What is the Behaviorist theory of language?
What is the Nativist theory of language?
What is the Interactionist theory of language?
Behaviorist Theories
Learn language through imitation, reinforcement and other principles of conditioning
Nativist Theories
Inborn, or “native,” propensity to develop language
Learn rules of language
Language acquisition device (LAD) – innate mechanism that facilitates learning a language
Interactionist Theories
Biology and experience both make important contributions
The human brain is hardwired to readily recognize the sound patterns that make up human languages
What is homeostasis?
Homeostasis: A state of physiological equilibrium or stability.
How is emotion defined?
is a subjective conscious experience, accompanied by bodily arousal and by characteristic overt expression.
What is Linguistic Relativity and why is it important?
The hypothesis that one’s language determines the nature of one’s thoughts.
What is a drive?
Drive: A hypothetical, internal state of tension that motivates an organism to engage in activities that should reduce this tension.
Internal states push someone to act.
These unpleasant states of tension are viewed as disruptions of the preferred equilibrium.
From an evolutionary perspective why did emotions develop?
Emotions developed because of their adaptive value
Largely innate reactions to certain stimuli
Emotion evolved before thought
Originate in subcortical structures that evolved before the higher brain areas associated with complex thought
What is Aphasia?
The loss of the ability to speak or understand language.
The closely related processes of reading and writing may also be affected by aphasia, but this is not always the case.
Different theories of motivation discussed in class?
Drive Theories - Humans seek to maintain homeostasis (physiological stability)
Incentive Theories- Incentive: External goal that has the capacity to motivate behavior. External stimuli pull someone to act.
There can also be intrinsic motivators as well.
Evolutionary Theories: Motives can best be understood in terms of the adaptive problems they have solved over the course of human history.
Different Theories of emotion:
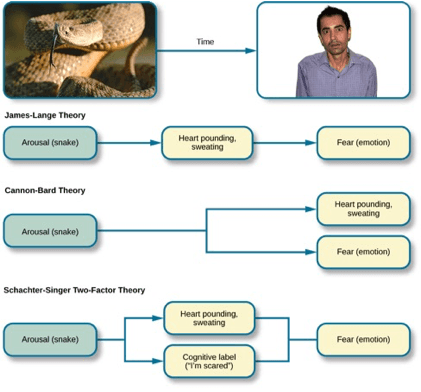
What is Broca's aphasia?
What is Wernicke's Aphasia?
Non-fluent Aphasia: This condition is characterized by difficulty producing speech. The speech that the patient manages to produce is slow and very effortful, but it generally makes sense.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JWC-cVQmEmY&ab_channel=tactustherapy
Fluent Aphasia: Speech is rapid and fluent, but virtually meaningless. If you don’t pay attention to the meaning, the speech of patients with Wernicke’s aphasia sounds rather normal, if slightly fast. Grammar is generally correct.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3oef68YabD0&ab_channel=tactustherapy
Key areas of hunger:
Hypothalamus
Lateral Hypothalamus involved in motivation to eat.
Ventromedial Hypothalamus involved in satiety
Arcuate nucleus and Paraventricular nuclei are especially important - hormones related to hunger/eating/digestion appear to converge here.
Physiological/anatomical structures related to emotion:
ANS
The Limbic System: hypothalamus, amygdala
Name and define the different types of problem-solving:
Inducing Structure: Discover the relationship among the parts.
Arrangement: Arrange parts to satisfy some criterion
Transformation: Complete sequence to reach a specific goal.
Hormones important for hunger/digestion:
Ghrellin – secreted by stomach and causes contractions and promotes hunger
CCK – released by upper in intestine to signal satiety
Leptin – provides hypothalamus with information about body’s fat stores
Insulin – secreted by pancreas and is sensitive to fat stores.
How are emotions expressed non-verbally? When can these expressions become problematic (give examples)
body language, facial expressions, with actions/behaviors
When those behaviors harm oneself or others (anger expressed as aggression, dysregulation expressed through self-harm)
What is the normal distribution? Average IQ and standard deviation?
Normal distribution: Represents the pattern in which many characteristics are dispersed in the population.
Average IQ: 100
SD: 15 (+ or -)
Enviornment Factors that motivate/influence hunger and eating:
•Palatability
•Quantity available
•Variety
•Presence of others
•Stress
•Exposure to food cues
Facial-feedback hypothesis assert that facial muscles send signals to the brain and that these signals help the brain recognize the emotion that one is experiencing
Facial expressions can reveal a variety of basic emotions, such as happiness, sadness, anger, fear, surprise, and disgust.