What 2 main hormones does the adrenal medulla secrete?
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
Parasympathetic preganglionic neurons exit the brain stem via which cranial nerves?
III, VII, IX, and X
( 3, 7, 9, and 10 )
Oculomotor, facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus
What chemical(s) is involved in the perception of...
a. Salty
b. Umami
c. Bitter
d. Sweet
e. Sour
a. Salty - mineral salts, mainly sodium and chloride
b. Umami - glutamate or other amino acids
c. Bitter - alkaloids
d. Sweet - simple sugars like glucose, fructose
e. Sour - acids which release hydrogen ions
What kind of receptors are specific to the senses of smell and taste?
For an extra 100 points each: Name the receptor type for the other 3 special senses.
Chemoreceptors (photoreceptors for vision and mechanoreceptors for balance and hearing)
What is this area? (inner area)
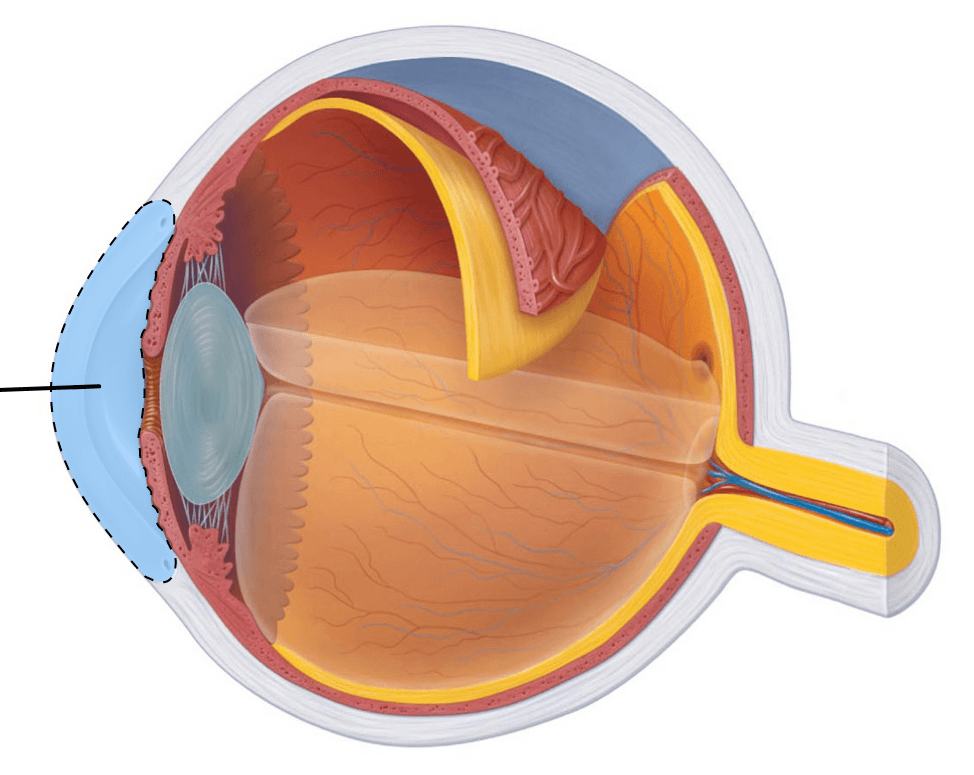
For an extra 100 points: what liquid nourishes this structure?
Anterior chamber, filled with Aqueous humor
The brain stem is responsible for the autonomic reflexes of _______. ( List 3 )
Respiration, Heart Rate, Blood pressure
Regulates pupil size, salivation
Name the neurotransmitter(s) released at:
1. preganglionic sympathetic neurons
2. postganglionic sympathetic neurons
3. preganglionic parasympathetic neurons
4. postganglionic parasympathetic neurons
5. somatic motor neurons
1. acetylcholine
2. Acetylcholine, epinephrine, norepinephrine
3. acetylcholine
4. acetylcholine
5. acetylcholine
What is the name of this area? What fluid does it contain?
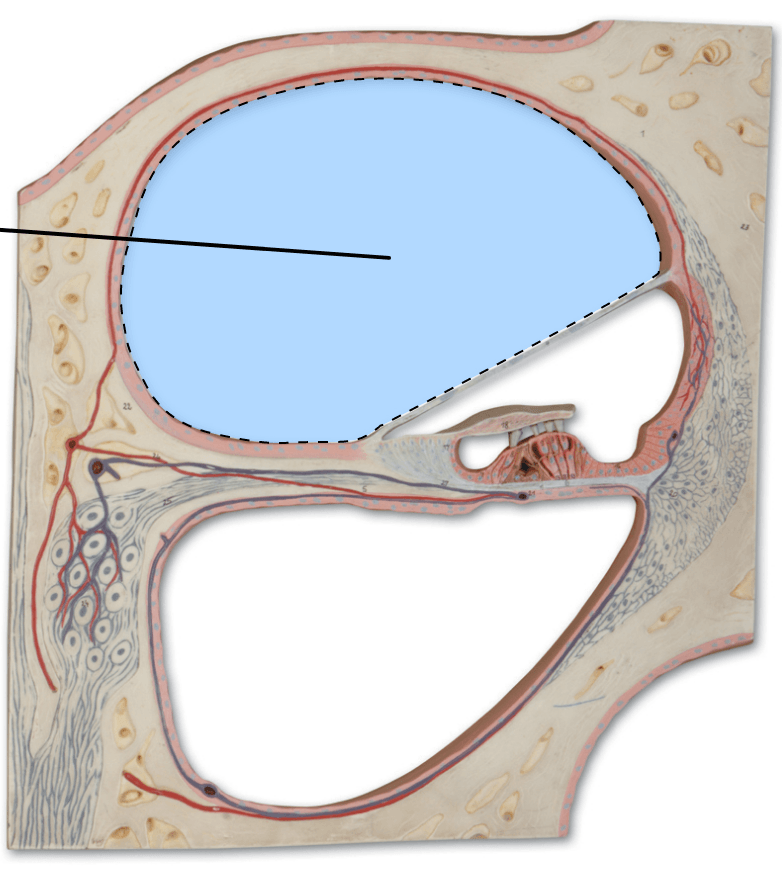
Scala Vestibuli - contains perilymph, which is high in SODIUM and low in potassium
List the three types of visual acuity, the shape of the eyeball, and the lens (if required) for correction.
Emmetropia/normal vision, normal eyeball; Hyperopia/farsightedness, shortened eyeball, convex lens;
Myopia/nearsightedness, elongated eyeball, concave lens
What is the name of the structure highlighted?
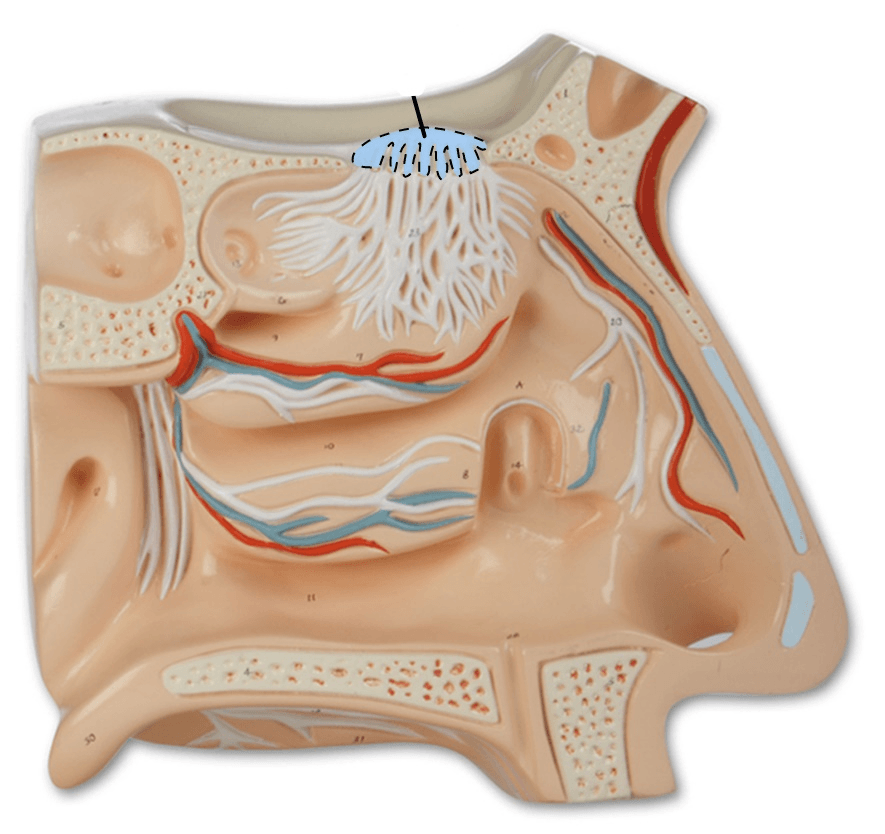
For an extra 100 points: What specific cells are found in this structure?
Olfactory Bulb (has mitral cells in it!)
What effect would the sympathetic division have on...
a. Salivary glands
b. Pupils
c. Heart rate
d. Liver
e. GI tract
a. Inhibitory (decrease secretions = dry mouth)
b. Relaxation of smooth muscle (pupils dilate)
c. Excitatory (increase heart rate)
d. Increases blood glucose by increasing glycogenesis (for cells to use for ATP)
e. Inhibitory (Slows contractions, food moves more slowly)
The sweat reflex is what type of reflex?
For an extra 100 points: If a person's sweat glands decrease their activity, what division(s) of the nervous system would cause this?
Autonomic reflex (any activity of the sweat glands is controlled by the by the sympathetic nervous system)
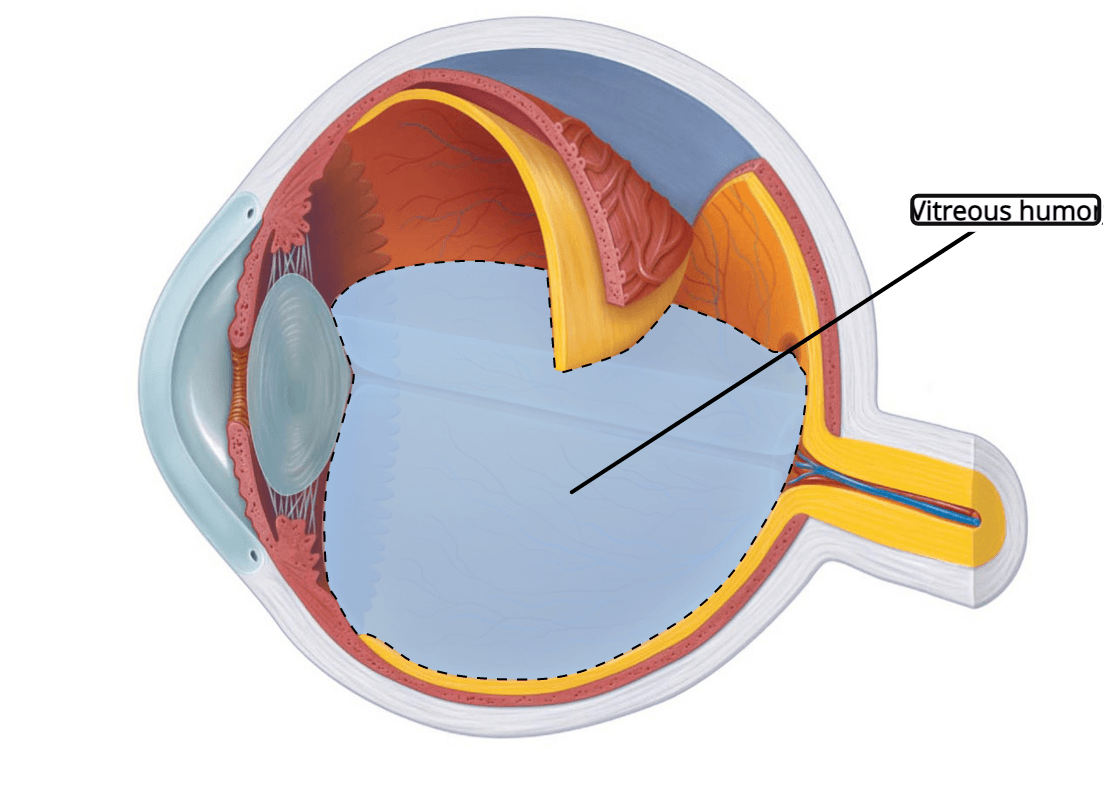
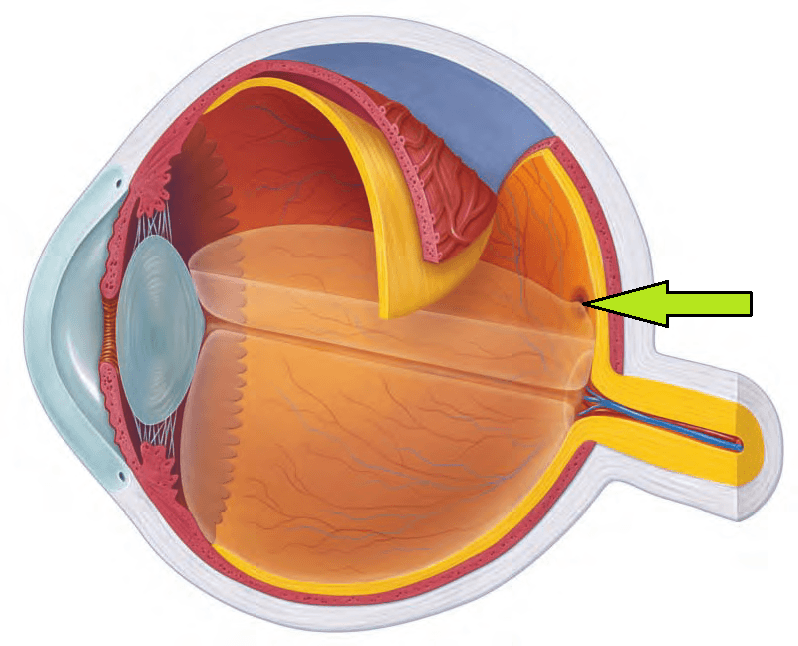
What is the name of the liquid that fills the posterior chamber?
For an extra 100 points: what is a function of this liquid?
Vitreous Humor (maintains infraorbital pressure/shape of eye and allows light to pass through the retina)
If ionized chemicals bonded to gustatory cells, what basic taste would the person perceive?
Salty
What is this? (them together)
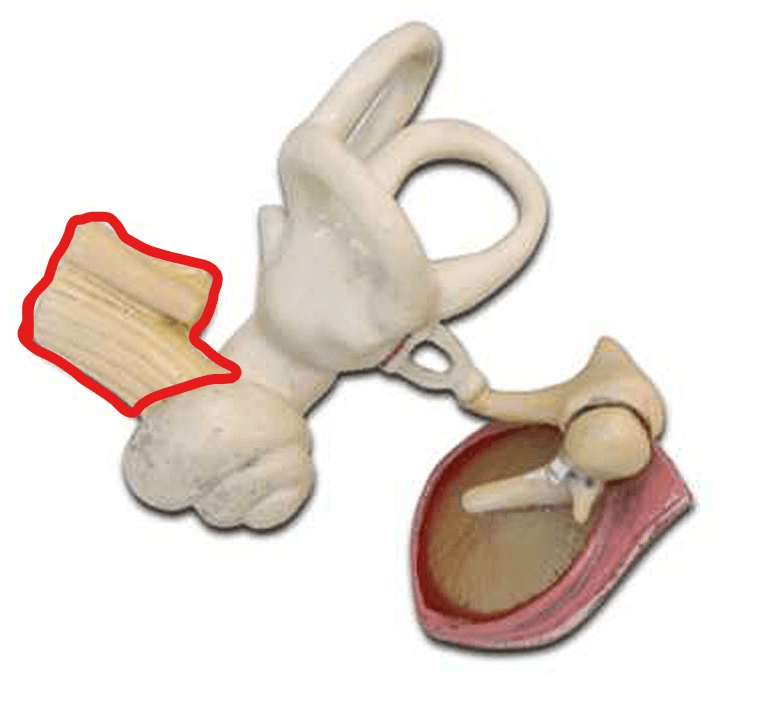
Vestibulocochlear Nerve
When norepinephrine binds to alpha 1 receptors on smooth muscle of blood vessels, what is the effect? What variable in the body changes as a result?
Vasoconstriction; increase in blood pressure
A neurotransmitter that binds to a nicotinic receptor is always _________
a. Stimulatory, norepinephrine
b. Stimulatory, epinephrine
c. Inhibitory, norepinephrine
d. Stimulatory, acetylcholine
e. Inhibitory, acetylcholine
d. Stimulatory, acetylcholine
The highlighted structure is a portion of what?
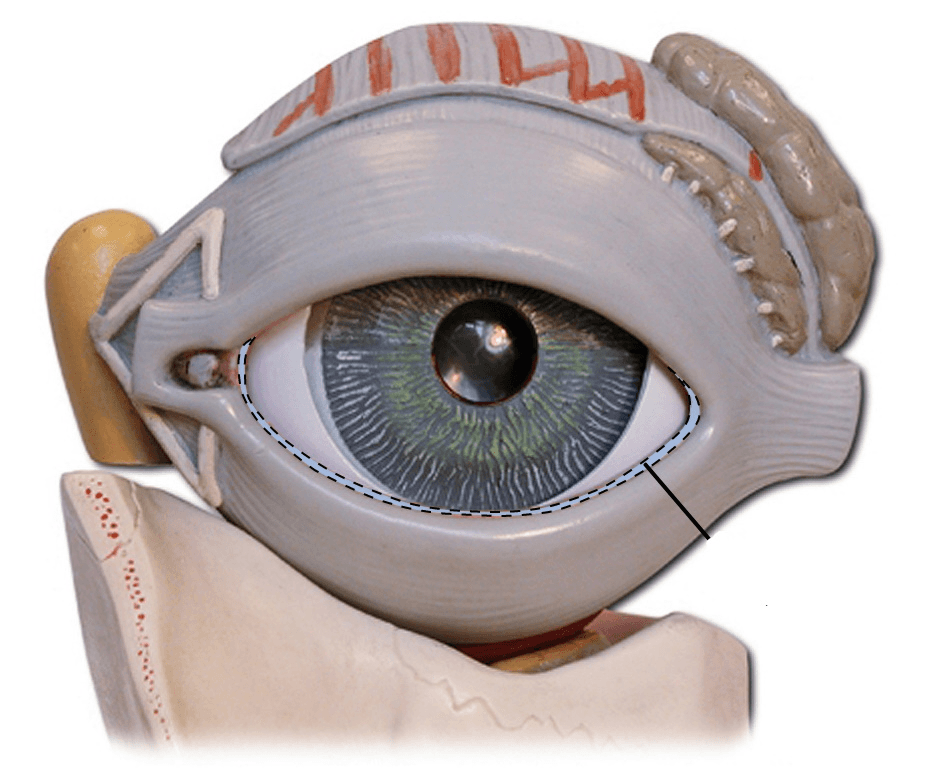
Conjunctiva
Which structure connects the ciliary body to the lens and allows for accommodation?
Suspensory ligaments
What is this and what specific receptors are found here?
Fovea centralis (contains only cones!)
An increase in Glycogenolysis and Lipolysis would be caused by what division?
Sympathetic division
- stimulates adrenal medulla, which releases epinephrine/norepinephrine: causes glycogen to break down into glucose and fatty acids to be released from adipocytes = more ATP for cells
Explain how beta-blocker drugs work & which types of patients would be prescribed these medications.
Beta-blocker drugs will block type 1 beta-adrenergic receptors on the heart in order to inhibit fight or flight/sympathetic effects of adrenaline (epinephrine).
Patients with irregular heart rates, hypertension, anxiety or other conditions may be prescribed these drugs in order to keep the heart rate from getting too high when under stress.
Describe the pathway of sound, saying each of the structures that play into it.
(From start to where sound transduction would occur)
Auricle → External auditory canal → Tympanic membrane → malleus → incus → stapes → oval window → cochlea → organ of corti → hair cells
In the dark, rod cells are _________ and bipolar cells _____ release neurotransmitters to stimulate the retinal ganglion cells.
a. Depolarized; do
b. Depolarized; do not
c. Hyperpolarized; do
d. Hyperpolarized; do not
b. Depolarized; do not
What is this?
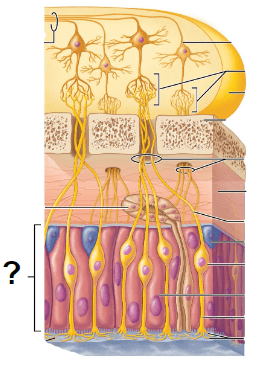
Olfactory epithelium