Name the two dependencies of energy. (think of the formula to calculate KE)
Mass and Velocity
This is a simplified version of what formula?
Conservation of Energy
If force and displacement are in the same direction work is _____. If force and displacement are in opposite directions work is _____.
Positive, Negative
Power is the rate in which ___ is being done.
Work
A new conveyor system at the local packaging plant will utilize a motor-powered mechanical arm to exert an average force of 898 Newtons to push large crates a distance of 9.1 meters in 15 seconds. Determine the power output required of such a motor.
544 Watts
Identify whether the object described below possesses kinetic energy, gravitational potential energy, both forms of energy, or neither form of energy.
A high school sprinter is moving at a high speed as she crosses the finish line.
Kinetic Energy
What is the Expanded form of the Conservation of Energy equation?
For work to be negative or positive. It depends on the direction of the acting ____ and direction of the ____ of the object
Force, Motion
Power is measured in ____.
Watts
Horace Wimp is out with his friends. Misfortune occurs and Horace and his friends find themselves getting a workout. They apply a cumulative force of 900 Newtons to push the car 230 meters to the nearest fuel station. Determine the work done on the car.
20.7*10^4
Identify whether the object described below possesses kinetic energy, gravitational potential energy, both forms of energy, or neither form of energy.
A marble, released from the top of a tall ramp, is a the half-way mark along its path to the floor below.
Both
Assume the 10kg rock is being held before it is dropped.
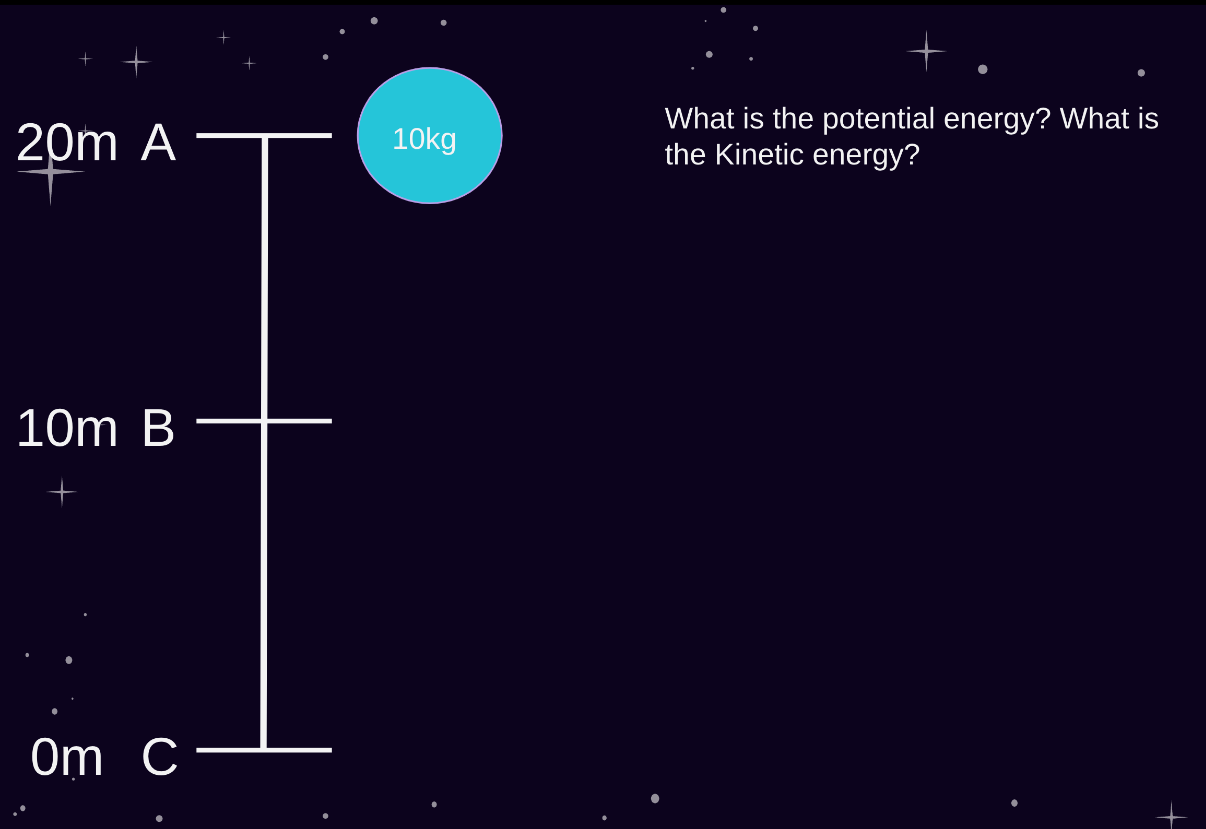
PE= 1960J
KE= 0J
Work is a ____ quantity; it is fully described by stating its ____.
Scalar, Magnitude
Alice and Bob decide to race from base camp to the top of Mt Everest. Alice decides to take steeper, more treacherous route to the top. Bob goes for the slow and steady route. Both reach the top, but Alice makes it to the peak in half the time that it took Bob. Who did more work, Alice or Bob?
They did the same amount of work. Work=mgh
Tohwal Pucher is pushing a load of towels at constant speed a distance of 14 meters using a horizontal force of 160 Newtons.
Determine the work done by Tohwal on the load of towels. Also determine the work done by friction on the load of towels.
Work done by Tohwal Pucher = 2240
Work done by friction = -2240
A toy car rolls across the low-friction track along the path that is shown. Rank the gravitational potential energy (PE) of the disk at the three marked locations. From greatest to least greatest PE.

A,C,B
Assume the rock has fallen 5m What is the PE? What is the KE?
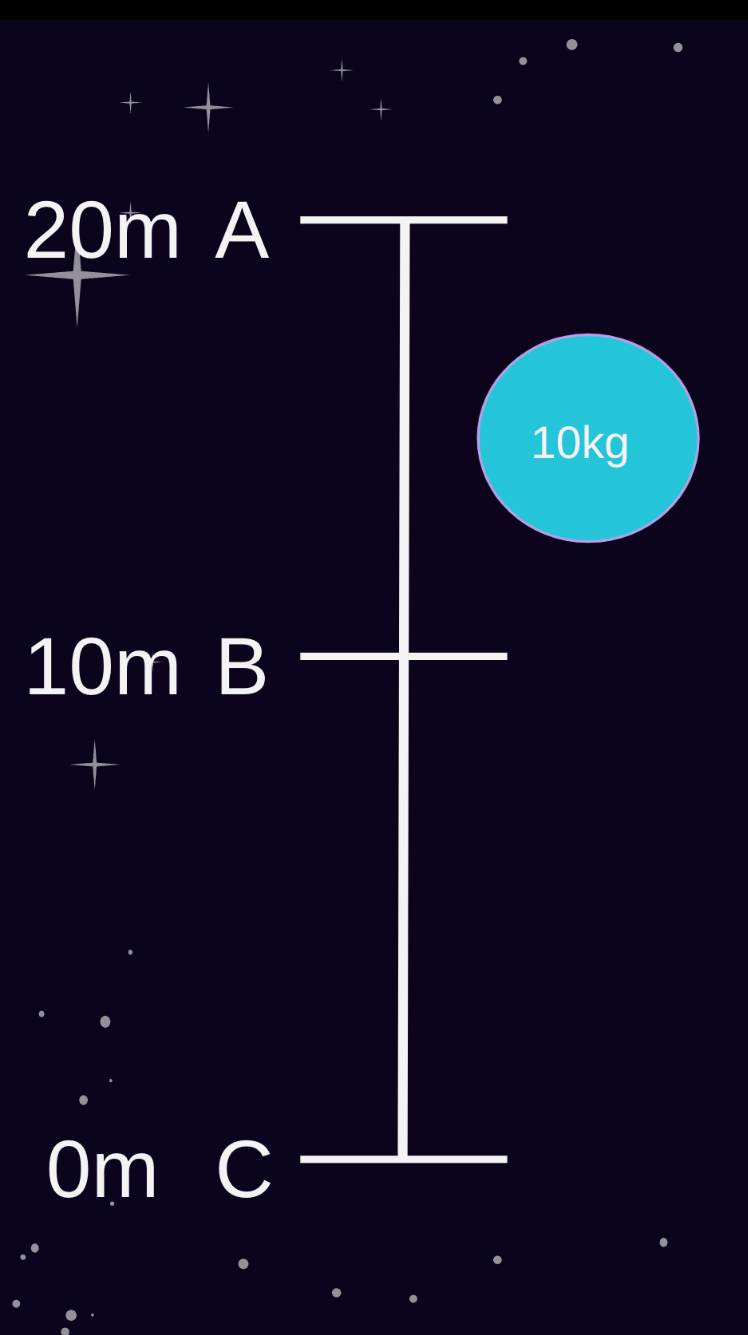
PE=1470J
KE=490J
The standard metric unit of work is the ____.
Joule
Alice and Bob decide to race from base camp to the top of Mt Everest. Alice decides to take steeper, more treacherous route to the top. Bob goes for the slow and steady route. Both reach the top, but Alice makes it to the peak in half the time that it took Bob. Who exerts more power, Alice or Bob?
Alice
There is a lot of work and energy transformation going on at the McDonalds PlayLand around noon time. An 12.3-kg toddler steadily climbs 7.4 meters upward from the floor to the top of a slide.
How much work did the toddler do during the climbing phase?
How much potential energy does the toddler have with respect to the ground?
Work = 891J
PE = 891J
A pendulum bob swings along its characteristic arc as shown. Rank the gravitational potential energy (PE) of the pendulum bob at the three marked locations. From Least to Greatest PE.
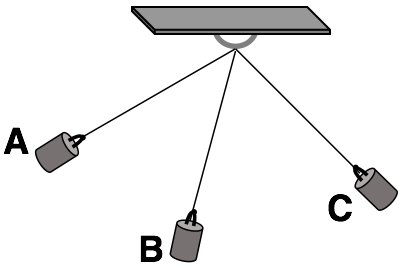
B,C,A
What is the rock's KE? What is the PE?
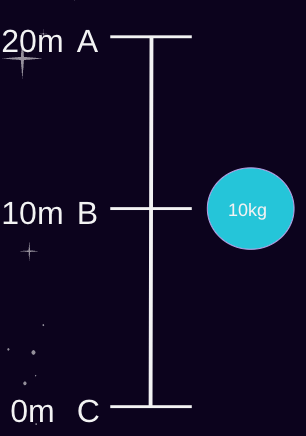
PE=980J
KE=980J
In order to have work done upon an object, there must be a(n) ____ to cause ____.
Force, Displacement
What is the power output of a car whose engine exerts a force of 7000 N when the car is traveling at 30 m/s
210,000 Watts
Ben Pumpiniron, a championship weightlifter, raises 254 kg of weights a distance of 2.3 meters.
How much work is done by Ben lifting the weights?
If Ben completes the lift in 2.55 seconds, how much power is developed?
Work done = 5725J
Power exerted = 2245 Watts
A disk slides along the low-friction surface along the path that is shown. Rank the kinetic energy (KE) of the disk at the three marked locations. From Least to greatest KE.
C,B,A
What is the rock's PE? What is the KE? Assume the rock is just about to hit the ground.

PE=0J
KE=1960J
A softball player is sliding into third base. Once she hits the dirt, the force of friction acts upon her to slow her down as she slides a distance of 1.5 meters across the distance. In this example, friction is doing ____ work upon the player.
Negative
In 1984, Don Cain threw a flying disk that stayed aloft for 15.7 s. Suppose Cain ran up a staircase during this time, reaching a height of 18.4 m. If his mass was 72.0 kg, how much power was needed for Cain’s ascent.
826 Watts
(776 Watts shame)
The path of a sledder is shown; upon descending the hill, the sledder ultimately glides up a ramp to a final resting position (at D). Frictional forces can be assumed to be negligible.
Given: mass = 30.4 kg; Height at A = 7.4 meters, Speed at A = 6.8 m/s,
Height at B = 4.08 meters
Perform an energy analysis to determine KE at A.
Perform an energy analysis to determine PE at A.
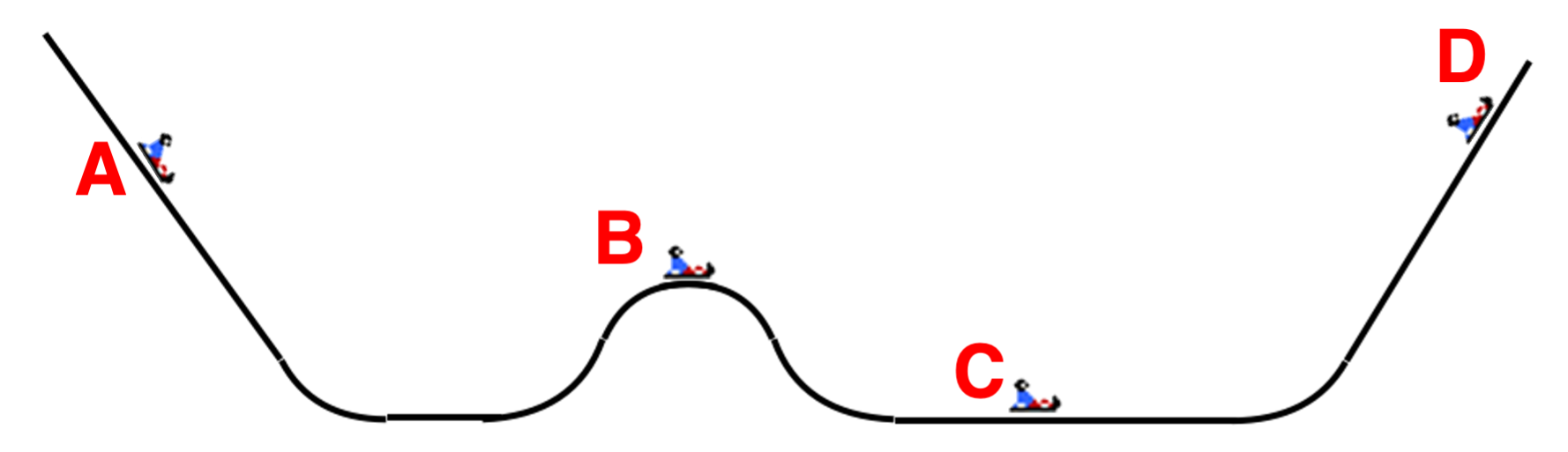
KE=702J
PE=2204J
A disk slides along the low-friction surface along the path that is shown.
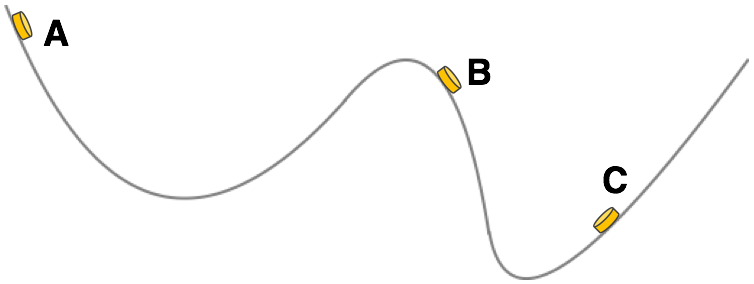
Rank the kinetic energy (KE) of the disk at the three marked locations. From greatest amount of KE to least amount of KE.
C,B,A
A man is walking through an airport with a suitcase. The man exerts a constant upward force upon the suitcase as he walks a distance of 20 meters. In this example, the man is doing ____ work upon the suitcase.
Zero
Power can be calculated as P= W/t
What other equation can be used to calculate power?
P=Fv
The path of a sledder is shown; upon descending the hill, the sledder ultimately glides up a ramp to a final resting position (at D). Frictional forces can be assumed to be negligible.
Given: mass = 30.4 kg; Height at A = 7.4 meters, Speed at A = 6.8 m/s,
Height at B = 4.08 meters
Perform an energy analysis to determine KE at C.

KE= 2906J