Innervation of the acroneus m.
Radial n.
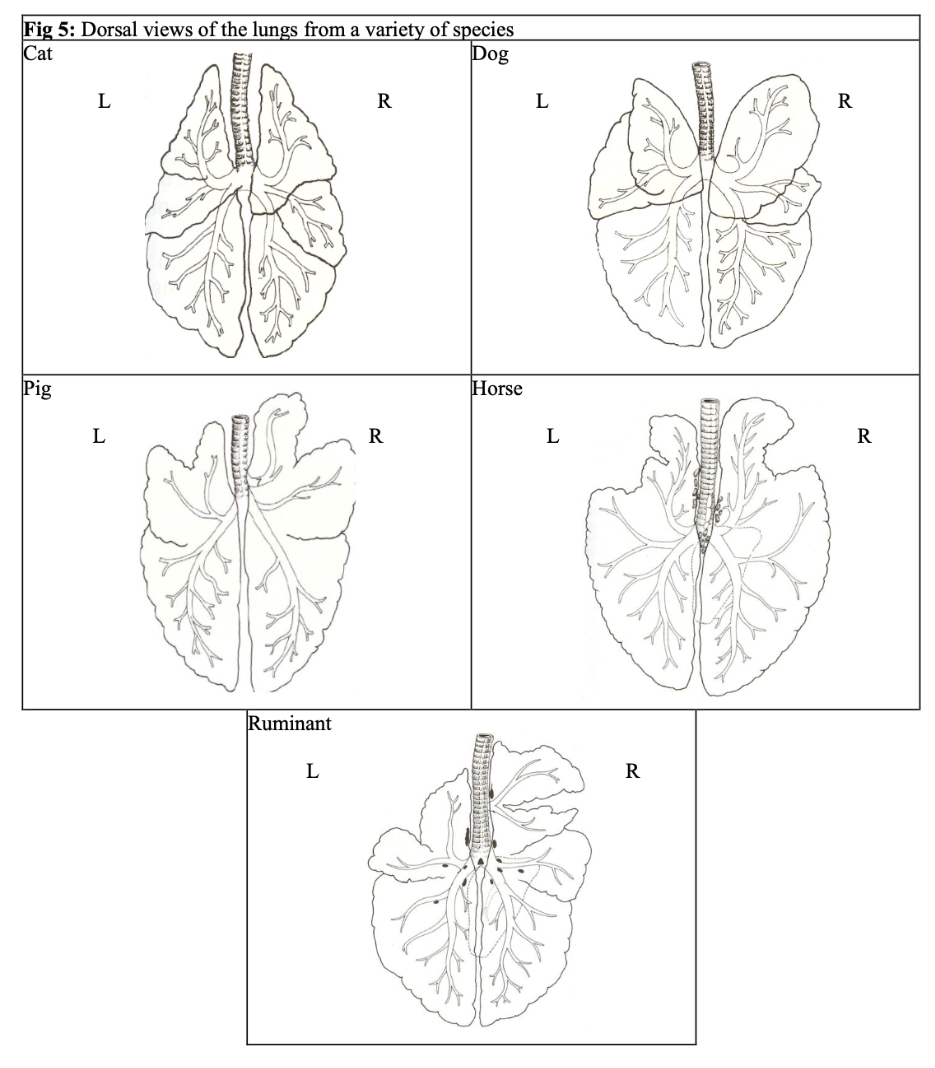
Size difference between left and right lung.
This is because of the cardiac im/depression on the left lung
The nerve that has a left and right division that runs through the thorax to the diaphragm (not a CN).
Phrenic n.
The embryonic layer that the notochord is "made up of" (it also migrates outward).
Mesoderm
Name the lymphatics at sit at the lung roots.
Left, right, and middle tracheobronchial lymph nodes
This vein is a tributary of the external jugular v.
Cephalic v.
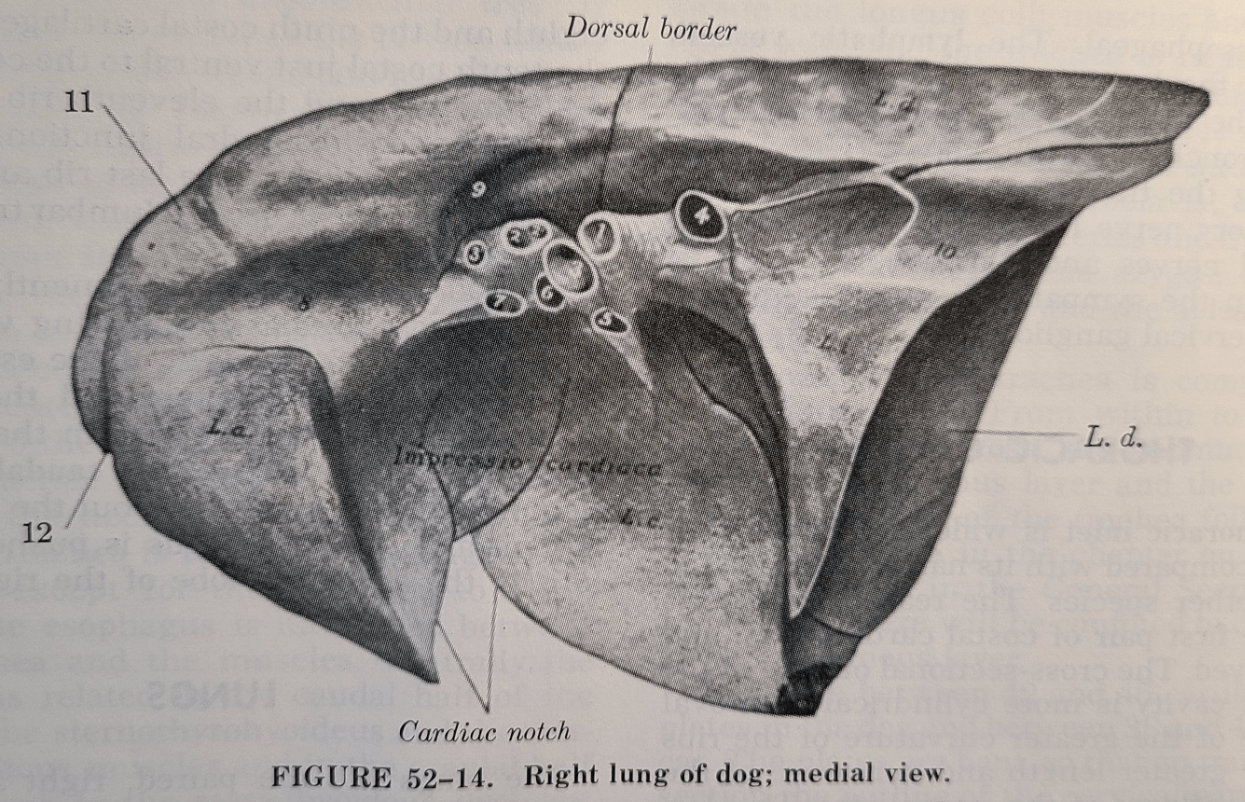
Location and (clinical) function of the cardiac notch.
An inverted V shaped area between the cranial and middle lobes that provides a window to the heart without any overlaying lung tissue.
Innervation of cutaneous trunci m.
Lateral thoracic n.
The limb bud(s) that form first. The thickness at the tip of the limb bud.
The thoracic limb buds form more quickly than the pelvic limb buds.
Thickness at the end of limb bud: Apical ectodermal ridge
The structure/tissue that surrounds the heart.
Pericardium:
1) Parietal pericardium
2) Viceral pericardium (epicardium)
CN 12 - Accessory spinal n.
ALternate name for the bifurcation of the trachea.
Carina
Describe the origin and location of the Intercostal nerves.
The intercostal nn. arise as ventral branches of the thoracic spinal nn.
Intercostal nn. pass ventrally along the caudal edge of each rib in association with the intercostal arteries and veins.
The three parts of the somite(s) and their fates.
Dermatome: skin/dermis
Myotome: skeletal muscle
Sclerotome: migrate to become vertebral bodies, ribs.. axial skeleton
N/B:
- all are collagen derivatives
- neural connections follow segmental organization from neural crest cells: sclerotomes/dermatomes → esp. sensory n. & myotomes → esp. motor n.
The large lobe like structure in the cranial ventral aspect of the thorax. (Hint: not lung)
Thymus
The devisions of the brachial plexus.
(Suprascapular n.)
(Subscapular n.)
Musculocutaneous n.
Axillary n.
Radial n.
Median/Ulnar nn.
Label the species.
Crevicothoracic ganglion (Left/Right)
Middle cervical ganglion
Sympathetic trunk ganglion
The lateral mesoderm is divided into two layers. These layers join with ectoderm to form what aspects of the embryo.
Superficial lateral mesoderm + ectoderm = somatic mesoderm → body wall
Deep lateral mesoderm + ectoderm = splanchnic mesoderm → gut tube/mesenteries
(somatic = body)
(splanchnic = visceral)
Animal(s) that lack diaphragms.
Birds and Reptiles
(0) a. starts the path into the forelimb and goes into (1) a. which goes into brachial a. which branches into (2) a. and (3) a.
(3) a. lead into (4) a. which branches into (5) a.
(think larger/primary vessels)
(0) = subclavian a.
(1) = axillary a.
(2) = subscapular a.
(3) = brachial a.
(4) = median a.
(5) = radial a.
Name five of the primary muscles involved in inspiration and expiration.
Inspiration:
External intercostal mm. (fibers: caudal/ventral)
Levator costae mm. (transverse processes of vertebrae to proximal ribs)
Scaleneus m.
Serratus doralis cranialis m.
Diaphragm (Pars sternalis/costalis/lumbalis)
(Rectuc thoracis mm.)
Expiration:
Internal intercostal mm. (fibers: caudal/dorsal)
Serratus doralis caudalis m.
(Transverse thoracis mm.)
Describe how the vagus n. travels through the thorax.
Left and right vagus nn. → divide into dorsal and ventral branches of the left and right (→ eventually join into singular dorsal and ventral branches)
Name two embryological digital defects and two embryological vertebral defects, and define them.
Digital:
Syndactyly: fused digits
Brachydactyly: short digits
Polydactyly: too many digits
(Grk: syn=together/fused; brachy=short; poly=many; -dactyly="fingers")
Vertebral:
Block vertebrae: adjacent fusions or arches or whole vertebrae
Hemivertebrae: only a portion of the vertebrae is present
Spina bifida: midline cleft in the vertebral arch
Transitional vertebrae: vertebrae/rib in the wrong place
Torticollis: wry neck (Latin: torti = twist, coll = neck/column)
Kyphosis: ventroflexed deviation (Grk: kyph- = humped, -osis =state of disease)
Lordosis: dorsiflexion deviation (Grk: lord- = bent/backwards)
Scoliosis: laterally flexed deviation (Grk: scoli- = bent/crooked)
The side of the thorax for best viewing of the vena cavas and the best side of the thorax for viewing the pulmonary trunk.
Vena cavas: right side of the thorax.
Pulmonary trunk: left side of the thorax.