Organisms that sustain themselves without eating anything derived from other organisms vs organisms that obtain their organic material from other organisms.
What is Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs?
What is this?
A spontaneous/exergonic reaction
What is the general structure of ATP?
Ribose, adenine, and three phosphate groups.
What are the two types of fermentation and what type of organisms use them?
Alcohol fermentation is used by microorganisms
Lactic acid fermentation is used by microbes and larger organisms
What is the general formula for photosynthesis?
Energy + 6CO2 + 6H2O -> C6H12O6 + 6O2
An energetically favorable process that occurs without an overall input of energy vs processes can happen with input of energy.
What is spontaneous vs nonspontaneous processes?

What is this showing?
Lactic acid fermentation.
What are the three main kinds of work in the cell?
Chemical, transport, and mechanical.
Which metabolic pathway is common to both fermentation and cellular respiration of a glucose molecule?
Glycolysis
What are the three phases of the Calvin Cycle?
Carbon fixation (catalyzed by rubisco), Reduction, and Regeneration of starting molecule (RuBP)
When a substance loses electrons vs when it gains electrons.
Oxidation vs reduction

What are C, D, E, and A?
C - glycolysis
D - Citric Acid Cycle
E - oxidative phosphorylation
A - ATP
What is this and what do the terms mean?
∆G = ∆H – T∆S
This is the free energy equation.
∆G = free energy
∆H = change in enthalpy
T = temperature
∆S = change in entropy
In fermentation, ___ is reduced to ___ or lactic acid and ___ is oxidized back to____
pyruvate; ethanol
NADH;NAD+
The Calvin cycle uses the chemical energy of ___ and ____ to reduce ___ to form ___
ATP; NADPH; CO2; Sugars
When the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an enzyme earlier in the pathway.
What is feedback inhibition?
 What are F, H, I, G, C, and L?
What are F, H, I, G, C, and L?
C = CO2
F = Light reactions
G = Calvin Cycle
H = ATP
I = NADPH
L = sugars
What are enzymes impacted by?
pH, temperature, cofactors, and inhibitors.
How is the proton gradient formed by the electron transport chain?
NADH and FADH2 donate electrons to carriers in the electron transport chain which are then passed down the transport chain. Energy released by electron transfers coupled to pump H+ from the matrix to the intermembrane space.
What do light reactions in the thylakoid do?
Split H2O, release O2, reduce NADP+ to NADPH, and generate ATP from ADP by photophosphorylation
____ couples electron transport to ATP synthesis through ____, which uses coupling energy in an electrochemical H+ gradient to drive cellular work
What is Oxidative phosphorylation; chemiosmosis?
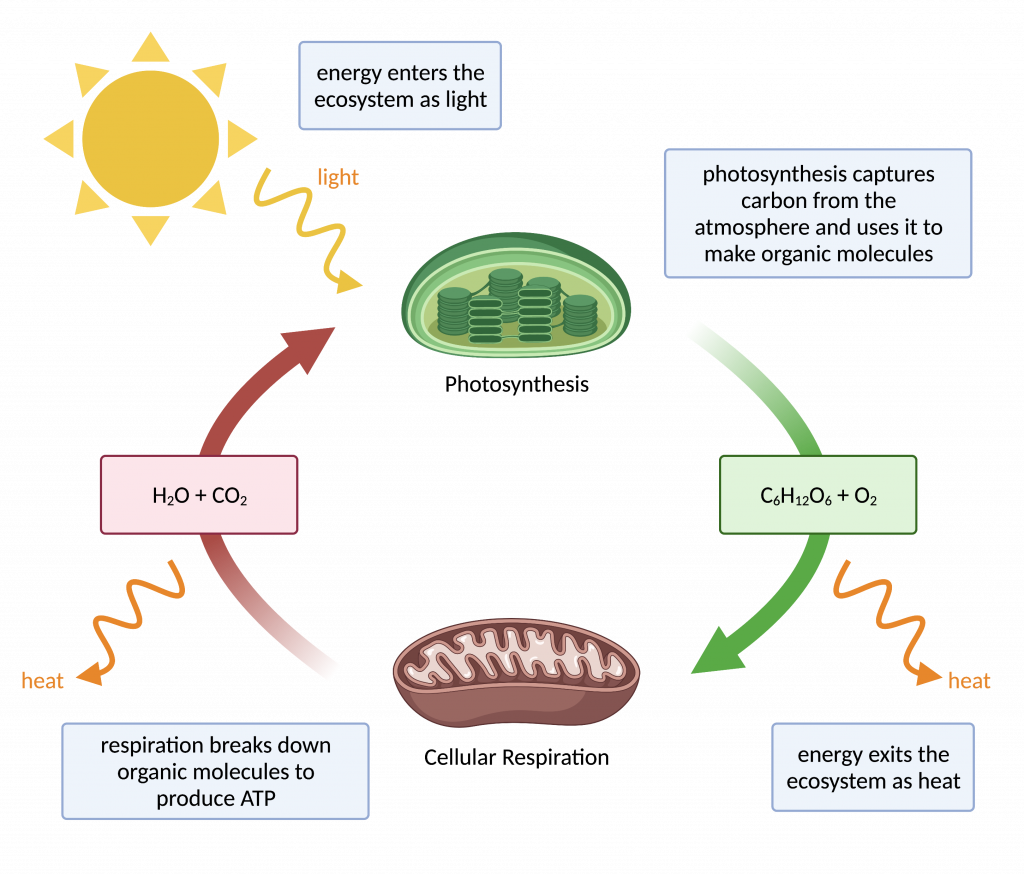
1. 
2. 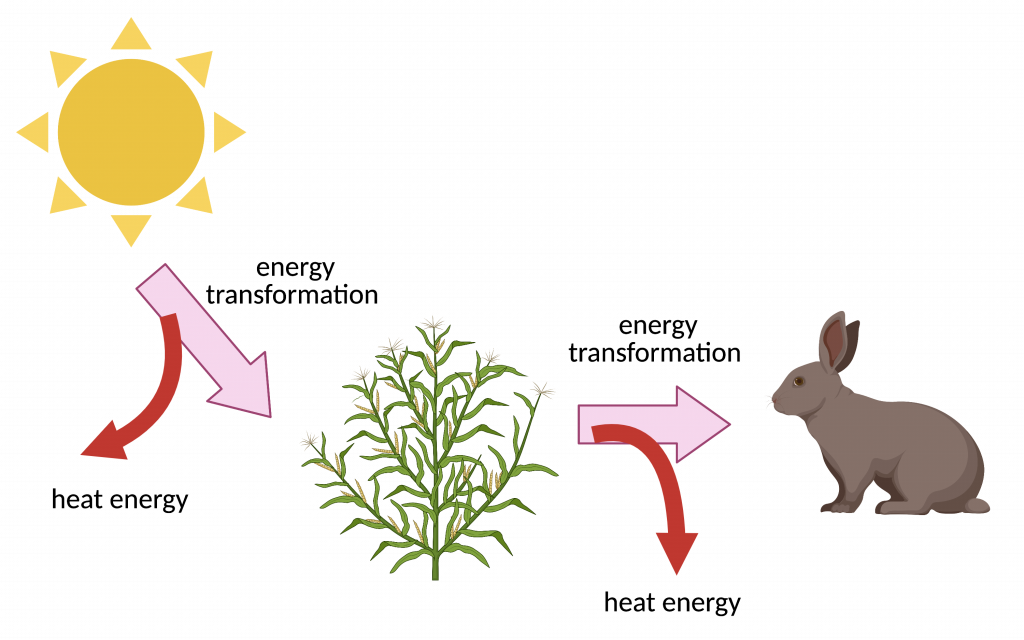
What is image 1 showing? What is image 2 showing?
1. First Law of thermodynamics
2. Second Law of thermodynamics
Choose the pair of terms that correctly completes this sentence: Catabolism is to anabolism as ____________ is to ____________.
exergonic; endergonic
What are the differences between fermentation, aerobic respiration, and anaerobic respiration?
Fermentation is partial degradation of sugars that occurs without O2, Aerobic respiration is complete degradation of organic molecules consuming O2 and yielding maximum amount of ATP, and Anaerobic respiration is complete degradation of organic molecules consuming compounds other than O2.
H2O -> p680 -> primary electron acceptor (in PSII) -> electron transport chain #1 -> p700 -> primary electron acceptor (in PSI) -> electron transport chain #2 -> NADP+ (forming NADPH)