1. The main function of the skin include:
A. support, nourishment, and sensation
B. protection, sensory perception, and temperature regulation
C. fluid transport, sensory perception, and aging regulation
D. support, protection, and communication.
Answer is B.
The skin's main function involve protection from injury, noxious chemicals, and bacterial invasion; sensory perception of touch, temperature, and pain; and regulation of body heat
1. A nurse caring for patients in a skilled nursing facility performs risk assessments on the patients for foot and nail problems. Which patients would be at a higher risk? Select all that apply
A. A patient who is taking antibiotics for chronic bronchitis
B. A patient diagnosed with Type II diabetes
C. A patient who is obese
D. A patient who has a nervous habit of biting his nails
E. A patient diagnosed with prostate cancer
F. A patient whose job involves frequent handwashing
Answer is B, C, D, F
Variables known to cause nail and foot problems include deficient self-care abilities, vascular disease, arthritis, diabetes, history of nail biting or improper nail trimming, frequent or prolonged exposure to chemicals or water, trauma, ill-fitting shoes, and obesity
1. The integumentary system comprises skin, hair, and nails but also includes which of the following? Select all that apply.
A. Glands
B. Tendons
C. Mucous membranes
D. Capillaries
E. Cartilage
Answer is A, C
Glands are part of the integumentary system. Mucous membranes are part of the integumentary system.
Incorrect Answers. Tendons are part of the musculoskeletal system. Capillaries are part of the circulatory system. Cartilage is part of the musculoskeletal system.
1. The patient reports that she is feeling tired all the time and has been gaining weight. She thinks that her face is “puffy.” You assess the thyroid gland and find it to be enlarged. The healthcare provider suspects the patient has hypothyroidism. You expect that the healthcare provider will order which of the following blood work to assess the thyroid gland?
A. Triiodothyronine (T3)
B. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) only
C. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and free thyroxine (Free T4)
D. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free thyroxine (Free T4), and triiodothyronine (T3)
Answer is D.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free thyroxine (Free T4), and triiodothyronine (T3) tests are used to differentiate thyroid malfunction.
Incorrect Answer. This test is ordered for hyperthyroidism. Triiodothyronine (T3) is a blood test that is used with the TSH and T4 blood tests to diagnose an overactive thyroid gland. This hormone is converted from the T4 hormone in the tissues rather than directly from the thyroid gland.
The thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) would not be ordered by itself. The TSH would be ordered with the triiodothyronine (T3) and free thyroxine (Free T4).
All three thyroid tests would be ordered—thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free thyroxine (Free T4), and triiodothyronine (T3)—to differentiate thyroid malfunction.
Identify the letter in OLDCARTS mnemonic
Onset
Location
Duration
Characteristic
Alleviating/aggravating factors
Radiation or relieving
Timing
Severity
The healthcare provider is using an otoscope to evaluate the tympanic membrane. Which of the following describes a normal finding?
A. A pearly-gray surface with a light reflex and a visible umbo.
B. A pink surface with a small opening in the anterior lower quadrant and small air bubbles.
C. A reddened bulging surface with visible vesicles.
D. A dull gray surface with no light reflex.
A. A normal tympanic membrane has a pearly-gray surface with a light reflex and a visible umbo.
Match the cranial nerves
1. CN I 2. CN III 3. CN IV 4. CN V
5. CN VI 6. CN VIII 7. XII
A. Pupil constriction, upper eyelid movement
B. Smell
C. Enables tongue movement
D. Control external eye muscles, turns eye inward an downward
E. Hearing
F. Facial sensation
G. Abduct the eyeball, rotate the gaze away from midline
1. B 2. A
3. D. 4. F
5. G. 6. E
7. C
When doing a respiratory assessment on an adult, the nurse remembers that which of the following are normal findings? Select all that apply.
A. The normal respiratory rate is 15 to 25 breaths per minute.
B. The normal inspiratory-to-expiratory ratio is 1:2.
C. The chest is a conical shape: larger at the top and narrows at the bottom.
D. The chest movement is symmetrical.
E. Skin color is uniform and intact
Answer: B, D, E
Normal inspiratory-to-expiratory ratio (I: E) is 1:2. The expiratory phase is longer than the inspiratory phase. Chest movement is symmetrical. Skin color should be uniform and intact.
Normal adult respiratory rate (eupnea) is 12 to 20 breaths per minute, not 15 to 25 per minute. The chest is a conical shape but it is smaller at the top and widens at the bottom.
2. Which type of wound closes by primary intention?
A. Second-degree burn
B. Pressure ulcer
C. Traumatic injury
D. Surgical incision
Answer is D.
A surgical incision is an example of a wound that closes by primary intention in which there's no deep tissue loss and the wound edges are well approximated.
2. The pink color of the nail beds is due to:
A. Pigment from melanocytes.
B. Vascularity of epithelial cells.
C. Genetic predisposition.
D. Inflammation of the epidermis.
Answer is B.
The pink color of the nail beds is due to highly vascular epithelial cells.
Incorrect answers. The pink color of the nail beds is not related to skin color. Genetics are not related to vascularity. The pink color of the nail beds is not related to inflammation.
2. You are performing a skin assessment on a patient’s face and inspect many freckles on both sides. A freckle is a:
A. Macule.
B. Papule.
C. Vesicle.
D. Nodule.
Answer is A
A macule is a circular, small, flat spot less than 1 mm to 1 cm in diameter. Macules are red, brown, or white in color, and the color is not the same as that of nearby skin. They present in different shapes.
Incorrect Answers. A papule is a solid, elevated spot that appears rough in texture and measures less than 1 cm in diameter. Papules are pink, red, or brown in color.
A vesicle is raised, round, or oval with a thin mass filled with serous blood or clear fluid measuring less than 0.5 cm in diameter.
A nodule is solid, elevated, and palpable, measuring greater than 2 cm in diameter.
2. A patient comes to the urgent care center with a nosebleed. During the focused health history, the patient states that this is the first time she has ever had a nosebleed and is scared. You assess her nose and observe blood coming from the right nostril. What should the nurse do to try to stop the bleeding?
A. Have the patient apply pressure with an ice pack and tilt her head back.
B. Hold pressure on the nares by pinching the nostrils tightly for 10 minutes.
C. Have the patient lean forward and press on the bridge of the nose for 5 minutes.
D. Instruct the patient to sit up, tilt the head forward, and pinch the nostrils for 5 minutes.
Answer is D.
Instruct the patient to sit up, tilt the head forward, and pinch the nostrils for 5 minutes. If bleeding continues, hold for another 10 minutes.
Incorrect Answers. This is the wrong position. If you have the patient tilt her head back, the blood will drip down the pharynx. The patient should sit up, lean forward, and pinch the nostrils for 10 to 15 minutes.
This answer is missing the position to instruct the patient to be in while she holds pressure to the nares. The patient should sit up, lean forward, and pinch the nostrils for 10 to 15 minutes.
The nostrils that are highly vascular should be pinched, not the bridge of the nose.
Identify the letter in OPQRST mnemonic
Onset
Provocation/palliation
Quality
Region/Radiation
Severity
Time
The patient has a headache. Concerning symptoms in need of rapid evaluation would include:
A. multi-decade history of migraine headaches.
B. Onset of headaches after the age of 20 years.
C. Associated systemic symptoms such as marked hypertension, fever, and malaise, or neurologic signs.
D. Headache onset and symptoms typical of other headache the patient has experienced for many years.
C. Associated systemic symptoms such as marked hypertension, fever, and malaise, or neurologic signs
Concerning symptoms in need of rapid evaluation would include the onset of symptoms after the age of 50; headaches described as the worst headache of my life; significantly elevated blood pressure; signs of infection; or associated with neurologic deficits.
Match the word with the definition
A. Cheyne-stokes B. Kussmaul
C. Tachypnea D. Dyspnea
1. An abnormal breathing pattern characterized by rapid, deep breathing at a consistent pace. It’s a form of hyperventilation.
2. Shortness of breath; is the feeling that you can’t get enough air into your lungs. It might feel like your chest is tight, you’re gasping for air or you’re working harder to breathe.
3. An abnormal pattern of breathing characterized by progressively deeper, and sometimes faster, breathing followed by a gradual decrease that results in a temporary stop in breathing called an apnea
4. Abnormally rapid breathing
A. 3- Cheyne–Stokes respiration is an abnormal pattern of breathing characterized by progressively deeper, and sometimes faster, breathing followed by a gradual decrease that results in a temporary stop in breathing called an apnea
B. 1- Kussmaul is an abnormal breathing pattern characterized by rapid, deep breathing at a consistent pace. It’s a form of hyperventilation.
C. 4- Tachypnea is abnormally rapid breathing
D. 2- Dyspnea, or shortness of breath, is the feeling that you can’t get enough air into your lungs. It might feel like your chest is tight, you’re gasping for air or you’re working harder to breathe.
In the lungs, gases move across systemic capillaries and an exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs at the cellular level. Which of the following is true regarding carbon dioxide? Select all that apply.
A. It is a waste product of carbon metabolism.
B. It is released from the lungs at the alveoli tissue level.
C. It influences the respiratory center of the brain to increase or decrease respiratory rate.
D. It helps maintain acid-base balance.
E. It keeps the alveoli moist.
Answer is: B, C, D
Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged at the alveoli tissue level. Changes in carbon dioxide influence the respiratory center in the brain by increasing or decreasing the respiratory rate. Changes in carbon dioxide influence the respiratory center in the brain by increasing or decreasing the respiratory rate to maintain the acid-base balance.
Carbon dioxide is a waste product of oxygen metabolism. Surfactant is a substance that reduces the surface tension and keeps the alveoli moist.
3. Which wound bed color indicates normal, healthy granulation tissue?
A. Red
B. Yellow
C. Tan
D. Black
Answer is A.
Red tissue indicates healthy granulation tissue
3. An inflammation of a hair follicle with white pustules is called:
A. Alopecia.
B. Folliculitis.
C. Seborrhea dermatitis.
D. Tinea capitis.
Answer is B.
Folliculitis is inflammation of a hair follicle developing on the face, arms, legs, or buttocks; white pustules appear around the hair follicle.
Incorrect answers: Alopecia, defined as hair loss, may be due to nutritional deficiencies, medications, illness, endocrine disorders, radiation, or the physiological changes of aging. Seborrhea dermatitis, also called cradle cap in infants, is a chronic, greasy scale that accumulates and thickens on the scalp with or without redness. Tinea capitis, also called scalp ringworm, is a fungal infection of the scalp causing round, patchy hair loss, pustules, and scale on the skin.
3. A patient presents with concern about yellowing of her skin. The nurse assesses that there is no yellowing of the sclera of the eye and inquires about the patient’s:
A. Exposure to the sun.
B. Dietary intake.
C. Exposure to chemicals.
D. Allergies.
Answer is B
Carotenemia is a yellowing of the skin due to increased dietary intake of carotene in the diet from foods such as carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, corn, yams, spinach, and beans. The sclera of the eye does not become yellow.
Incorrect Answers. Exposure to the sun does not cause yellowing of the skin. Allergies do not cause yellowing of the skin. Exposure to chemicals does not cause yellowing of the skin.
3. A patient comes to the emergency room stating that he woke up this morning with swollen lips. He reports that he has just started a new medication for his allergies. What is the name of this condition?
A. Anaphylaxis
B. Angioedema
C. Herpes simplex
D. Angular cheilitis
Answer is B.
Angioedema is edema of the lips, usually related to an allergic reaction.
Incorrect Answers. Anaphylaxis is a general term for severe allergic reaction.
Herpes simplex virus manifests with cold sores or blisters on the lips.
Angular cheilitis is sore, cracked corners of the lips, commonly caused by yeast infections, dry mouth, or vitamin deficiency.
Identify the ABCDE mnemonic for melanoma
Asymmetry
Borders
Color
Diameter
Evolving
The leading cause of blindness in African Americans is:
A. Cataracts
B. Trauma
C. Glaucoma
D. Retinopathy
C. The leading cause of blindness in African Americans is glaucoma.
Match the disorder with the definition
A. Club Fingers B. Bell's Palsy
C. Cushing Syndrome D. Parkinson's Disease
E. Graves Disease
1. An immune system disorder that results in the overproduction of thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism)
2. A disorder that occurs when your body makes too much of the hormone cortisol over a long period of time.
3. A progressive disorder that affects the nervous system and the parts of the body controlled by the nerves. The first symptom may be a barely noticeable tremor in just one hand. Tremors are common, but the disorder may also cause stiffness or slowing of movement.
4. The tips of the fingers enlarge and the nails become extremely curved from front to back. A symptom of disease, often of the heart or lungs which cause chronically low blood levels of oxygen.
5. An unexplained episode of facial muscle weakness or paralysis. It begins suddenly and worsens over 48 hours. This condition results from damage to the facial nerve (the 7th cranial nerve
A. 4- The tips of the fingers enlarge and the nails become extremely curved from front to back. Clubbed fingers is a symptom of disease, often of the heart or lungs which cause chronically low blood levels of oxygen.
B. 5- Bell's palsy is an unexplained episode of facial muscle weakness or paralysis. It begins suddenly and worsens over 48 hours. This condition results from damage to the facial nerve (the 7th cranial nerve
C. 2- Cushing's syndrome is a disorder that occurs when your body makes too much of the hormone cortisol over a long period of time
D. 3- Parkinson's is a progressive disorder that affects the nervous system and the parts of the body controlled by the nerves. The first symptom may be a barely noticeable tremor in just one hand. Tremors are common, but the disorder may also cause stiffness or slowing of movement.
E. 1- Graves' disease is an immune system disorder that results in the overproduction of thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism)
You are performing the respiratory assessment technique of tactile fremitus. The purpose of this technique is to:
A. Palpate voice sound vibrations through the bronchi.
B. Palpate tissue density in the upper lobes.
C. Auscultate breath sounds as they travel down the larger bronchi.
D. Percuss for adventitious sounds in the upper bronchi.
Answer is A
The purpose of tactile fremitus is to palpate voice sound vibrations through the bronchi.
Tactile fremitus does not palpate tissue density, but palpates voice sound vibrations that can assess changes in tissue density. Tactile fremitus is not auscultated. Adventitious sounds are auscultated, not percussed.
4. After an initial skin assessment, the nurse documents the presence of a reddened area that has blistered. According to recognized staging systems, this pressure injury would be classified as:
A. Stage 1
B. Stage 2
C. Stage 3
D. Stage 4
Answer is B.
A stage 2 pressure injury involves partial-thickness loss of dermis and presents as a shallow open ulcer with a red pink wound bed, without slough. It may also present as an intact or open/ruptured serum-filled blister.
4. When assessing the scalp of a patient, you notice a scaly rash on their head. The rash is confined to their scalp. Which of the following conditions could this indicate?
A. Contact dermatitis
B. Herpes zoster
C. Psoriasis
D. Tinea capitis
Answer is D.
Tinea capitis is a fungal infection of the scalp; also known as ringworm.
Incorrect Answers. Contact dermatitis is typically found around intertriginous areas, and not on the scalp. Herpes zoster (shingles) is caused by the chicken pox virus, and typically isn’t confined on a person’s scalp. Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease; red, rough scaly patches develop commonly on the extensor surfaces of the skin, and not on the scalp.
4. In the recovery room, the nurse assesses a bluish discoloration of the patient’s oral mucosa and conjunctiva of the eyes, lips, and tongue. These changes in color could indicate:
A. Jaundice.
B. Pallor.
C. Peripheral cyanosis.
D. Central cyanosis.
Answer is D.
Central cyanosis is bluish discoloration to the skin related to decreased circulating oxygen. It is best assessed in the oral mucosa and conjunctiva of the eyes, lips, and tongue.
Incorrect. Jaundice is yellowing of the skin due to excessive levels of bilirubin in the blood. Pallor is pale skin seen in anemia, a decrease in circulating red blood cells or blood flow, or absence of oxygenated blood. Peripheral cyanosis is a blue, gray, slate, or dark purple discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes caused by deoxygenated or reduced hemoglobin in the blood. It may occur with decreased cardiac output.
4. A 37-year-old female presents to the community health clinic complaining of a severe sore throat and swollen glands. You have already inspected the rising of the soft palate and uvula. Prior to using the tongue depressor to assess the oropharynx, which of the following should the nurse do first?
A. Ask the patient to open her mouth real wide.
B. Moisten the tongue blade with warm water.
C. Ask the patient to say “ahh.”
D. Assess for swollen glands.
Answer is B.
Moisten a tongue blade with warm water. A moistened tongue blade may help to decrease the chances of the patient gagging.
Incorrect Answers. Prior to using the tongue blade the nurse should moisten it with warm water to decrease the chances of the patient gagging. The patient has already opened her mouth wide when you inspected the rising of the soft palate and uvula.
The patient will have to say “ahh,” but first the nurse should moisten the tongue blade with warm water to decrease the chances of the patient gagging.
The nurse will assess for swollen glands after she inspects the oropharynx. Prior to using the tongue blade, the nurse should moisten it with warm water to decrease the chances of the patient gagging.
What does PERRLA stand for?
Pupils
Equal
Round
Reactive
Light
Accommodation
The healthcare provider is checking for pupillary reaction by shining a light into the patient's right eye. The pupil constricts. This is known as:
A. direct response
B. Consensual response
C. Convergence
D. Alignment
B. Consensual response
A consensual pupillary response is seen when the contralateral pupil constricts when a light is shone on the pupil.
During your assessment, you note a louder, deeper, lower-pitched wheeze occurring in the upper bronchi. You determine this may be related to obstruction of the larger airways. Which breath sound is this?
A. Crackles
B. Wheezes
C. Rhonchi
D. Stridor
E. Pleural Friction Rub
C. Rhonchi are louder, deeper, lower-pitched wheezes occurring in the upper bronchi; may be related to obstruction of the larger airways: commonly heard during exhalation; sounds like snoring.
A patient comes to the healthcare provider’s office stating she has been short of breath for the past 2 days. She rates her shortness of breath a 6/10. The patient has a past medical history of asthma. You are percussing the lungs and will do all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Percuss the intercostal spaces, moving from the apex to the base using direct percussion.
B. Percuss the intercostal spaces, moving on each side of the anterior lung fields.
C. Percuss the intercostal spaces, moving on each side of the posterior lung fields.
D. Percuss each side of the lateral lung fields using the direct percussion technique
Answer is D
You should not percuss each side of the lateral lung fields using the direct percussion technique. You should percuss the intercostal spaces moving from the apex to the base, on each side of the anterior lung fields, and on each side of the posterior lung fields.
5. Which intervention is most appropriate for preventing excessive heel pressure?
A. Flexing the knees
B. Placing a donut-shaped cushion under the feet
C. Suspending the heels by placing a pillow under the calves
D. Putting a pressure-reducing foam mattress under the heels
Answer is C.
Suspending the heels using a pillow under the calves is the best way to protect heels from pressure ulceration.
5. Nail growth can be affected by which of the following? Select all that apply.
A. Seasons
B. Stress
C. Disease
D. Hormone deficiency
E. Weight
Answer is A, C, D,
Nail growth is affected by seasons. Nails grow slower in the summer than in the winter. Nail growth is affected by certain diseases. Nail growth is affected by hormone deficiency.
Incorrect answer B, E. Nail growth is not affected by stress. Nail growth is not affected by a person’s weight.
5. The patient in the emergency room is assessed as having bruises caused by bleeding under the skin on his arms and legs following a motorcycle accident. This would be documented as:
A. Ecchymosis.
B. Hematoma.
C. Telangiectasia.
D. Petechiae.
Answer is A.
Ecchymosis is a bruise caused by bleeding under the skin or mucous membranes; occurs as a result of local trauma.
Incorrect answers. Hematoma is an elevated collection of clotted blood within the tissue caused by a break in a blood vessel. Telangiectasia is caused by vascular dilation of a small group of blood vessels; occurs anywhere on the body but most often on the face and legs. Petechiae are tiny, pinpoint hemorrhages caused by superficial bleeding from the capillaries of the skin; measure less than 3 mm; may be related to platelet deficiencies.
5. The nurse assesses the patient’s face. What documentation indicates normal findings of this assessment? Select all that apply.
A. Face square
B. Asymmetry of the face structures
C. Nasolabial folds and palpebral fissures equal
D. Flat affect
E. No involuntary muscle movement
F. Skin smooth and clear
Answer is A, C, E
Face round, square, or oval are normal findings of an assessment of the face. Nasolabial folds and palpebral fissures equal are normal findings of an assessment of the face. No involuntary muscle movements are normal findings of an assessment of the face.
Incorrect Answers. Symmetrical facial structures are normal findings of an assessment of the face. Asymmetry of the face may be related to abscess, infection, enlargement of parotid gland, or neurological disorders.
Expression relaxed is a normal finding of an assessment of the face. Flat affect indicates depression or chronic pain.
No involuntary muscle movements are normal findings of an assessment of the face.
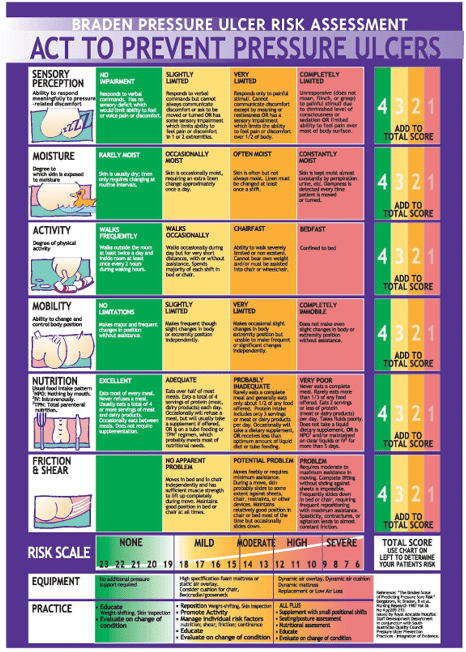
Spends most of the day in bed. Makes occasional slight changes in body or extremity position but unable to make frequent or significant changes independently. Occasionally slides down to foot of bed, requiring some assistance to move back to the top. Able to walk a short distance to the chair with assistance. Incontinent of stool. Continent of urine – uses urinal as needed. Skin occasionally moist from incontinence. Admitting Orders: Tube feeding formula 400cc q 4 hours per PEG. Dietician consult for tube feeding recommendations. Up in chair daily.
1. Based on the information above how would you score the Braden Scale sub-categories?
Sensory Perception _______
Moisture _______
Activity _______
Mobility _______
Nutrition _______
Friction and Shear _______
Total Score _______
Sensory perception = 3
Moisture = 3
Activity = 3
Mobility = 2
Nutrition = 3
Friction and shear = 2
TOTAL SCORE: 16 Mild Risk
When performing an ophthalmoscopic examination of the patients' right eye, you position yourself on the right side of the patient and look through the ophthalmoscope and then:
A. See the optic disk
B. Locate the lacrimal duct opening
C. Locate the red reflex
D. Compare the veins and arteries on the retina.
C. When performing an ophthalmoscopic examination, you position yourself to the side of the patient, look through the ophthalmoscope, and locate the red reflex.
Upon assessment you note a high-pitched whistling or musical sound. You know this could be caused by narrowed passageways in the trachea-bronchial tree by secretion, inflammation, obstruction, or a foreign body. Which breath sound is this?
A. Crackles
B. Rhonchi
C. Wheezes
D. Pleural Friction Rub
D. Stridor
C. Wheezes are caused by narrowed passageways in the trachea-bronchial tree by secretions, inflammation, obstruction, or a foreign body. High-pitched, whistling or musical sound
The serous membrane that lines and adheres to the thoracic wall and produces pleural fluid is the:
A. Surfactant.
B. Parietal pleura.
C. Visceral pleura.
D. Pulmonary pleura.
Answer is B.
Parietal pleura lines and adheres to the thoracic wall and produces a serous fluid known as pleural fluid.
Alveoli secrete a surfactant, a substance that reduces the surface tension and keeps the alveoli moist. Visceral pleura covers the outer surface of the lungs and produces a serous fluid known as pleural fluid. There is no pulmonary pleura.