What kind of narratives are told most by 5 and 6 year olds?
personal anecdotal
give 3 examples of derivational morphemes
-ity, un-, -less etc...
For the 2nd vocabulary spurt, what kind of words have the greatest growth?
derived words
Literacy is a ____ skill.
language
MLU is calculated by_____.
# of morphemes/# of total utterances
By what grade to children begin using beginning and ending markers in fictional stories?
2nd Grade
A relative clause immediately follows a ___.
noun
"burning the candle at both ends" is an example of an ______________ and is mastered around 9-10 years of age
idiom
What are the 4 phases of reading according to Ehri (2005)?
pre-alphabetic
partial-alphabetic
full alphabetic
consolidated alphabetic
What type of sentence is this?
Blake went to the park and he played with his friends.
compound sentence
What are a few characteristics of older children's narratives?
-fewer unresolved problems and unprepared resolutions
-less extraneous details
-more complex episode structure
-closer adherence to the story grammar model
What is a phrase?
a unit that does not contain a subject or predicate, is less than a sentence
understanding sound changes based on morpheme combination (i.e. electric---> electricity)
When do children start to read for pleasure?
4th Grade
Identify the syntactic structures present in this sentence:
Leah went to the store that had new labubus.
Independent clause
Relative clause
Embedded clause
Prepositional phrase
what is coherence?
what makes a narrative a well-developed story, including a sequence of related events which create meaning in a story
What type of sentence seems to be the hardest for kids to learn?
by around 11 years old, definitions are more __________________like
adult-like, dictionary-like
______________ language is more naturally learned through exposure and experience. It is not effortful
Oral
What do you do at the end of a sentence to indicate it is a question?
Rising intonation
What are the elements of story grammar?
hint: there are 8
characters, setting, problem, feelings, plan, actions, outcome, ending
What is metalinguistics?
the abiity to think about language as a thing and manipulate its components (i.e. words, syllables, phrases).
What is slow mapping?
acquisition and integration of adult-like semantic features into the semantic network comprising a word definition
What is morphological awareness?
used to process written text, understand meaning of new words encountered in print by combining grammatical units
Compare oral language to written language
Oral language is: universal, more contextualized, a primary language skill
Written language is: an artifact of humans, more decontextualized, not universal
TRUE or FALSE : By 11/12 years of age, development of cognitive and communicative skills are almost equal to an adult
True
Kids in the US are able to comprehend and produce most sentence types by what age?
5
During the 2nd vocabulary spurt, the least amount of growth is seen in _____________.
idioms

__________ are categories of items, _____________ are centered around an event
taxonomies; thematic
By age _____________, children produce and comprehend "this, those, that, these, etc."
age 7
Give an example of the instrumental -er (turns a verb into a thing)
print + er (printer), blend + er (blender)
At what age are all phonemes represented?
6 years 11 months
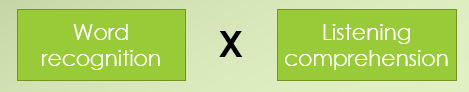
Background knowledge, vocabulary, language structures, verbal reasoning, literacy knowledge, phonological awareness, decoding, and sight recognition are all needed for _____.
skilled reading
Which part of language increases in complexity until adulthood and then stabilizes?
morphosyntax