Osteocytes are mature bone cells and live in these small depressions.
What are lacunae?
One function of the skeletal system is hematopoiesis, which means this.
What is blood cell production?
Synovial joints are synonymous with this functional classification.
What is diarthrosis?
Spreading your fingers is this type of movement.

What is abduction?
Another name for muscle cell.
What is muscle fiber?
This muscle type relies completely on the nervous system for contraction.
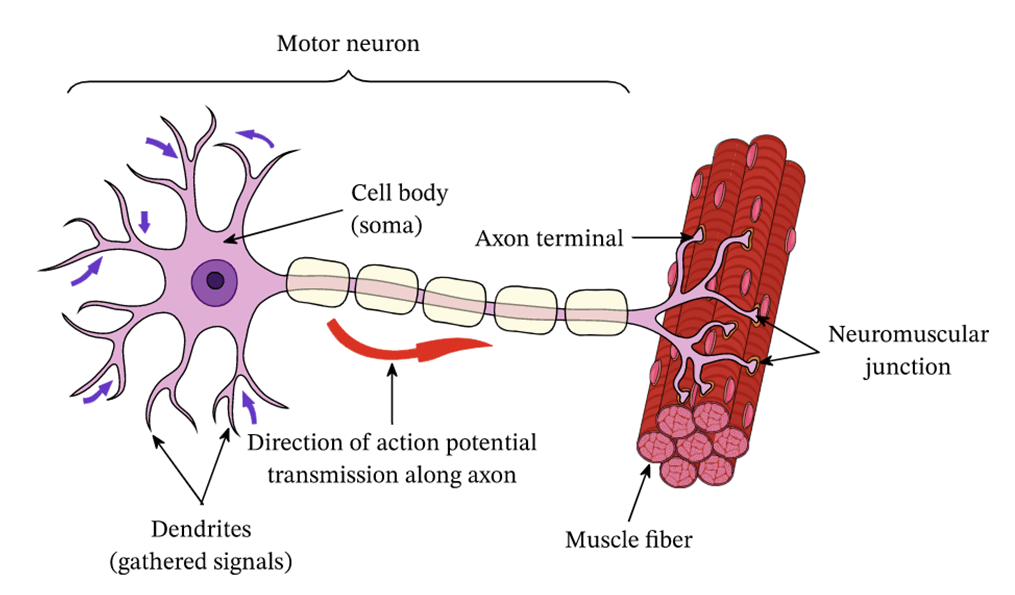
What is skeletal muscle?
The advantage of skeletal cells being multi-nucleated.
What is lots of protein production?
These are young bone cells and produce bone matrix and collagen fibers.
What are osteoblasts?
Compact bone contains blood vessels that reside in this part of the osteon.

What is the central canal?
A cranial suture falls into this functional classification.
What is synarthrosis?
Lubrication is one function of this.
What is synovial fluid?
The functional unit of a muscle fiber.
What is the sarcomere?
The connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone.

What is tendon?
The organelle responsible for ATP production.
What is the mitochondrion?
These bone cells have yet to develop into a particular cell.
The connective tissue that joins one bone to another.

What are ligaments?
The pubic symphysis is this type of articulation.

What is cartilaginous?
The type of joint that allows your thumb to be oppositional to your other fingers.

What is saddle joint?
The fusion of many myoblast cells results in this unique characteristic of skeletal muscle.
What is multi-nucleated?
The neurotransmitter that is released from vesicles into the synaptic cleft.

What is acetylcholine (ACh)?
At rest, the actin binding sites are blocked by this protein.
What is tropomyosin?
Derived from monocytes, these cells break down bone matrix.
What are osteoclasts?
Bones function as storage for this, which can be released when blood levels get too low.
What are calcium ions?
arthritis starts with wear and tear on this.
What is articular cartilage?
Bending you elbow reduces the angle of the joint, making it this type of movement.
What is flexion?
Thick filaments are composed of this protein.

What is myosin?
The influx of this at the terminal end of the neuron causes the release of neurotransmitter.
What are calcium ions (Ca++)?
Myosin releases its attachment to actin after this attaches to the myosin head.
What is ATP?
The percentage of bone that is made up of cells.
What is 2%?
The part of a long bone involved in articulation.
What is the epiphysis?
The structural joint that allows articulation of the mandible.
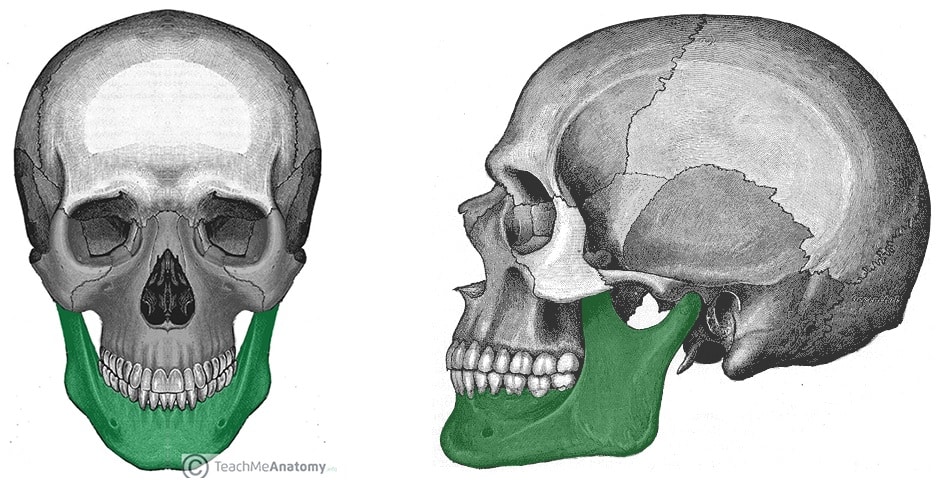
What is synovial?
Rotating the wrist so the palm is anterior, is this type of movement.

What is supination?
In addition to actin, thin filaments contain these two proteins.

What is troponin and tropomyosin?
During a contraction, the thick filaments pull the thin filaments towards this.

What is the M line?
Maximum muscle tension without relaxation is called this.
What is tetanus?
The molecule that stimulates absorption of calcium and phosphate ions from the small intestine.

What is calcitriol (vitamin D)?
The substance that makes up about 2/3rds of bone mass.
What is calcium phosphate?
The type of synovial joint between articulating carpals.
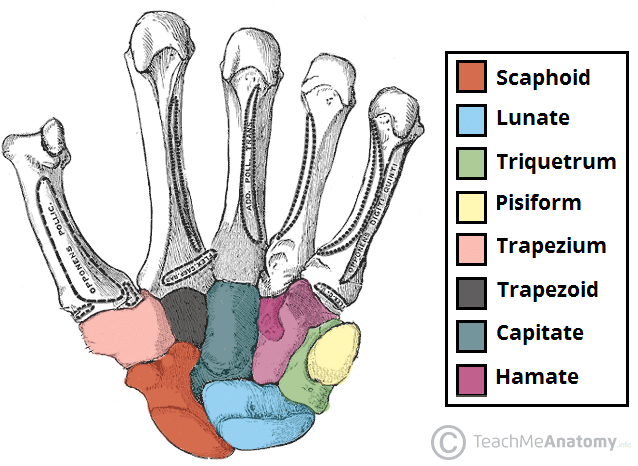
What is plane or gliding?
The synovial joint that allows maximal movement.
What is ball-and-socket?
Many tandem sarcomeres, or the grouping of thin and thick filaments, are collectively called this.
What is a myofibril?
Where a neuron communicates with a muscle fiber.
What is the neuromuscular junction (NMJ)?
The collective term for all the muscle fibers innervated by a single motor neuron.

What is a motor unit?
The roof of the skull and the clavicles ossify using this method.

What is intramembranous ossification?
Longitudinal bone growth happens at this location in a long bone.
What is the epiphyseal plate?
The definition of amphiarthrosis.
What is slightly moveable?
The atlantoaxial joint is an example of this type of joint.
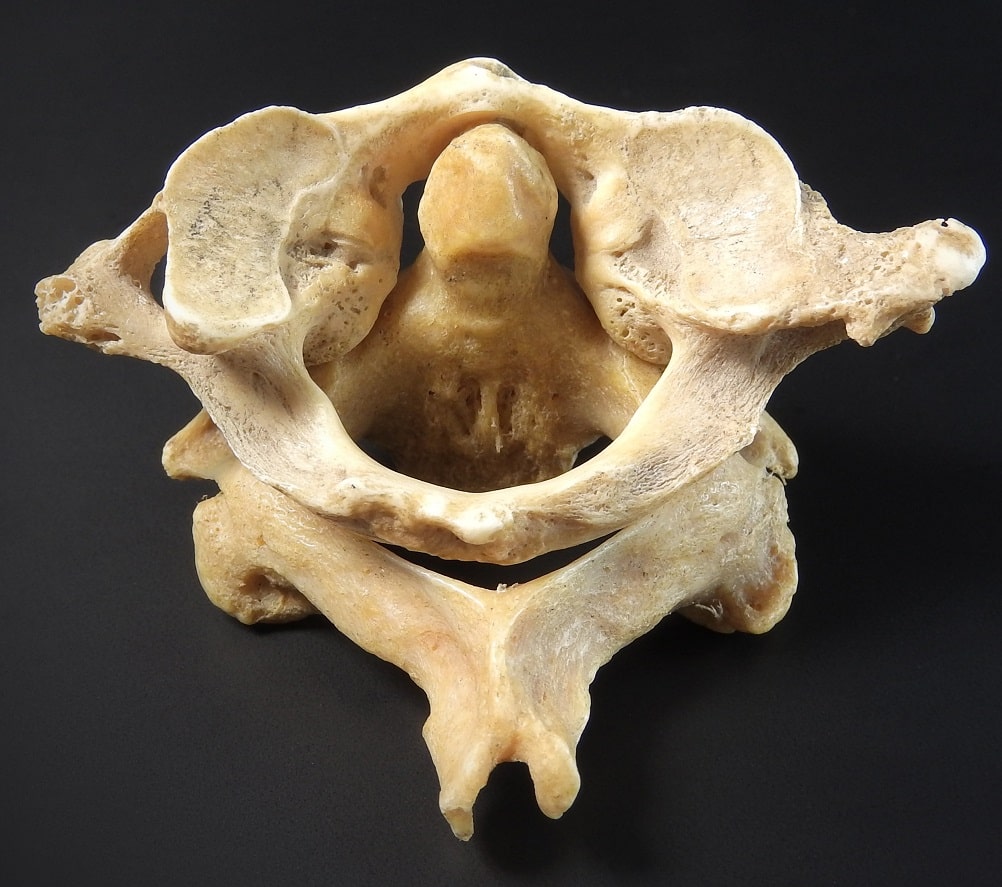
What is pivot?
The extension of the sarcolemma into the cell that surrounds each myofibril.

What are T-tubules?
T-tubules allow this to travel from the sarcolemma to the interior of the cell.
The molecule that acts as an energy reserve when ATP is needed quickly.
What is creatine phosphate?
The process of replacing cartilage with bone.
What is endochondral ossification?
The crystal form of calcium phosphate.
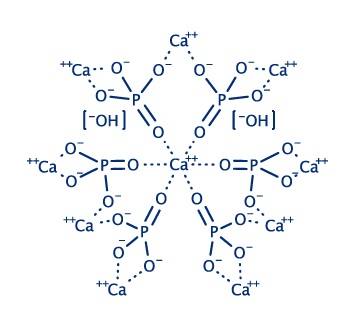
What is hydroxyapatite?
ankle extension can also be called this type of movement.
What is plantar flexion?
The bones of the pelvis are held together by this type of structural joint.
What is fibrous?
Specialized organelle that stores calcium ions.

What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
Influx of this into the sarcolemma at the motor end plate allow an action potential to propagate along the membrane.
What are sodium ions (Na+)?
This happens when an action potential quickly follows after another.
What is wave summation?
The osteon consists of these circles within circles.

What are concentric lamellae?
The term for when bones grow in diameter.

What is appositional growth?
Forming a fist is this type of movement.
What is flexion?
When you rub your tongue along your upper teeth, you do this to your mandible.
What is protract?
The leading theory behind muscle contraction.
What is the sliding filament theory?
An action potential stimulates release of calcium ions from the SR so it will bind to this.
What is the protein troponin?
The term that links the action potential signal to muscle contraction.
What is excitation-contraction coupling?