Unimolecular and bimolecular substitution reactions are called ____ and ____.
What are SN1 and SN2?
Unimolecular and bimolecular elimination reactions are called ____ and ____.
What are E1 and E2?
The three types of solvents are:
What are nonpolar, polar protic, and polar aprotic solvents?
Is this molecule cis or trans?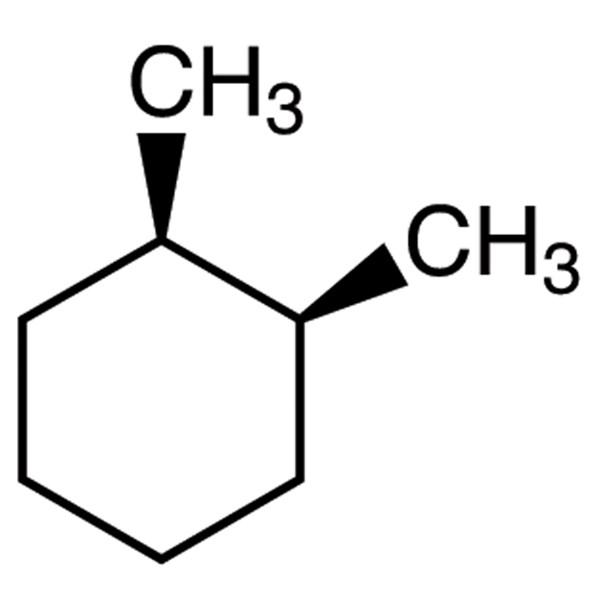
What is cis?
What is the Gibbs free energy equation?

What kind of carbocation is most stable?
Tertiary
An elimination reaction results in the formation of a/an ______.
What is an alkene?
State the characteristics of each solvent type.
Nonpolar solvents have no polarity or significant difference in electronegativity between atoms.
Polar protic molecules have F-H, O-H, or N-H bonds capable of hydrogen bonding with charged molecules and intermediates.
Polar aprotic molecules have a net dipole moment and can stabilize transition states, but they will overly solvate the nucleophile by hydrogen bonding.
List the requirements for a carbon to be a stereocenter.
How does activation energy affect a reaction?
(Hint: Does this relate to thermodynamics or kinetics?)
A higher activation energy translates to the transition state needing more energy to be achieved, resulting in a slower reaction rate.
What change in stereochemistry is characteristic of an SN2 reaction?
Inversion of configuration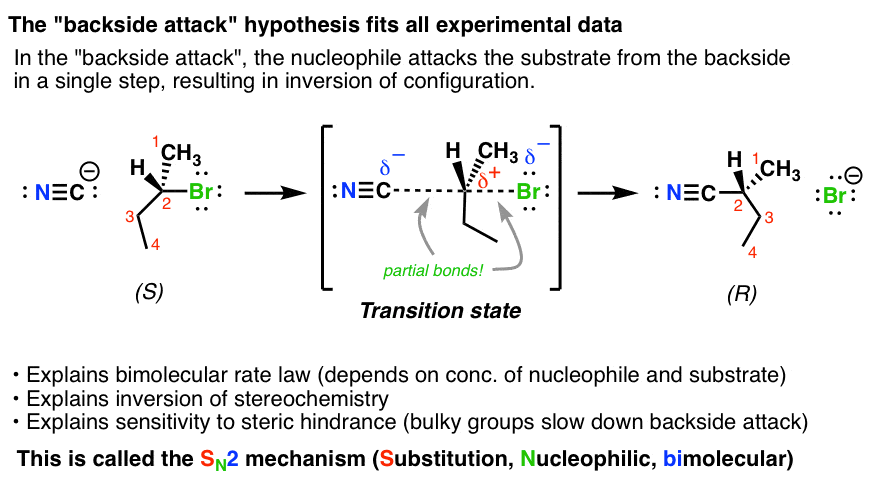
Describe the substitution vs elimination trend as the degree of substitution in the nucleophile and/or electrophile increases.
As either becomes more substituted, elimination becomes likelier.
Acetone is what kind of solvent?
What is nonpolar?
What is the difference between an enantiomer and a diastereomer?
An enantiomer has reverse configurations at all stereocenters. A diastereomer has reverse configurations at only some.
What is the difference between the thermodynamic and kinetic product(s)?
The kinetic product forms faster due to a lower activation energy. Kinetic control favors the product that is made fastest.
The thermodynamic product is more stable and is the major product under equilibrium conditions, typically at higher temperatures.
What needs to be stabilized in a SN1 reaction?
The carbocation intermediate
Why are alkoxide salts better for an elimination reaction than a halide ion?
Alkoxide salts are great bases. Halide ions are excellent nucleophiles, but they are weak bases.
DMF is a ______ solvent.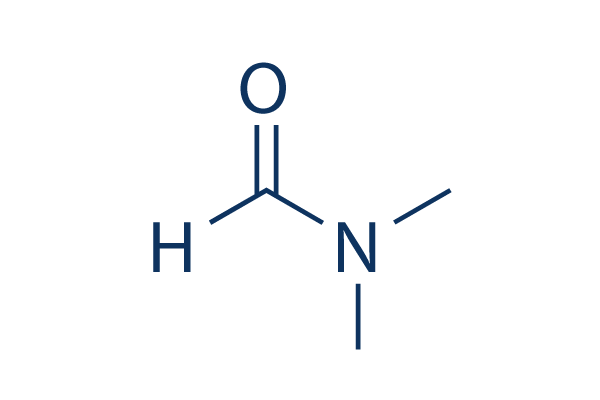
What is polar aprotic?
The stereocenter test: If the molecule has an odd number of stereocenters, it is chiral. If it has an even number, more investigation is needed.
The symmetry test: If a molecule is symmetrical, it will rarely have a stereo
If you have a positive enthalpy for a reaction, is it likelier that you are breaking down a molecule or making a bigger one from smaller molecules?
Making a bigger one
Ex: Think of photosynthesis!
In a reaction with tert-iodobutane, doubling HBr will affect the reaction rate by:
There will be no effect.
Solution: You know that the rate equation for this reaction is k[iodobutane] because tert-iodobutane will undergo an SN2 reaction. Therefore, doubling the HBr concentration will have no impact on the reaction.
Can the reaction of benzyl bromide with isopropyl alkoxide form an elimination product?
No. There are no available beta protons in the electrophile (benzyl bromide).
What is polar protic?
Is this molecule chiral or achiral?
Calculate change in entropy (S) for the complete combustion of 1 mol of hexene.
6
Solution: The formula is C6H12 + 9O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H20 . S = (3)(number of molecules). For the reactant side, that is 3*10. For the product side, that is 3*12. 36-30= 6.