This type of muscle is striated, multinucleated, and voluntary
Skeletal Muscle

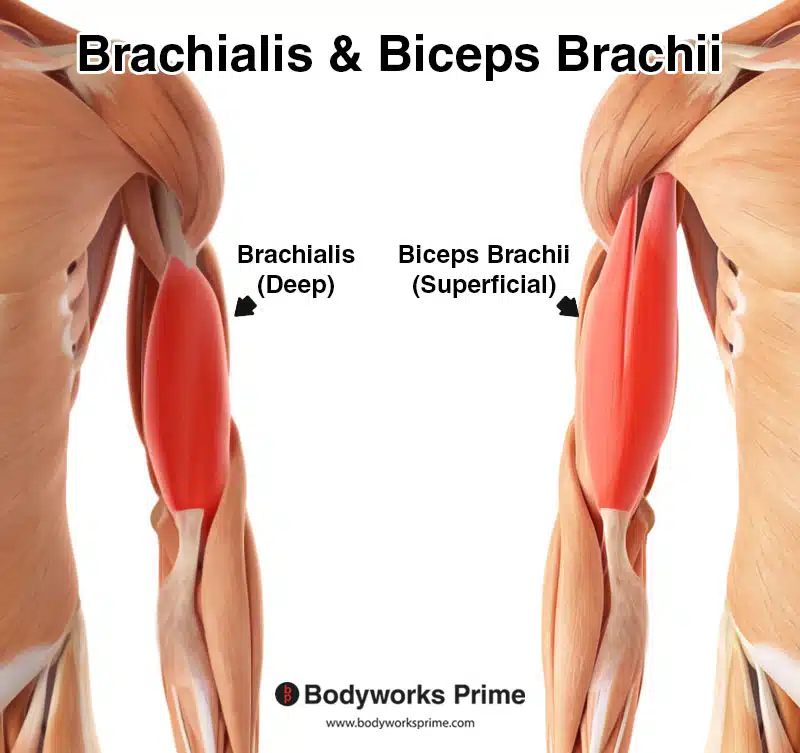
The main flexor of the elbow located deep to the biceps brachii
Brachialis
The Hamstrings include all of the following except: Semitendinosus, rectus femoris, semimembranosus, biceps femoris
Rectus femoris is not a part of the hamstrings

This muscle originates on C1-C4 and inserts on the medial borders of your scapulas. Elevates your scapulas
Levator Scapulae
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13916/levator_scapulae.png)
The name of the line of fibrous tissue that runs down the center of the abdomen
Linea alba
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13106/jtDy9YtpbGFCf4sSHxm48w_Linea_alba_1.png)
This main mastication muscle originates on the zygomatic arch and inserts on the mandible
Masseter
The name for the ability of a muscle to respond to stimuli
Excitability
The outermost layer of muscle is surrounded by what type of tissue
Epimysium

The main elbow extensor
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13946/aHliOOl62koJhumoZcUysg_vsBTp2iDc2_M._triceps_brachii_1.png) Triceps Brachii
Triceps Brachii
This quadriceps muscle lies lateral to the rectus femoris muscle.
Vastus Lateralis

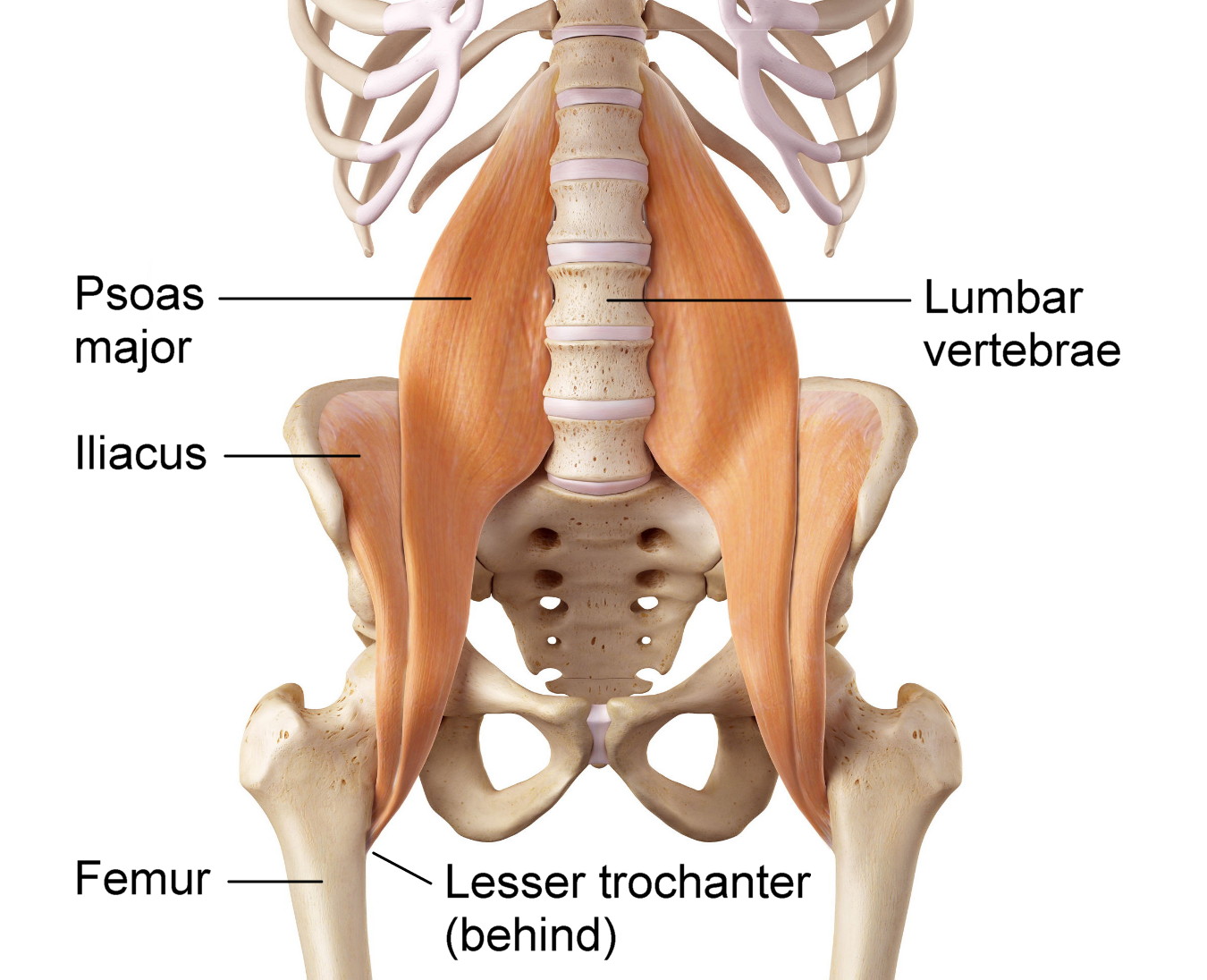
What 2 hip flexors make up the iliopsoas group
Iliacus and Psoas Major
The most lateral muscle of the erector spinae group
Iliocostalis

This type of muscle found in the face is only able to close, not open
Orbicularis (oculi or oris)
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/orbicularis-oris-muscle/e1HTO3sjqPhfSGPAMu9vA_sbzEu7YwVgV3CH95mY9jhg_Orbicularis_oris_muscle_01.png)
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13058/vcrefJ8Pj16AgRaoFe8Hg_Orbicularis_oculi_muscle_01.png)
This type of muscle opposes the action of another
Antagonist
This layer of muscle is made up of multiple muscle fibers
 Muscle Fascicle
Muscle Fascicle
Originating from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, this muscle extends the 5th digit
Extensor digiti minimi
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/extensor-digiti-minimi-muscle/UIQkfmVsMaNosXmnAYw_y776fbVDJ73xLaSaKGflVQ_Dwp6qWzbWg_Musculus_extensor_digiti_minimi_2_copy.png)
This muscle is the most medial and superficial thigh muscle, assists with hip adduction, knee flexion, and internal knee rotation
Gracilis

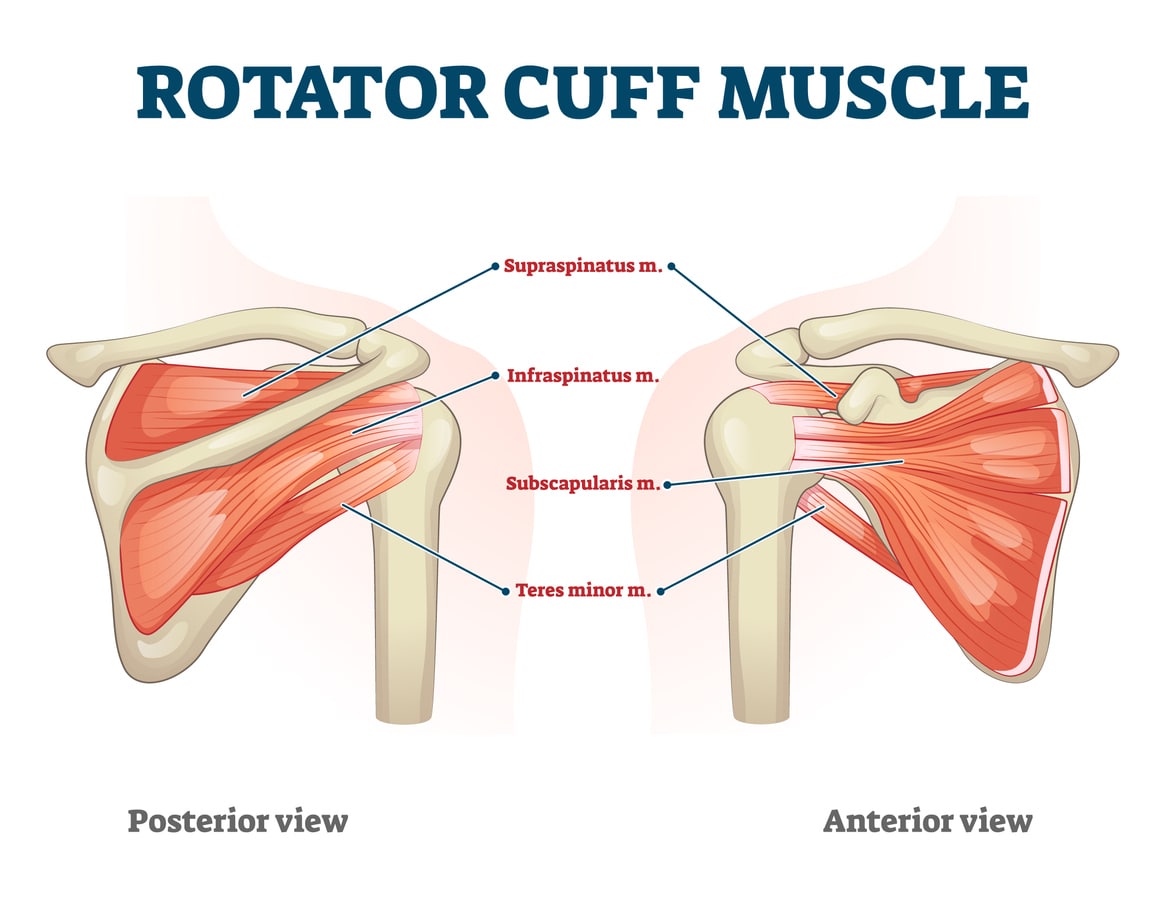
Which of the following is NOT a part of the rotator cuff: Teres Minor, Infraspinatus, Supraspinatus, Deltoid, and Subscapularis
Deltoid
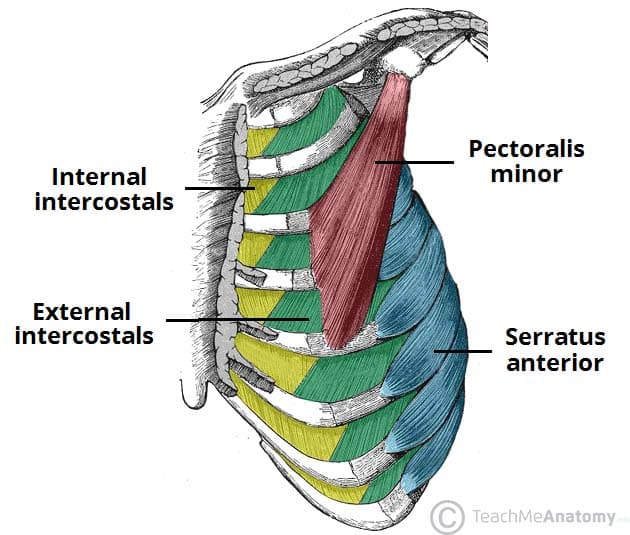
These muscles are used for expanding the thoracic cavity and drawing the ribs up, like during inhalation
External Intercostals
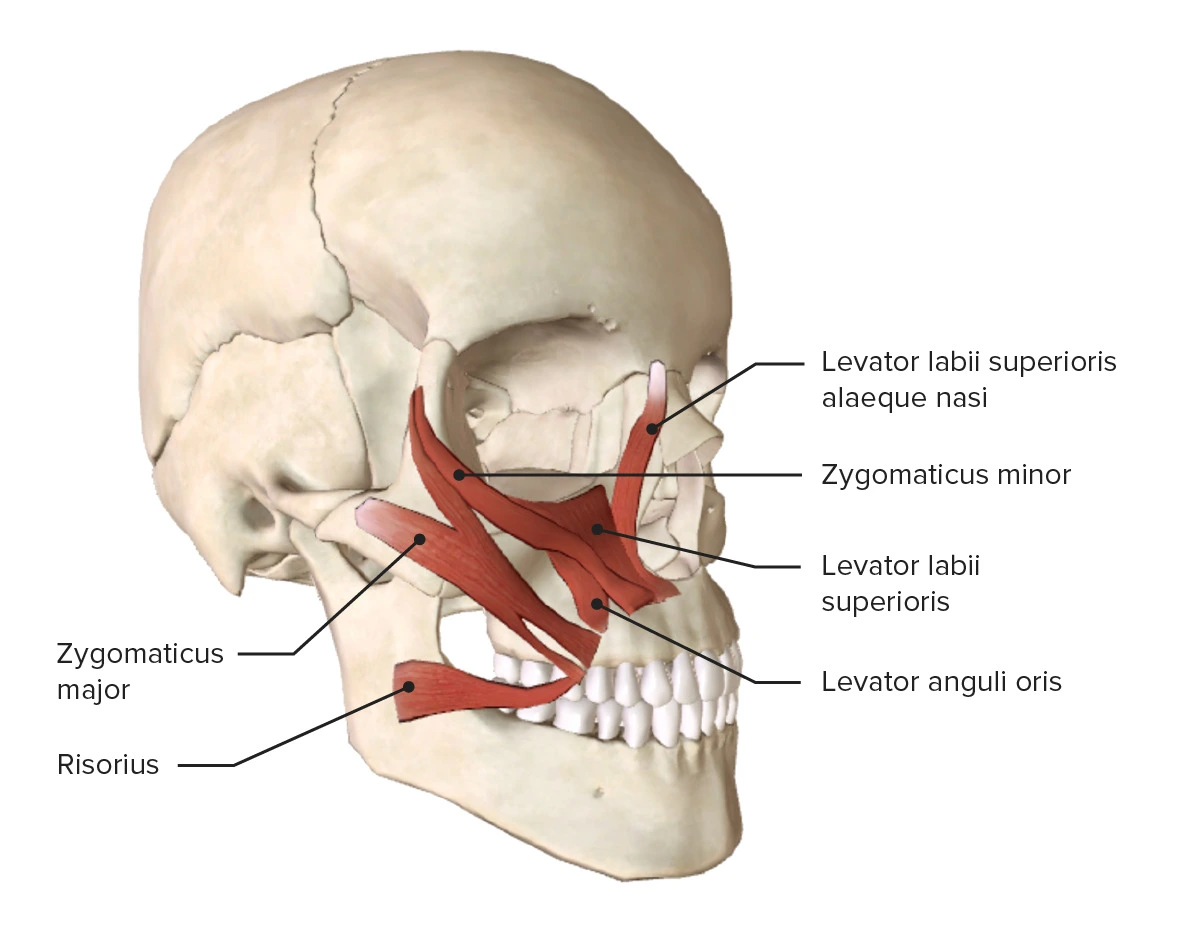
This muscle originates on the zygomatic bone and inserts on the orbicularis oris. One of the main muscles used for smiling
Zygomaticus major (and minor a little)
- pulls lips up and back
The thing that makes muscles red
Myoglobin
The H band is only made up of what type of filament
Thick filament, aka myosin
The muscle originates on the humerus and inserts on the styloid process of the radius. Assists with elbow flexion.
Brachioradialis
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13121/v4cjWb9YRtBJX2uCql7Sg_G2szyLxpqm_M._brachioradialis_1__1_.png)
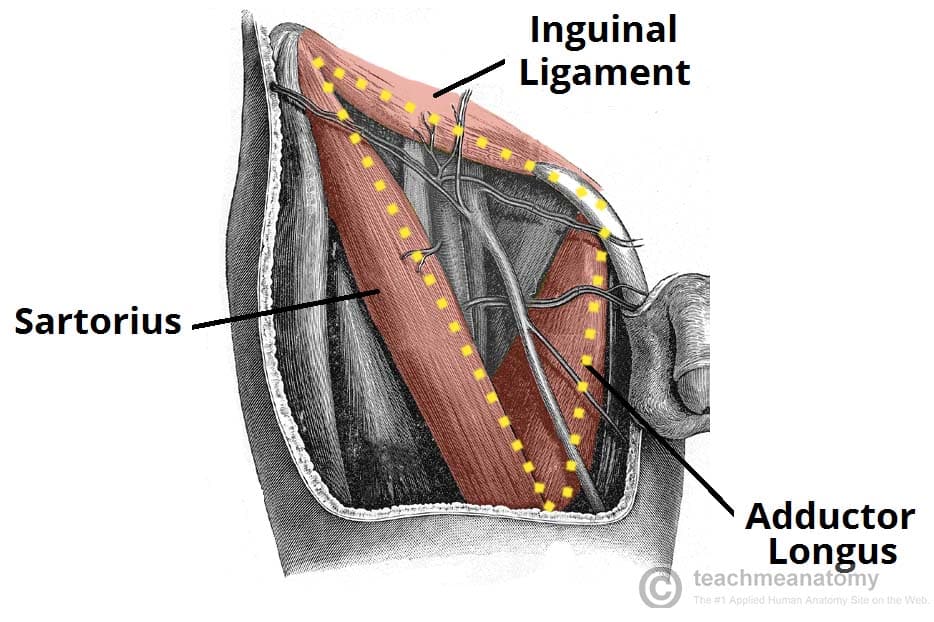
Name the 3 boundaries of the Femoral Triangle
Inguinal Ligament - superiorly
Sartorius - laterally
Adductor Longus - medially
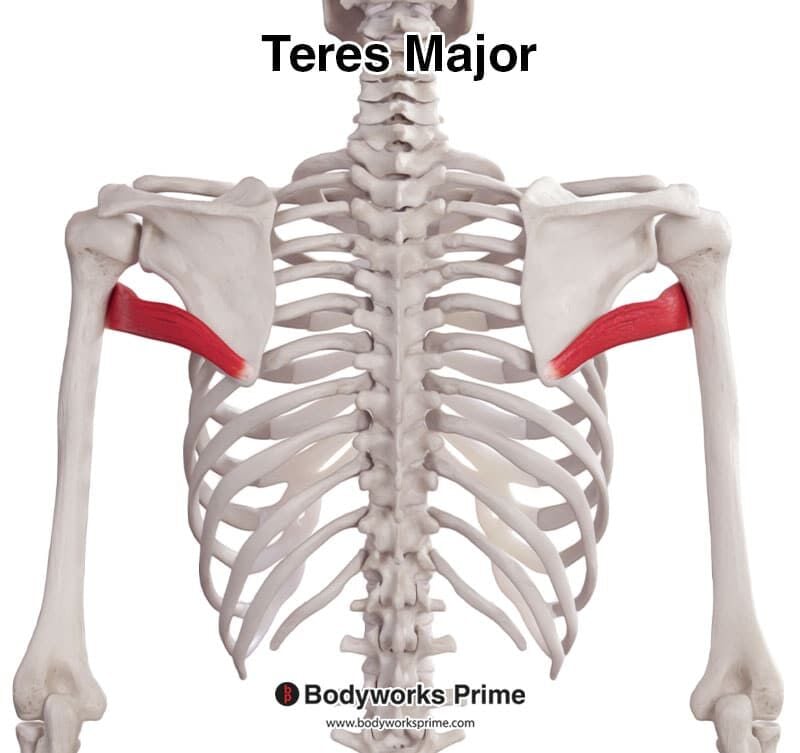
This muscle is not part of the rotator cuff, it originates on the scapula, inserts on the humerus, and is assists with medial rotation and adduction of the humerus
Teres Major
The most medial muscle of the erector spinae group
Spinalis

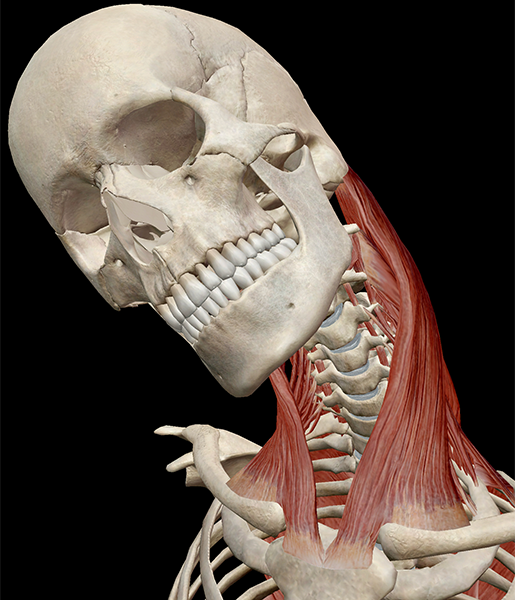
This muscle originates on your manubrium and clavicle, inserts on your mastoid process, and flexes, extends, laterally flexes, and rotates the head
Sternocleidomastoid

The ability of a muscle to contract
Contractility
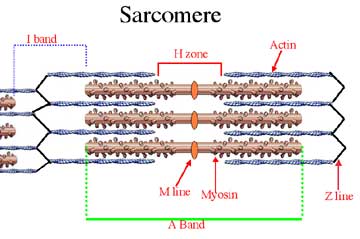
The only part of the sarcomere that gets bigger during contraction
 The zones of overlap
The zones of overlap
This wrist flexor originates on the medial epicondyle of the humerus and inserts on the palm
 Palmaris Longus
Palmaris Longus
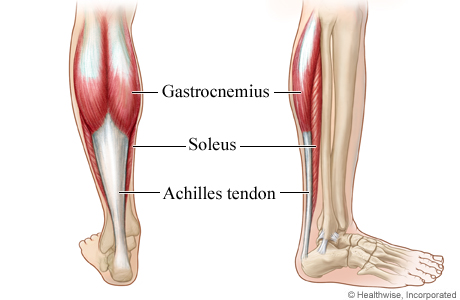
This muscle can be found superficial to the Soleus muscle
Gastrocnemius
This muscle originates on the pubic bone and inserts on the posterior femur and is responsible for hip adduction and flexion
Pectineus:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12925/vaES39uEJjYbb5F0tkxhDA_WSz1YLHvfG_M._pectineus_NN_1.png)
These muscles are used for compressing the thoracic cavity like during exhalation
Internal Intercostals

This muscle compresses the cheeks against the teeth and is used for activities like blowing out a candle
Buccinator
The ability of a muscle to stretch
Extensibility
This band contains both thick and thin filaments and doesn't change size during muscle contraction
 The A band
The A band
This synergistic elbow extensor originates on the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and inserts on the olecranon of the ulna (Dr. Yard will ask this)
Anconeus, synergistic to the triceps brachii

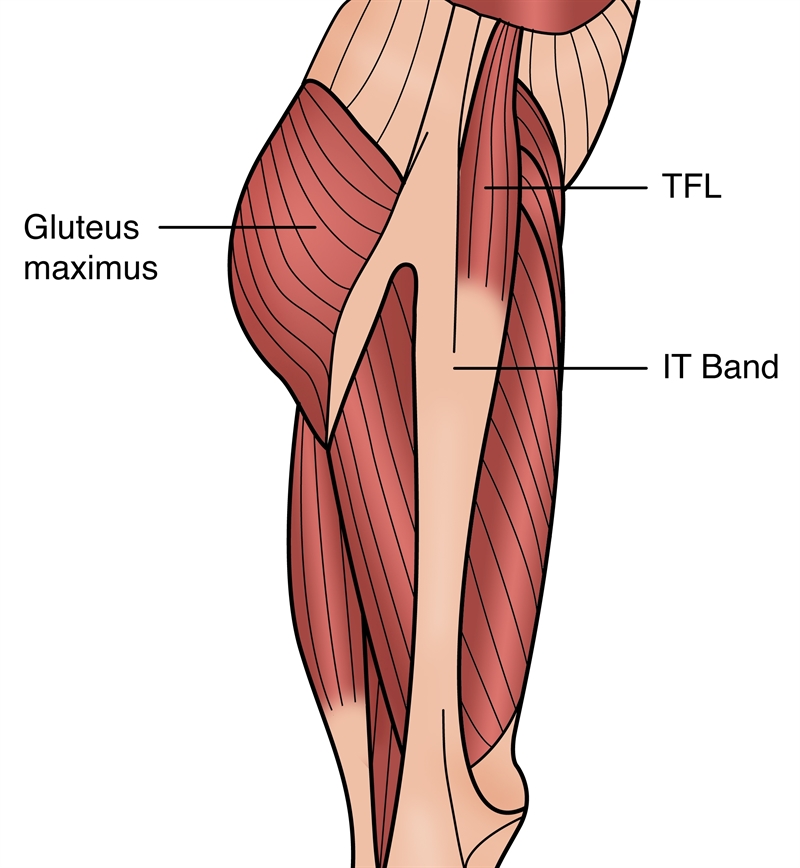
This muscle is continuous with the iliotibial tract and is responsible for knee extension and lateral rotation, and weak hip ABduction.
Tensor Fascia Latae
This muscle originates in the lumbar region and inserts on the humerus. Responsible for adduction, internal rotation, and extension of the shoulder.
Latissimus Dorsi:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13441/IrtirBf6PsVLImfncXQHWQ_Musculus_latissimus_dorsi_1.png)
This muscle is the main muscle responsible for scapular protraction, originates on the lateral edges of the first 8-9 ribs and inserts on the anterior scapula

Serratus Anterior
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13978/Serratus_anterior_muscle.png)
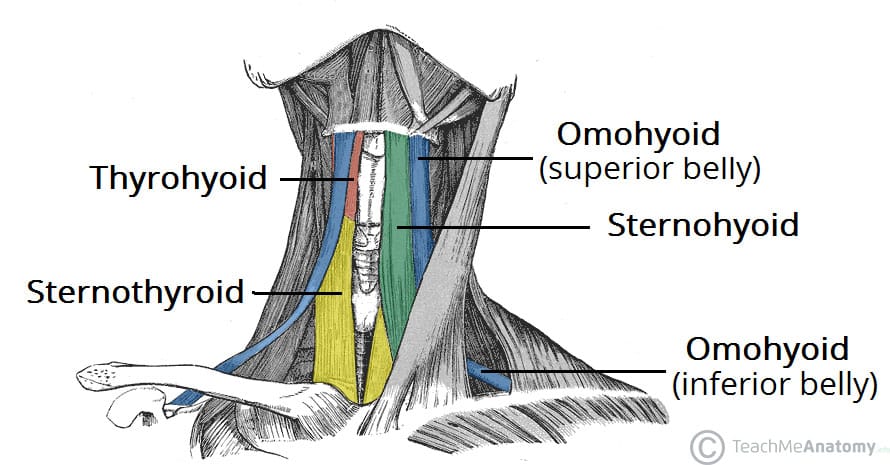
The Omohyoid Muscle runs from:
A) Manubrium to Hyoid Bone
B) Manubrium to Thyroid Cartilage
C) Thyroid Cartilage to Hyoid Bone
D) Suprascapular Notch to Hyoid Bone
D) Suprascapular Notch to Hyoid
A = Sternohyoid (sternum to hyoid)
B = Sternothyroid (sternum to thyroid)
C = Thyrohyoid (thyroid to hyoid)
The ability of a muscle to return to its original size
Elasticity
This ion binds to troponin, causing tropomyosin to move off the myosin binding sites
 Calcium
Calcium
This powerful wrist flexor originates on the medial epicondyle of the humerus and the olecranon, inserts on the pisiform bone, and is more medial in anatomical position
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13031/UT0aPd4QW1Zl7MuKo0Q_PA6RuDjVxK_M._flexor_carpi_ulnaris_2.png)
Put these structures in order from lateral to medial in the femoral triangle
Femoral Vein, Nerve, Artery, and Lymphatics

N - Nerve
A - Artery
V - Vein
L - Lymph
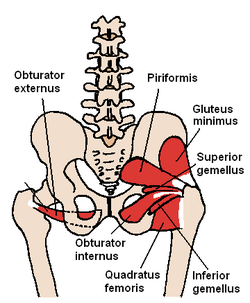
Name the missing lateral hip rotator: Piriformis, Gemellus Superior, Obturator Internus, Quadratus Femoris, Obturator Externus
Gemellus Inferior

This muscle that originates on the shoulders/superior trunk and inserts on the mandible tenses the neck and is partially responsible for frowning and opening the jaw
Platysma
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/the-platysma/elcYGWc1cNC7GM1388qgg_elH1AhZYjzqftzpMzoMY1g_Platysma_02.png)
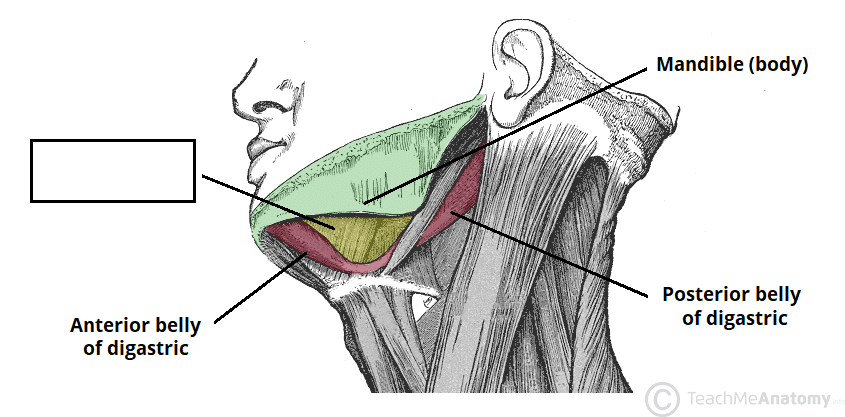
This image is showing which triangle
A) Suprahyoid Triangle (SHT)
B) Submandibular Triangle (SMT)
C) Superior Carotid Triangle (SCT)
D) Inferior Carotid Triangle (ICT)
B) Submandibular Triangle (SMT)
The name for all of the muscle cells/fibers that one neuron innervates
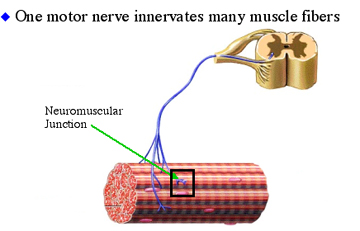 Motor Unit
Motor Unit