Label the parts of the spine

1. Cervical
2. Thoracic
3. Lumbar
4. Sacrum
5. Coccyx
What is the outer most covering of the CNS?
Bone (skull and verterbrae)
What is this describing?
- Rest and Digest
- Dominant autonomic controller
- Brain Stem and Cervical Spine
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Extroceptor: outside stimulus
Visceralceptor: inside stimulus
Proprieceptor: bodily orientation w/o seeing (consciousness)
How old am I?
Label the three indicators of Mengial Space.
A (Epidural Space)
B (Subdural Space)
C (Subrachnoid Space)
Within the white matter, there are ascending and descending tracts. What type of fibers do ascending tracts have? Descending?
Ascending: sensory fibers
Descending: motor fibers
What are the 4 Nerve Plexuses?
Cervical, Brachial, Lumbar, Sacral
Specifically, what are the 5 Gustation receptors?
**Think Taste Buds**
Sweet, Sour, Salty, Bitter, Umami
What is the ETSU womens basketball record right now?
4-2
Which letters indicate the meninges and what are they?
J (meninges)
D (Pia Mater)
E (Arachnoid Mater)
F (Dura Mater)
What is the function of the brainstem?
1. Conduction (contains tracts for motor and sensory neurons)
2. Contains reflex centers
How is the Autonomic PNS different from the Somatic PNS?
Autonomic is...
- Involuntary (homeostatic responses)
- Afferent and Efferent Reflex Arc
- Sympathetic and Parasympathetic divisions
What organs within the ear have to do with balance? What are the 2 types of equilibrium?
Organs: Vestibule and Semicircle Canals
Equilibrium: Static and Dynamic
Where am I from?
Asheville, NC
Label the parts of the somatic reflex arc.

1. stimulus
2. receptor
3. sensory neuron
4. integration center
5. interneuron
6. Spinal Cord
7. motor neuron
8. effector
9. response
What are the 5 functions of the Cerebellum?
1. Coordinating Movement
2. Muscle memory (skilled movement)
3. Balance
4. Posture
5. Processing sensory information
What is the difference in the somatic and visceral reflex arc?
Everything is the same except in the output where visceral has preganglionic and postganglionic motor neurons.
Describe Rods and Cones.
Rods: light sensitive, can work in dim light, monochrome
Cones: color sensitive, work in bright light
Which part of the spine does this belong?
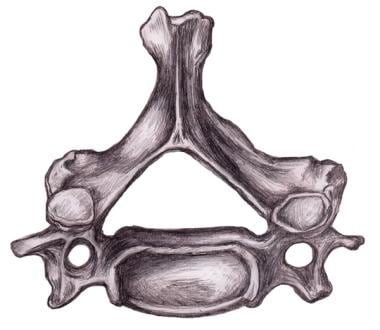
Cervical
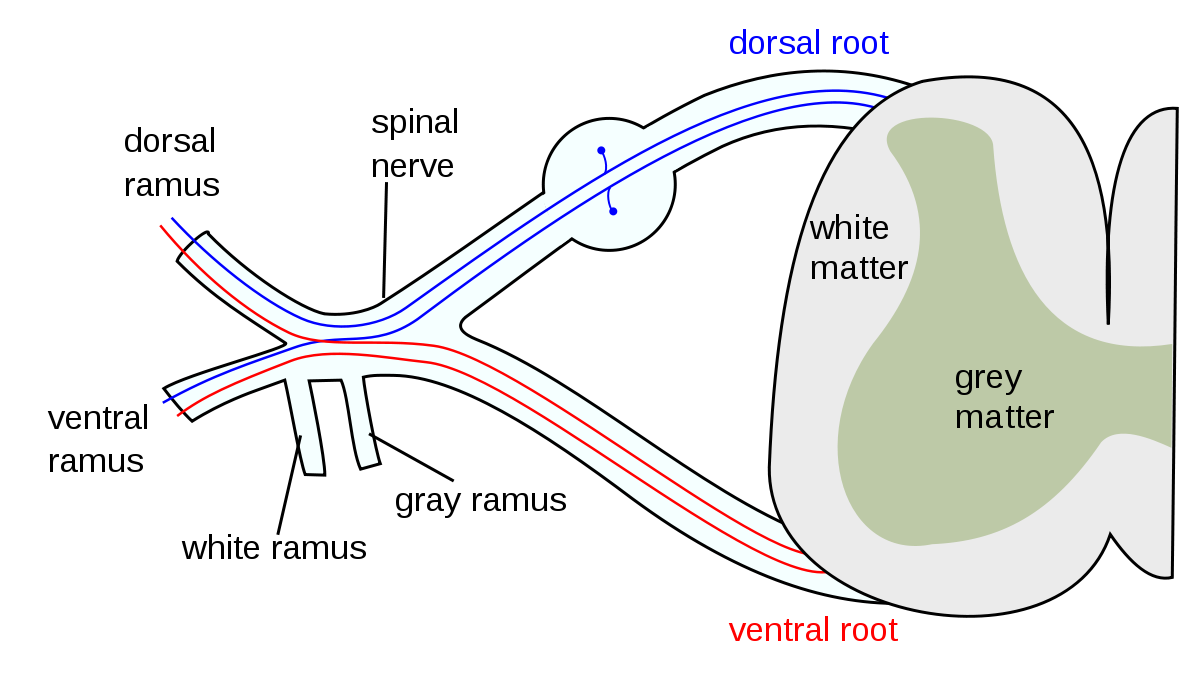
Draw a Spinal Nerve
What are the main functions of the Thalamus, Hypothalamus, and Pineal Gland?
Thalamus: relay point of sensory information, associating senses with memories
Hypothalamus: Links Mind and Body
Pineal Gland: Internal Clock
Name the 12 cranial nerves and if they are sensory/motor/both.
Olfactory: S
Optic: S
Occulomotor: M
Trochlear: M
Trigeminal: B
Abducens: M
Facial: B
Vestibulocholear: S
Glossopharngeal: B
Vagus: B
Accessory: M
Hypoglossal: M
What parts of the brain help with olfaction?
Temporal Lobe, Hypothalamus, Hippocampus
Should you decorate for Christmas before Thanksgiving?
NO