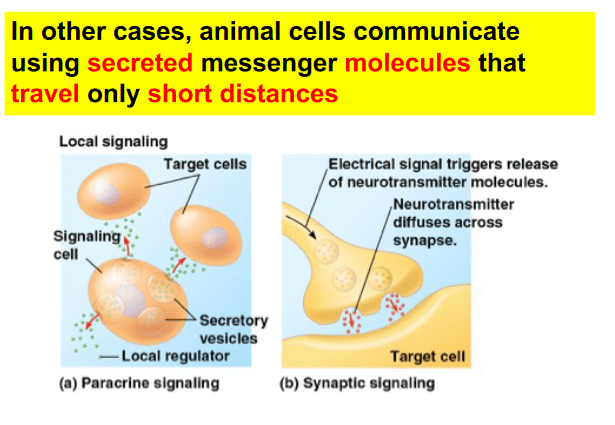
Which of the following is an example of paracrine signaling?
a. Glucagon being secreted by the pancreatic alpha cells and traveling through the blood to reach the liver
b. The T-cell receptor on T cells binding to the MHC molecule with antigen expressed on dendritic cells
c. A parasympathetic neuron releasing the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine, which diffuses across the synapse to bind to a cholinergic receptor on the pacemaker cells of the SA node.
d. Epinephrine being secreted by the adrenal medulla and traveling through the blood to reach beta 1 receptors on the heart
c. A parasympathetic neuron releasing the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine, which diffuses across the synapse to bind to a cholinergic receptor on the pacemaker cells of the SA node.
Which of the following statements are true about mitosis/meiosis? (Select all that apply)
a. Mitosis results in 2 daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and the parent cell
b. Meiosis results in 4 daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other
c. Meiosis results in 4 daughter cells that can be genetically different from the parent cell
d. Mitosis results in 4 daughter cells that are genetically variable from each other
a. Mitosis results in 2 daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and the parent cell
c. Meiosis results in 4 daughter cells that can be genetically different from the parent cell
Which of the following statements are true regarding crossing over? (select all that apply)
a. It occurs during prophase II of meiosis
b. It occurs during prophase I of meiosis
c. It occurs during prophase of mitosis
d. It causes genetic variation in gametes
e. It causes genetic variation in diploid daughter cells
f. It occurs between homologous chromosomes
g. It occurs between sister chromatids
h. It occurs between two random chromosomes
b. It occurs during prophase I of meiosis
d. It causes genetic variation in gametes
f. It occurs between homologous chromosomes
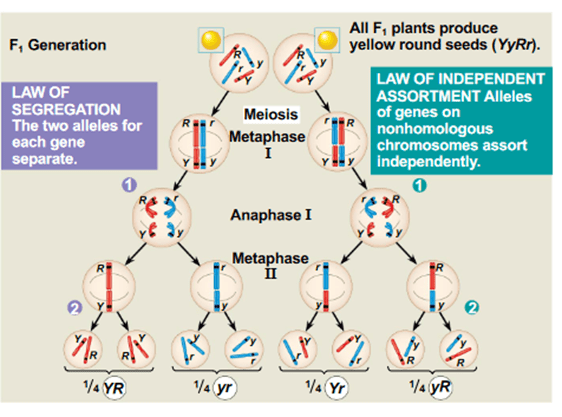
2. Which of the following correctly identifies the relationship between the laws of inheritance and meiosis?
a. The law of segregation refers to the separation of sister chromatids in meiosis II.
b. The law of segregation refers to the random orientation of homologous pairs on the metaphase plate in meiosis I.
c. The law of independent assortment refers to the separation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I.
d. The law of independent assortment refers to the random orientation of homologous pairs during metaphase I.
d. The law of independent assortment refers to the random orientation of homologous pairs during metaphase I.
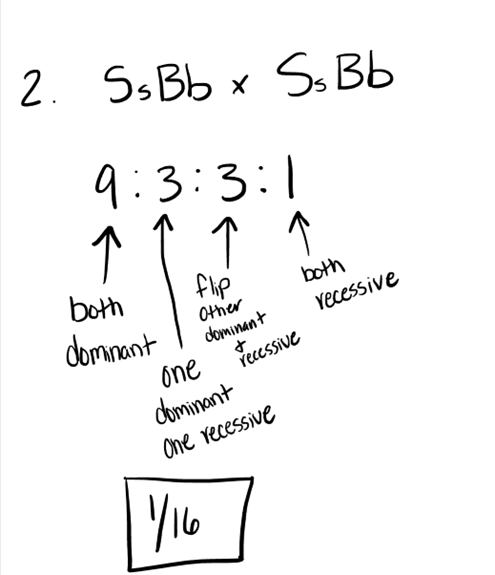
DOUBLE POINTS
In frogs, stripes (S) is dominant to spots and blue (B) color is dominant to yellow color. If a dihybrid stripped blue frog mates with another dihybrid stripped blue frog, what is the probability of producing an offspring that has spots and is yellow?
a. 9/16
b. 6/16
c. 3/16
d. 1/16
e. 4/16
Which of the following is correctly paired? Select all that apply
a. Epinephrine; first messenger
b. G-protein; phosphatase
c. cyclic AMP; secondary messenger
d. GPCR; kinase
e. Adenylyl Cyclase; membrane bound enzyme
a. c. e.
Identify which stage of mitosis or cytokinesis each cell is in:
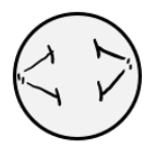
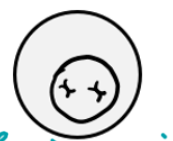
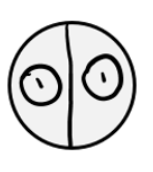
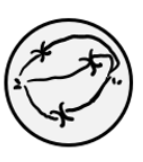
Anaphase
Prophase
Cytokinesis
Prometaphase
Which of the following changes in the process of meiosis would reduce the genetic variation within the offspring daughter cells?
a. The alignment of homologous chromosomes during Anaphase II is no longer random.
b. The process of fertilization becomes much more organized in which only specific sperm must fertilize the egg.
c. The process of crossing over now occurs between sister chromatids, instead of between non-sister chromatids.
d. Two of the answer choices are correct.
d. Two of the answer choices are correct.
3. Dr. Mallory Sadd is studying the characteristic of rizz in humans. She wants to determine whether having rizz is dominant or recessive. Thus, she performs a true-breeding cross between an individual who has rizz and one who does not. The F2 generation was comprised of three individuals without rizz and one individual with rizz. What is the inheritance of an individual having rizz?
a. Dominant
b. Recessive
c. Incomplete dominance
d. Incomplete recessive
b. Recessive
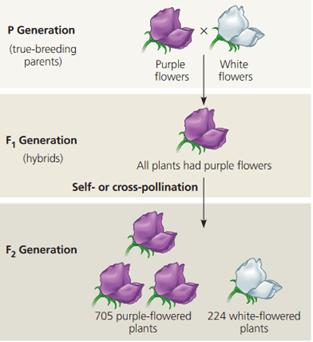
Which of the following statements about cell cycle checkpoints is true?
a. For a cell to pass the G2 checkpoint, there must be a sufficient amount of cyclin to bind to MPF
b. If a cell does not get the go-ahead signal at the G1 checkpoint, it will enter the non-dividing state called G4
c. During the M checkpoint, the cell is checking that all chromosomes are aligned on the metaphase plate and all spindles are properly attached.
d. A cell does not pass the G2 checkpoint, when cyclin binds to and activates a kinase.
c. During the M checkpoint, the cell is checking that all chromosomes are aligned on the metaphase plate and all spindles are properly attached.
All the statements are false EXCEPT:
a. Gap junctions and plasmodesmata are examples of paracrine signaling
b. An example of the first stage of cell signaling is phosphorylation cascades
c. Kinases phosphorylate proteins by transferring a phosphate group from ATP onto the substrate
d. Adenylyl cyclase produces cAMP from 2 AMP molecules
c. Kinases phosphorylate proteins by transferring a phosphate group from ATP onto the substrate
An organism has gametes that contain 6 chromosomes. A somatic cell in this organism is currently in metaphase. How many chromosomes and DNA molecules does this cell have?
a. 6 chromosomes and 12 DNA molecules
b. 12 chromosomes and 24 DNA molecules
c. 3 chromosomes and 6 DNA molecules
d. 24 chromosomes and 24 DNA molecules
b. 12 chromosomes and 24 DNA molecules
It is discovered that crossing over in porcupines is causing a lot of porcupines to die. An enzyme is created that stops crossing over from occurring. However, the enzyme will also be degraded by lysosomes within 10 minutes of being placed in the cell. During which phase should the enzyme be inserted into the cells?
a. Prophase
b. Prophase I
c. Prophase II
d. Metaphase
e. Metaphase I
b. Prophase I
In plants, purple flowers are dominant to white flowers. Dr. Noe performs a test cross to determine the genotype of a plant with purple flowers. Which of the following results would correspond to the plant being heterozygous.
a. All the offspring have white flowers
b. All the offspring have purple flowers
c. Half the offspring have white flowers
d. Three-fourths of the offspring have purple flowers
c. Half the offspring have white flowers
Test Cross: Is crossing a individual with a unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive individual. Based on the offspring produced, the genotype of the unknown individual can be determined.
If the individual were RR, crossing RR with rr would produce only produce heterozygous offspring (Rr) expressing the dominant phenotype (Purple flowers)
If the individual were Rr, crossing Rr with rr would produce half Rr expressing the dominant trait (Purple flowers) and half rr expressing the recessive trait (white flowers)
DOUBLE POINTS
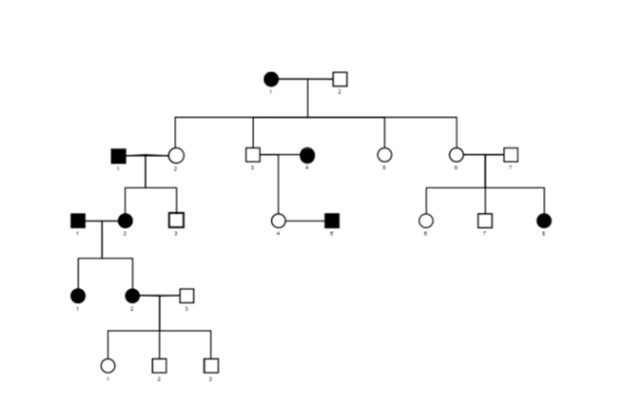
What is the likely mode of inheritance?
If individual II-6 and IV-1 were crossed, what is the probability that their offspring would possess the trait?
The mode of inheritance is recessive because individual III-8 has the trait but neither of their parents express the trait.
If two parents who do not have the trait have an offspring which possesses the trait in Autosomal Recessive inheritance, both of the parents must be heterozygous for the trait- so II-6 is Aa genotype. Since we know the trait is autosomal recessive, we also know that IV-1 must be aa because he possesses the trait.
The cross of these two genotypes (Aa x aa) yields a ½ chance their offspring would possess the trait (aa genotype).
For each statement identify whether it is true or false. For each false statement, make it a true statement.
a. Epinephrine initiates a GPCR signaling pathway that results in the breakdown of glucose into pyruvate, in hepatocytes (liver cells)
b. Hydrophobic hormones can diffuse across the plasma membrane and bind to intracellular receptors.
c. Often, phosphatases turn off signaling pathways by adding a phosphate group to proteins.
d. The same first messenger can bring about different cellular responses based on which receptor it binds to and subsequently signaling pathway initiated.
a. False: results in the breakdown of glycogen into glucose
b. True
c. False: phosphatases removes phosphate groups
d. True
A cell in an organism has 30 homologous pairs of chromosomes. When this cell goes through mitosis, how many chromosomes and DNA molecules would be present during prophase, and how many during anaphase?
In prophase, there would be 60 chromosomes and 120 DNA molecules. In anaphase, there would be 120 chromosomes and 120 DNA molecules.
An individual with 46 chromosomes is looking at their karyotype, which happened to depict their chromosomes during G2 of the cell cycle. What would be seen in this karyotype and how could it be explained to this individual?
a. The karyotype would show 46 chromosomes in sets of 2 for a total of 23 sets. Each chromosome would have 2 sister chromatids that contain the same information and the same alleles. Each set of two chromosomes are homologous pairs that have the same information and possibly different alleles.
b. The karyotype would show 46 chromosomes in sets of 2 for a total of 23 sets. Each chromosome would have 2 sister chromatids that contain the same information and possibly different alleles. Each set of two chromosomes are homologous pairs that have the same information and the same alleles.
c. The karyotype would show 46 chromosomes in sets of 2 for a total of 23 sets. Each chromosome would have 2 homologous pairs that contain the same information and possibly different alleles. Each set of two chromosomes are sister chromatids that have the same information and the same alleles.
d. The karyotype would show 46 chromosomes in sets of 2 for a total of 23 sets. Each chromosome would have 2 homologous pairs that contain the same information and the same alleles. Each set of two chromosomes are sister chromatids that have the same information and possibly different alleles.
a. The karyotype would show 46 chromosomes in sets of 2 for a total of 23 sets. Each chromosome would have 2 sister chromatids that contain the same information and the same alleles. Each set of two chromosomes are homologous pairs that have the same information and possibly different alleles.
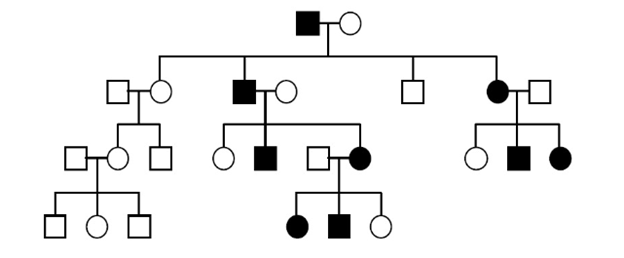
What is the mode of inheritance of the following trait? What is the genotype of individual I-1 (First square top box)?
The mode of inheritance is dominant because every affected individual has an affected parent which is necessary for dominant traits.
Individual I-1 must be heterozygous because the offspring from the mating of I-1 and I-2 is a mixture of individuals with and without the trait.
For each statement, identify whether it is true or false. For every false statement, make it a true statement.
a. Interphase is comprised of G1,S, G2 phase. The mitotic phase is comprised only of mitosis
b. The original source of genetic variation is mutations, which produce different alleles.
c. Sister chromatids appear after the S phase and thus the amount of DNA molecules doubles too
d. The number of chromosomes double during anaphase and anaphase I
a. False: M phase is comprised of mitosis and cytokinesis
b. True
c. True
d. False: Anaphase and anaphase II
Order the following steps of the GPCR Signaling Pathway:
I Active Adenylyl Cyclase converts 4 ATP into 4 cAMP
II The G-protein diffuses along the plasma membrane and interacts with an enzyme
III The activated GPCR switches GDP for GTP on the G-protein
IV Protein Kinase A phosphorylates a protein
V First messenger binds to the G-protein coupled receptor
Also, identify the OFF switch for the GPCR Signaling Pathway
V, III, II, I, IV
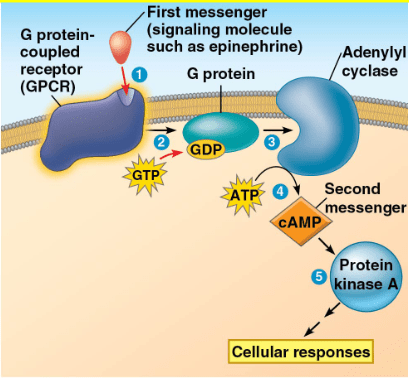
OFF Switch: The G-protein has intrinsic GTPase activity; thus it can hydrolyze the bound GTP into GDP switching itself into the inactive form
If at the end of the phase during which sister chromatids are separated in meiosis, a giraffe has 30 chromosomes, how many DNA molecules did a cell have immediately prior to prophase 1?
60
Anaphase II: Number of chromosomes in the cell doubles because sister chromatids separate = 30
Prior to anphase II, there was 15 chromosomes, each with 2 sister chromatids
We know that meiosis I results in haploid cells = 15 chromosomes
Prior to meiosis I we would have 30 chromosomes
Finally, each of those 30 chromosomes would have 2 sister chromatids because prophase I occurs after S phase
Identify which stage of mitosis or meiosis each cell is in, using the following options:
Anaphase, Anaphase I, Anaphase II, Metaphase, Metaphase I, Prometaphase, Prophase I, Prophase II
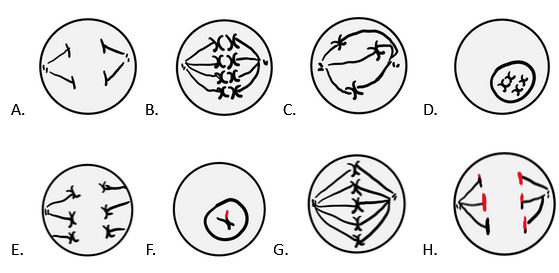
A. Anaphase
B. Metaphase I
C. Prometaphase
D. Prophase I
E. Anaphase I
F. Prophase II
G. Metaphase
H. Anaphase II
In frogs, blue spots are dominant to orange spots and smooth skin is dominant to rough skin. If a orange spotted, rough skin frog mates with a blue spotted, smooth skin frog that is heterozygous at both loci, what is the probability of producing an offspring with BbSs or bbss?
1. Make a key
- Blue (B)
- orange (b)
- Smooth (S)
- rough (s)
2. Determine the genotypes of the parents
bbss x BbSs
3. Determine the probability of the first genotype: BbSs
- Based on bb x Bb: 1/2 Bb
- Based on ss x Ss: 1/2 Ss
- Probability of having Bb AND Ss = 1/2 * 1/2= 1/4
4. Determine the probability of the second genotype: bbss
- Based on bb x Bb= 1/2 bb
- Based on ss x Ss= 1/2 ss
- The probability of having bb AND ss= 1/2*1/2=1/4
5. Determine the probability of BbSs OR bbss:
- ADDITION RULE
- 1/4 + 1/4= 2/4
In cows, red coat color is incompletely dominant to white coat color. Also, short hair is dominant to long hair. If a heterozygous short haired, roan colored cow were to mate with a heterozygous short haired, white colored cow, what is the probability of producing an offspring with a roan colored coat and short hair?
1. Create a key
RR= red
Rr= roan
rr= white
S= short hair
s= long hair
2. Genotype of parents:
RrSs x rrSs
3. Genotype of offspring:
RrS_
4. Probability of Rr:
Rr x rr: 1/2 Rr
5. Probability of S_:
Ss x Ss: 3/4 S_
6. Probability of RrS_:
1/2 * 3/4= 3/8