Cellular Respiration
Gene Expression
What are the three stages of cellular respiration?
1. Glycolysis
2. Pyruvate Oxidation
3. Oxidative Phosphorylation
What ion passes through ATP synthase from the intermembrane space back into the matrix? What causes them to move in this direction?
hydrogen, concentration gradient
What two things is the DNA backbone made out of? (specific sugar name)
Deoxyribose and phosphate
Where are codons and anti-codons found?
codons are on mRNA, anti-codons are on tRNA
How many different combinations of codons are there? How many amino acids are there?
64 codons, 21 amino acids
What is the output of glycolysis?
2 ATP, 2 pyruvate, 2 NADH
What process will occur in both anaerobic respiration and aerobic respiration, why?
Name the DNA bases, what are the base pairs?
Guanine and Cytosine
What is the function of RNA polymerase? Is it active during transcription or translation?
an enzyme that is responsible for copying a DNA sequence into an RNA sequence during transcription
In cellular respiration, what is happening to hydrogen during oxidation and reduction?
Glucose loses hydrogen during oxidation, oxygen gains hydrogen during reduction
What is the output of the citric acid cycle for every molecule of glucose
2ATP, 8 NADH, 2 FADH2, 6 CO2
How many ATP molecules are created from aerobic cellular respiration and how many are produced during anaerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration: 28-30+
Anaerobic respiration: 2
List where transcription and translation occur in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
Eukaryotic: transcription- nucleus
translation- cytoplasm
Prokaryotic: transcription- cytoplasm
translation- cytoplasm
In eukaryotic cells, why is RNA essential for gene expression?
What causes lactic acid to build up in the muscles?
lack of oxygen
What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 ---> 6 CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
Where does oxidative phosphorylation take place?
inner mitochondrial membrane
Where is ATP synthase located?
inner mitochondrial membrane
What is transcription? What is significant about the base pairs in the mRNA in this process?
The process of going from DNA to mRNA, RNA has uracil instead of thymine
What is citrate and how is it formed?
acetyl CoA joining with oxaloacetate, citrate has 6 carbon atoms
What is the output of the citric acid cycle per pyruvate?
3 NADH, 2 CO2, 1 FADH2, 1 ATP
What are the acronyms for the two electron carriers in cellular respiration and how are they presented when they're not carrying hydrogen electrons?
NADH and FADH2. NAD and FAD aren't cayying hydrogen electrons
What is translation? Explain the process
mRNA goes into the cytoplasm where the ribosome travels along the strand from the 5' end to the 3' end. The ribosome reads the codon, the tRNA's anti-codons bind with the codons on the mRNA, an amino acid is formed and a peptide bond forms to form a polypeptide chain and the ribosome shifts to the right
What happens at the A site, P site, and E site?
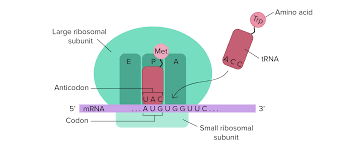
A site: where the appropriate tRNA initially binds to the codon (a tRNA with one amino acid)
P site: Where the polypeptide chain is
E site: The tRNA that was initially in the P site and is now exiting the ribosome
What is the purpose of oxygen in cellular respiration?
It combines with hydrogen ions to form water in the electron transport chain