease?
- Loss of dopamine-producing neurons in substantia nigra
- Resulting in motor symptoms (tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia)
PE TUBES: why we use PE Tubes, what do we do if they want to be in the water and what do what do we monitor for an infection drainage?
Purpose: Drain fluid from middle ear, improve hearing, reduce ear infections
Water precautions: Use earplugs or swim cap when swimming
Infection drainage: Monitor for color, odor, and amount of drainage
How will the nurse monitor F+E balance for a patient with diarrhea?
Assess hydration status
Monitor electrolyte levels
Replace fluids and electrolytes as needed
True or False: Ear drops must be placed with the refrigerator and can be given to a patient right away after taking it out for administration.
FALSE- Ear drops must be set at room temperature
List some Parkinson's eating and assistive devices:
Parkinson's eating and assistive devices:
Weighted utensils
Non-slip mats
Plate guards
Rocker knives
Cups with lids and straws
What Parkinson's eating and assistive devices would you recommend for your patient?
Weighted utensils
Non-slip mats
Plate guards
Rocker knives
Cups with lids and straws
You have a child patient who recently came out of an eye surgery, what are the nursing interventions that you will perform to ensure safety?
- Elevate head of bed
- Avoid sudden movements
- Remove tripping hazards
- Ensure proper lighting
- Use side rails on bed
What are some signs and symptoms to monitor when you suspect your patient has hypokalemia?
- Muscle weakness
- Fatigue
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Constipation
- Hypotension
Tinnitus is a side-effect of this potassium wasting diuretic.
Furosemide
Upon assessment, you notice U-Waves on your patient's monitor. What does this indicate?
Hypokalemia
What are some infection risks for a patient with MS?
Urinary tract infections
Respiratory infections
Skin infections (due to decreased mobility)
 What is this, and what is it used for?
What is this, and what is it used for?
Snellen Chart, used to measure visual acuity at a standard distance (usually 20 feet)
Name the two calcium concentration hormones:
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) (Increases serum calcium levels)
Calcitonin (Decreases serum calcium levels)
List some communication technique for sensorineural hearing loss
Face the patient directly
Speak clearly and at a moderate pace
Reduce background noise
Use visual cues when possible
During the eye assessment of an older patient, what will you look out for and ask?
Lens opacity (cataracts)
Decreased elasticity of lens (presbyopia)
Issues with night vision and glare sensitivity / Night Driving Difficulty?
What nursing interventions would you perform for a patient with ALS?
Assist with mobility and positioning
Provide respiratory support
Manage nutrition and hydration
Facilitate communication
Educate on disease progression
Upon assessment, your patient tells you that their vision is 20/40, what does this mean?
means that a person needs to be 20 feet away to see what someone with normal vision can see at 40 feet. In other words, their visual acuity is below average but still functional for many daily activities. This level of vision indicates that the individual can read letters on the Snellen eye chart at 20 feet that a person with normal (20/20) vision could read from 40 feet away. While 20/40 vision may not meet certain standards for tasks like driving without correction in some jurisdictions, it is generally considered adequate for most daily activities.
Name the Calcium purposes in the body:
Bone and tooth formation
Muscle contraction
Nerve conduction
Blood clotting
***F+E QUESTION**
What will you monitor for a patient with SIADH?
- Monitor serum sodium (typically low)
- Assess for hyponatremia symptoms
- Note: Urine output may be normal or increased, not decreased
Your patient has been diagnosed with Hyperkalemia, what are some medications the nurse will expect to see?
- Calcium gluconate
- Insulin with glucose
- **Sodium bicarbonate (Kayexalate)
- Beta-agonists (e.g., albuterol)
What type of disease genetics is involved with Hunting's Disease?
Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern
When administering Beta-blocker eye drops, for a patient with glaucoma, your patient asks what they do: what would be the appropriate response?
Beta-blocker eye drops: Used to reduce intraocular pressure in glaucoma treatment
You walk into your patient's room and see this: What is this, and what F+E imbalance does this indicate?
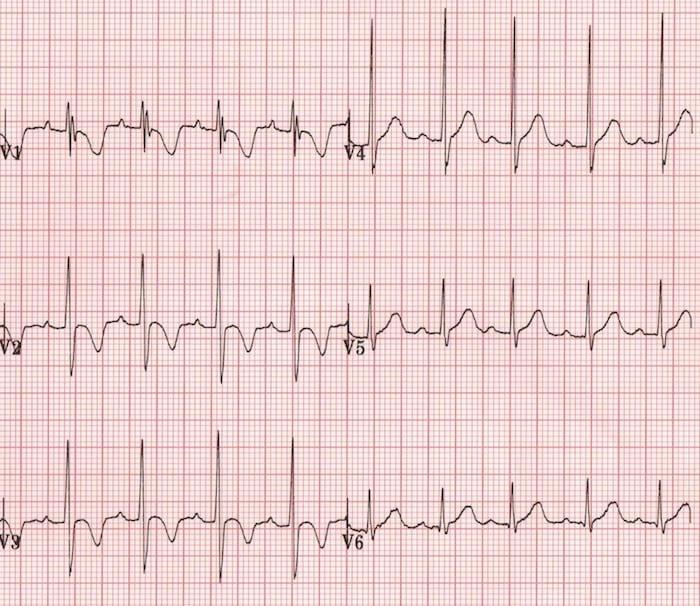
What is it: Peak T-Waves
Indication: HYPERkalemia
**F+E QUESTION**
Fluid volume excess signs and symptoms...
- Edema
- Weight gain
- Elevated blood pressure
- Distended neck veins
- Crackles in lung bases
Name some examples of insensible water loss
- Breathing
- Sweating
- Diffusion through skin
What are some important things to remember to note for medication administration for Myasthenia Gravis?
- Consistent timing is crucial for symptom management
- Helps maintain steady drug levels in the body
List Cataracts signs and symptoms
Cloudy or blurry vision
Difficulty seeing at night
Sensitivity to light and glare
Seeing halos around lights
Fading or yellowing of colors
Hypercalcemia signs and symptoms:
Constipation
Fatigue
Confusion
Muscle weakness
Increased urination
**F+E QUESTION**
Hypomagnesemia signs and symptoms...
- Muscle weakness and cramps
- Tremors
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Seizures
- Nausea and vomiting
After speaking with the patient, you notice the caregiver begins to interrupt and shows signs of agitation and fatigue. The caregiver notices these actions and asks for your assistance, what would you recommend for caregiver fatigue?
- Respite care services
- Support groups
- Education on self-care
- Assistance with daily tasks
- Counseling or therapy
What are some recommendations a nurse would teach for someone who has RLS (Restless Leg Syndrome)?
- Regular exercise
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol
- Establish a consistent sleep schedule
- Massage or stretch legs before bed
- Consider iron supplementation if deficient
List Cataract post-op precautions:
Wear eye shield while sleeping
Avoid rubbing or pressing on the eye
Use prescribed eye drops as directed
Avoid bending or heavy lifting
Wear sunglasses outdoors
These two signs may indicate what F+E imbalance?

Hypocalcemia
** Parkinson's Question**
What is LSVT LOUD therapy for Parkinson's?
Speech therapy to improve voice volume and clarity
Define Dyskinesia
Involuntary, erratic movements often associated with long-term levodopa use in Parkinson's disease
Stroke can lead to emotional changes such as...
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Emotional lability
- Apathy
- Irritability
What are some age-related macular degeneration assistive devices that you can recommend for a patient?
Magnifying glasses
Large-print books and newspapers
Talking watches and clocks
Text-to-speech software
Geriatric fluid and electrolyte imbalance causes...
- Decreased thirst sensation
- Reduced kidney function
- Medication side effects
- Chronic illnesses
- Poor nutrition
What are the electrolyte ranges for Sodium, Potassium, Chloride, Calcium, and Magnesium?
- Sodium: 135-145 mEq/L
- Potassium: 3.5-5.0 mEq/L
- Chloride: 98-106 mEq/L
- Calcium: 8.5-10.5 mg/dL
- Magnesium: 1.5-2.5 mEq/L
How do you know when a patient is ready to be transferred from bed to chair?
If the pt can straighten their posture instead of leaning to the weaker side when sitting on the edge of the bed