What are the ranges for pH, HCO3, CO2?
pH 7.35 to 7.45, HCO3 (Base) 22-26, CO2 (Acid) 35-45
When are vagal maneuvers (Valsalva) used?
What are different types of vagal maneuvers can a patient do?
-used when patient is awake and in a high HR or abnormal new onset HR (SVT, Afib, Vtach)
-bearing down, coughing, squatting, holding of breath, blowing through a straw, submersion of face in ice water, stimulation of gag reflex.
A patient comes into the clinic with uticaria after eating tree nuts in a salad. The nurse knows that based off this symptom the patient could be experiencing what type of shock?
Urticaria is vascular swelling in the skin accompanied by itching. The patient had this after ingesting tree nuts. The nurse would anticipate the patient is having a anaphylactic reaction and would want to notify the MD right away.
A patient has experienced full-thickness burns to the face and neck. As the nurse it is priority to:
A. Prevent hypothermia
B. Assess the blood pressure
C. Assess the airway
D. Prevent infection
The answer is C Assess the airway. Due to the location of the burns (face and neck), the patient is at major risk for respiratory issues due to damage to the upper airways and the risk of an inhalation injury.
Legally defines and describes the scope of
nursing practice, which the law seeks to regulate.
Nurse Practice Act
Oral care for a patient who is intubated is important in the prevention of….
Ventilator Assisted Pneumonia - VAP
 You go into a patient's room and the patient is unresponsive and you see the above rhythm on the monitor. What would the nurse do next?
You go into a patient's room and the patient is unresponsive and you see the above rhythm on the monitor. What would the nurse do next?
BLS
-Ensure the patient is in a safe position and place
-Check for response (yelling, sternal rub, shaking)
-If unresponsive still check for breathing (chest rise) and pulse for no greater than 10 seconds
-Call for help, push code button
-Start high quality CPR
-When AED arrives have help place AED pads on patient and when AED prompts to stop CPR switch roles
Patient comes into the ED with a back injury from a fall off of a ladder. The patient is thought to be in neurogenic shock. What symptoms would the nurse anticipate to see with this type of shock?
-severe hypotension
-bradycardia
-warm, dry, flushed skin
-hypothermia
-absence of sweating below the level of injury
A 58 year old female patient has superficial partial-thickness burns to the anterior head and neck, front and back of the left arm, front of the right arm, posterior trunk, front and back of the right leg, and back of the left leg. Using the Rule of Nines, calculate the total body surface area percentage that is burned?
The answer is 63%. Anterior head and neck (4.5%), front and back of the left arm (9%), front of the right arm (4.5%), posterior trunk (18%), front and back of the right leg (18%), back of the left leg (9%) which equals 63%
Prohibited acts of the LPN role.
The LPN cannot:
- Perform nursing triage
Perform the responsibilities of or in the role of
circulating nurse in the intra-operative phase of
surgery
Perform the comprehensive nursing assessment
Serve as the case manager for client care
Supervise the nursing practice of RN’s
Analyze client data in order to determine client
outcome identification and formulation of a nursing
diagnosis.
The patients chest tube is out upon assessment. How should the nurse dress the site?
Gauze with securing tape on 3 sides. Do not occlude opening taping the 4 sides down or placing gauze into the hole.
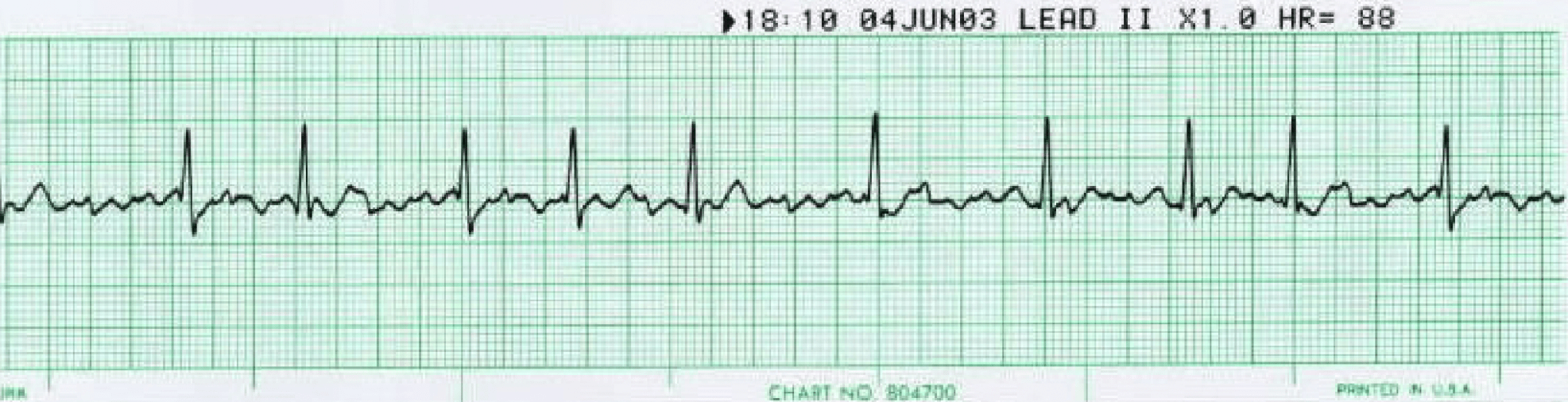
The EKG strip above indications what rhythm?
What type of treatment would the nurse anticipate this patient to be on?
-Atrial Fibrillation
-Anticoagulant therapy (heparin, Eliquis, Warfarin)
-Antidysrhythmics (amioderone)
-Rate control (beta blocker (metoprolol), Ace Inhibitor (lisinopril)
-Cardiversion if afib is new onset
Septic shock has two phases. What are those phases?
Warm phase/ hyperdynamic
Cold phase/ hypodynamic
A 29 year old male patient has superficial partial thickness burns on the anterior right arm, posterior left leg, and anterior head and neck. The patient weighs 78 kg. Use the Parkland Burn Formula to calculate the total amount of Lactated Ringers that will be given over the next 24 hours?
The answer is 5,616 mL.
Formula: Total Amount of LR = 4 mL x BSA % x pt's weight in kg. Pt's weight 78 kg. BSA percentage: 18%...Anterior right arm (4.5%), posterior left leg (9%), and anterior head and neck (4.5%) which equals 18%.....4 x 18 x 78 = 5,616 mL
Five rights of delegation.
• Right task
• Right circumstances
• Right person
• Right direction/communication
• Right supervision/evaluation
1. Bag valve mask
2. Trach replacements of same size or size smaller
3. Suction equipment
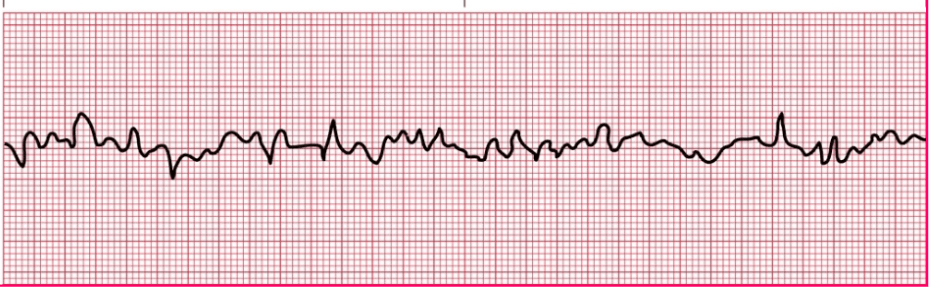
True or False: In the rhythm above the heart is adequately pumping blood.
False- The rhythm strip shows Vfib. The heart is not pumping blood to the rest of the body. Start BLS steps.
What is happening during uncompensated shock?
Perfusion of the skin, skeletal muscles, kidneys, and GI organs is greatly decreased
• Cells in the heart and brain become hypoxic while other cells and tissues become ischemic and anoxic
•Acidotic state
•Hyperkalemia
Slide 23 in Shock Lecture
Knowing that the adult client weighs
174.74 lbs and has a TBSA that is 36% use the Parkland Formula calculate the fluid to be infused over the first 24 hours after the burn injury _____ ml.
11,376 mL in 24 hours
4mL x 36% x 79 kg= 11,376
Kübler-Ross—Five reactions (Stages of Grief)
Denial, Anger, Bargaining, Depression, Acceptance
pH=7.44 | PaCO2=30 | HCO3=21
Interpret the above ABG using the Tic Tac Toe Method.
- Answer is Respiratory Alkalosis
- Remember the normal values.
- Make your tic-tac-toe grid.
- pH of 7.44 is NORMAL but slightly leaning towards ALKALOSIS, so we place pH under the NORMAL column with an arrow pointing towards the ALKALOSIS column.
- PaCO2 of 30 is ABNORMAL and ALKALOSIS, so we place PaCO2 under the ALKALOSIS column.
- HCO3 of 21 is ABNORMAL and ACIDOSIS, so we place HCO3 under the ACIDOSIS column.
- pH of 7.44 is NORMAL but leaning towards ALKALOSIS, therefore solving for goal #1, we have ALKALOSIS.
- pH is NORMAL but is leaning towards ALKALOSIS, therefore under the same column as PaCO2. Solving for goal #2, we have RESPIRATORY.
What is a heart block?
What would the nurse anticipate as treatment for a heart block?
The SA node is not firing appropriately allowing for the relationship between the P and QRS to be too close together or in the middle of a QRS complex or a P wave is not present at all. A complete heart block shown below indicates the patient needs a pacemaker emergently. Patients are usually paced with pads on the AED until they can go to the cardiac cath lab for a pacemaker insertion.
How does the body compensate during shock?
SNS – releases epinephrine and norepinephrine from adrenal medulla causing:
• Vasoconstriction in blood vessels that supply the skin,
periphery, and abdomen – we see a decreased perfusion to these areas
• Vasodilation of the cardiac and skeletal muscles
therefore increasing the HR and increasing the force of contraction
• Vasodilation of the respiratory system – increasing the respiratory rate
Renin-Angiotensin – blood flow to the kidneys is decreased causing:
• Renin released → angiotensin II → vasoconstriction →aldosterone → now kidneys reabsorb water and sodium while they lose potassium
• Hypothalamus – releases adrenocorticotropic hormone further causing the adrenal glands to secrete more aldosterone and promoting reabsorption of water and sodium by the kidneys → preserving blood volume and blood pressure
Posterior pituitary gland – releases antidiuretic hormone
(ADH) → increases renal reabsorption of water → increasing intravascular volume
Slide 19-21 in Shock Lecture
An adult patient came in to the ED suffering massive burns. Using the rule of nines, what is the estimate extent of burn injury to the following patient. The following areas are burned: Anterior trunk, anterior left arm, and posterior left leg.
Anterior trunk-18%
Anterior left arm-4.5 %
Posterior left leg-9 %
Total- 31.5%
Legal document of written statement of person’s wishes concerning medical care and life-sustaining treatments
Living Will
Measurement of arterial blood gas shows pH 7.3, PaCO2 68 mm Hg, HCO3 28 mmol how would you interpret this?
Respiratory Acidosis
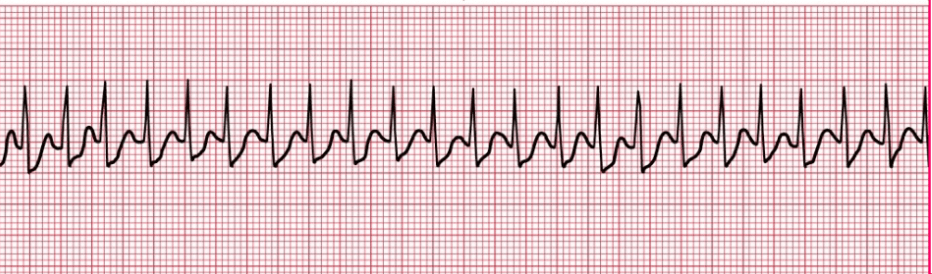
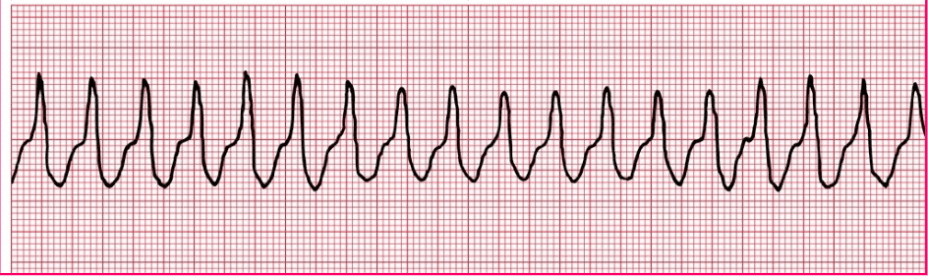
Name this rhythm!
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Name 3 Vasoactive medications that can be used for patients in shock.
1. norepinephrine (Levophed)- vasoconstrictor
2. epinephrine (Adrenalin)- vasoconstrictor
3. milrinone (Primacor) - vasodilator
4. amrinone (Inocor)-vasodilator
5. vasopressin (Pitressin)- vasoconstricts
6. phenylephrine (Neo-synephrine)-vasoconstriction
All medications above help move blood flow to the body's core to protect heart, brain and kidneys. They also help increase the pumping mechanisms of the heart therefore increase preload and afterload.
A 45 year old female patient has superficial partial thickness burns on the posterior head and neck, front of the left arm, front and back of the right arm, posterior trunk, front and back of the left leg, and back of right leg. The patient weighs 91 kg. Use the Parkland Burn Formula to calculate the total amount of Lactated Ringers that will be given over the next 24 hours?
The answer is 22,932 mL.
Formula: Total Amount of LR = 4 mL x BSA % x pt's weight in kg. Pt's weight 91 kg. BSA percentage: 63%... posterior head and neck (4.5%), front of the left arm (4.5%), front and back of the right arm (9%), posterior trunk (18%), front and back of the left leg (18%), back of right leg (9%) equals: 63%......4 x 63 x 91 = 22,932 mL
Person designated to make medical decisions
Durable power of attorney for
healthcare