The name, modality, function, and foramen of cranial nerve I
Olfactory Nerve
S - Sensory
- Sense of Smell
Olfactory Foramen
The 3rd and 4th ventricles of the brain are connected by this structure
Cerebral Aqueduct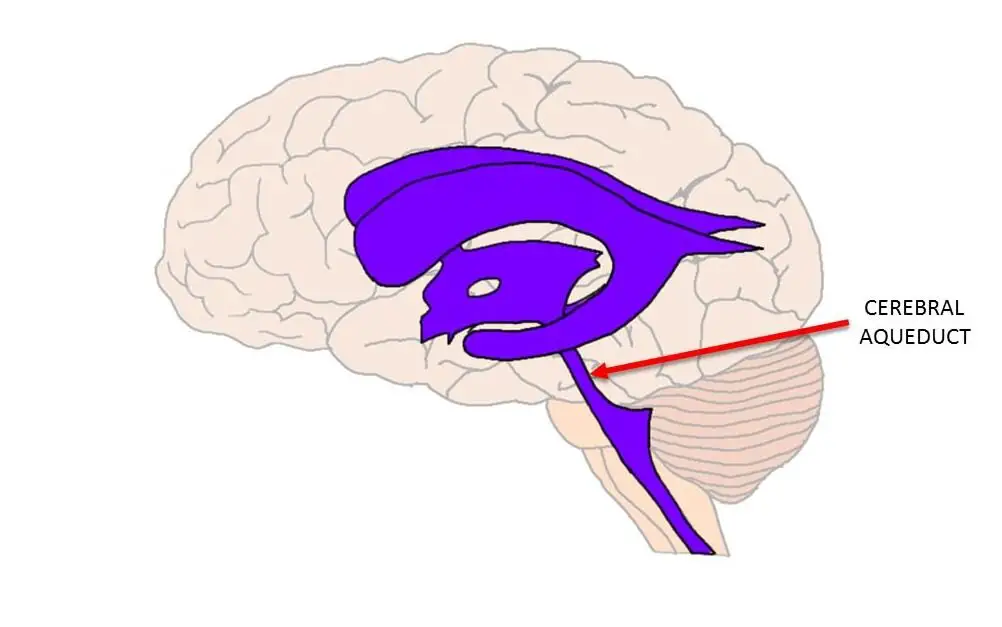
This cell helps maintain the blood-brain barrier (BBB)
Astrocytes
The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) is divided into these 2 nervous systems
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous Systems
The ventral side of the spinal cord is responsible for what?
Sending motor information away from the CNS
Efferent, descending
These types of receptors monitor body position in space
Proprioceptors
If someone had problems with moving their tongue, you might suspect damage to this cranial nerve
XII - Hypoglossal Nerve
This part of the Hypothalamus, located above the optic chiasm, is associated with circadian rhythms
SCN -Suprachiasmatic nucleus
Produces CSF
Ependymal Cells
This neuron in a sensory pathway carries information from the receptors to the CNS
First-Order Neuron
All preganglionic neurons release this neurotransmitter at their synapses with ganglionic neurons
ACh - Acetylcholine
3 Locations of CSF in the CNS
Central Canal of the spinal cord
Ventricles of the brain
Subarachnoid space (brain and spinal cord)
(In Roman Numerals & Name) List the 3 Cranial Nerves associated with taste
CN VII - Facial Nerve (Front 2/3 of the tongue)
CN IX - Glossopharyngeal Nerve (Back 1/3 of the tongue)
CN X - Vagus Nerve
These are the 2 parts of the corpora quadrigemina and they're associated with these different functions
Superior Colliculus: Visual Reflex
- Orient head and eyes to stimulus
Inferior Colliculus: Auditory Reflex
- Processing auditory info quickly (threat or no threat)
Name the 2 types of cells of the PNS
Satellite Cells
Schwann Cells
This center in the Temporal Lobe is associated with language comprehension
Wernicke's Area
These structures are found in the spinal cord around T1-L2 and contain the visceral motor neurons/preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system
Lateral Gray Horns
A Chronic Vegetative State is considered a(n) (conscious/unconsious) state.
A Chronic Vegetative State is considered a conscious state.
(In Roman Numerals) The parasympathetic nervous system is associated with these 4 cranial nerves
CN III - Oculomotor Nerve
CN VII - Facial Nerve
CN IX - Glossopharyngeal Nerve
CN X - Vagus Nerve
One of these is the "emotional cortex" of the brain and one of these is the white commissure that connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain.
Cingulate Gyrus: Emotional Cortex
Corpus Callosum: White Commissure
This cell is responsible for removing cell wastes in the CNS
Microglia
A third order neuron carries information from here to here
From the thalamus to the cerebral cortex
Sympathetic preganglionic neurons are (short/long) and their ganglionic neurons are (short/long)
Sympathetic
preganglionic neurons are short
ganglionic neurons are long
A Coma is considered a(n) (conscious/unconsious) state.
A Coma is considered an unconsious state.
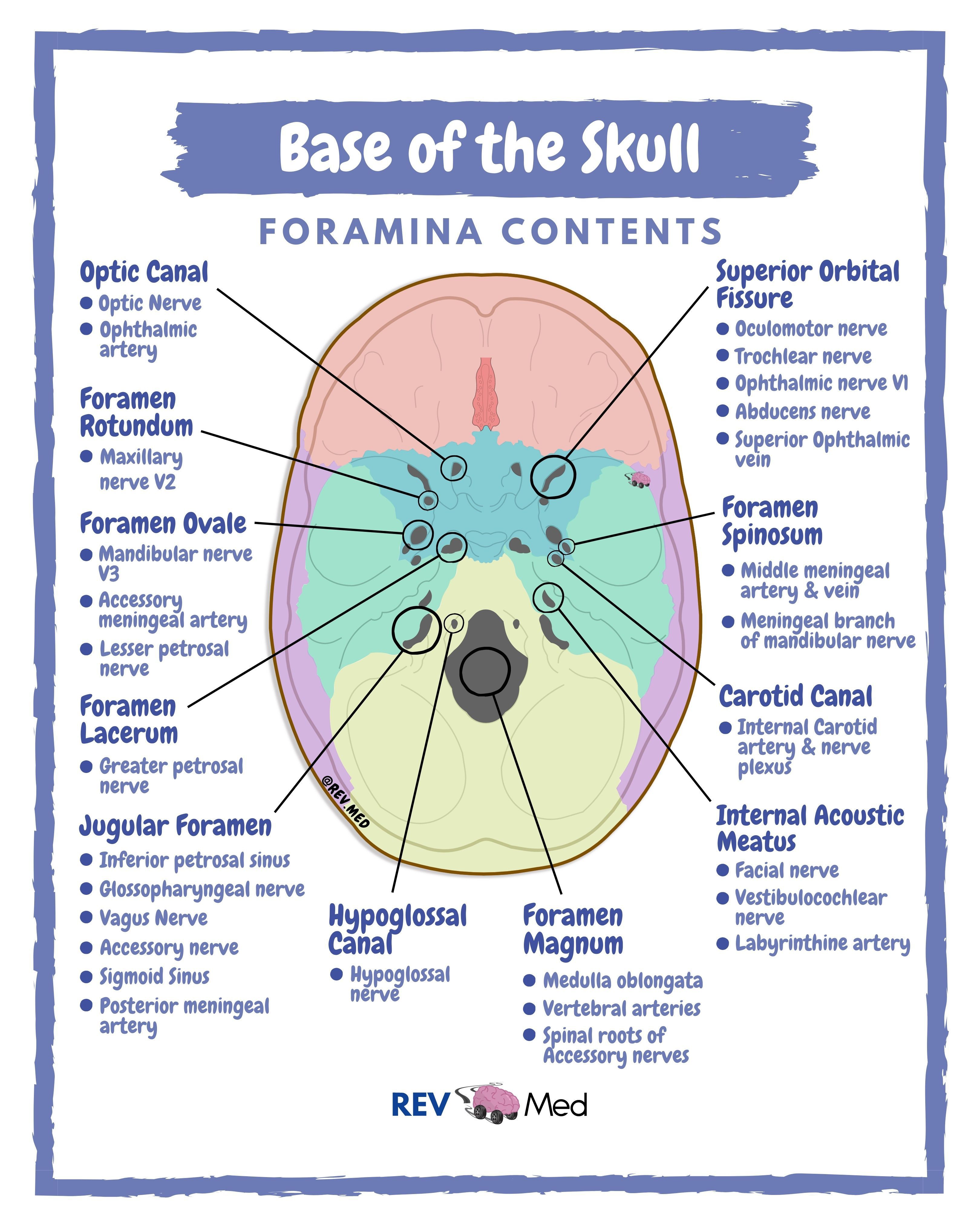
Give the name, modality, function, and foramen of cranial nerve V
Trigeminal Nerve
B - Both/Mixed
- Facial sensations and jaw movement
V1: Superior Orbital Fissure
V2: Foramen Rotundum
V3: Foramen Ovale
Name the 4 outer lobes of the brain, including the cortex/cortices you could find in each one.
Frontal Lobe - Primary Motor Cortex (in Pre-Central Gyrus), skeletal muscle control
Parietal Lobe - Primary Sensory Cortex (in Post-Central Gyrus), sensory information on touch, temperature, pressure, pain, and proprioception
Occiptal Lobe - Visual Cortex
Temporal Lobe - Primary Auditory and Primary Olfactory cortices, hearing, smell, language

This cell myelinates axons and is found only in the CNS
Oligodendrocytes
Damage to this area in the Frontal Lobe would affect someone's ability to speak even if they could still fully understand
Broca's Area
Parasympathetic preganglionic neurons are (short/long) and their ganglionic neurons are (short/long)
Parasympathetic
preganglionic neurons are long
ganglionic neurons are short
This type of receptor constantly sends action potentials so signals are differentiated by the frequency of the signals
Tonic Receptors
List each cranial nerve modality from I-XII
(S/M/B)
I - S
II - S
III - M
IV - M
V - B
VI - M
VII - B
VIII - S
IX - B
X - B
XI - M
XII - M
The diencephalon includes which majors structures, give general functions of each
Thalamus - relay center
Hypothalamus - Satiety (Hunger, Thirst, Sleep, and Sexual Satiety), homeostasis
Epithalamus - Circadian Rhythms (Pineal gland)
All peripheral nerves are surrounded by this cell that can help with regeneration in the case of peripheral nerve damage
Schwann cells
The 3 ascending (sensory) nerve tracts/pathways that Dr. Yard talked about
Posterior Column Pathway
- Fine-Touch, Vibration, Pressure, and Proprioception
Spinothalamic Pathway
- Crude-Touch, Deep Pressure, Pain, and Temperature
Spinocerebellar Pathway
- No 3rd Order Neuron, doesn’t reach level of consciousness at post-central gyrus
- Proprioception, Muscle Memory: Golgi Tendon Organs, Muscle Spindles, Joint Capsules
Give 3 effects of sympathetic activation and 3 effects of parasympathetic activation
Sympathetic Activation
- Pupil dilation
- Bronchodilation
- Vasoconstriction/BP increase
- HR and RR increase
- Arrector pili stimulation
- Digestive functions decrease
- Urinary bladder smooth muscle relaxes
- Release of glucose and lipids from stores
Parasympathetic
- Pupil constriction
- Bronchoconstriction
- Vasodilation/BP decrease
- HR and RR decrease
- Digestive functions return to normal
- Urinary bladder smooth muscle contraction
- Increased smooth muscle activity
- Nutrient absorption by peripheral cells
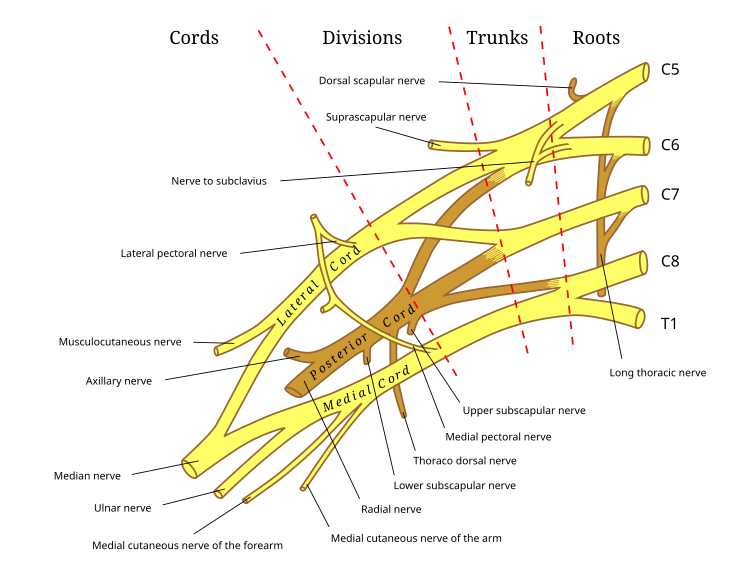
Damage to this nerve of the brachial plexus, also termed Saturday Night Palsy, could result in wrist drop
Radial Nerve