Explain the carbon sources that form coal, oil, and natural gas.
Coal and oil are both derived from the undecomposed and compressed remains of ancient organisms. Coal is formed on land, where the remains can be dried into a solid, whereas oil is formed underwater, where it is pressurized but remains liquid. Natural gas may form over oil deposits as a byproduct of the same process.
Which form of renewable energy is most common in the United States? How does it compare in cost to coal?
Hydropower is the most common in the US -- it is similar in cost to coal, almost 1:1.
Look at the graph below:
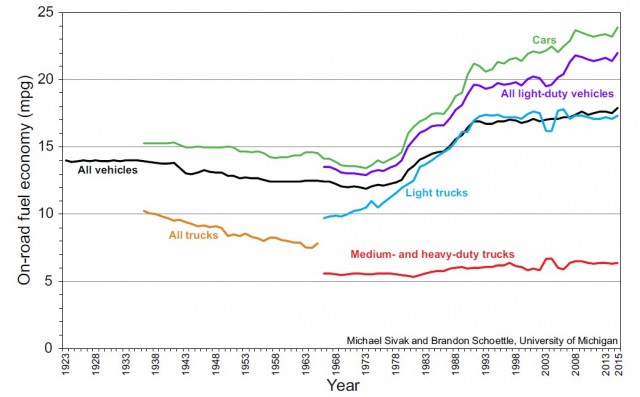
In the grand context of this data, summarize fuel-efficiency in the US for the last 30 years.
In the last 30 years, it has remained fairly stable over time, with small increases in MPG over the three decades.
This substance is an indoor pollutant that enters from subterranean pockets of released gas. It's also radioactive.
Radon
DAILY DOUBLE: How is it removed once it's been found?
This is the city of Smell-A. I mean, LA. In a comparison of 1968 to 2005...
1. Which legislation likely led to the changes seen in the two photos?
2. What are 2 pollution issues likely prevalent in LA?

1. Clean Air Act
2. Photochemical smog, tropospheric ozone production, thermal inversion, noise pollution, light pollution, thermal pollution
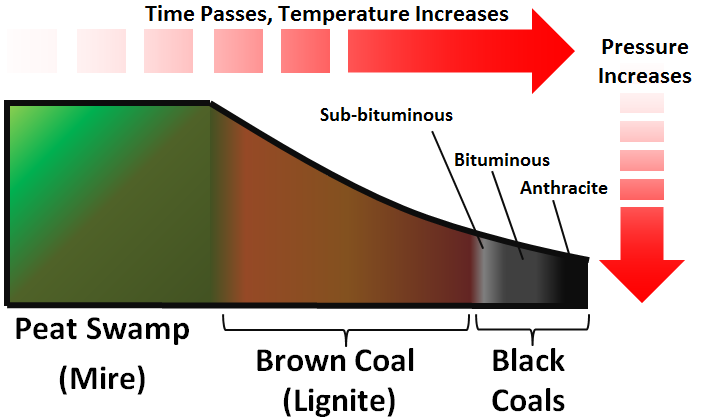
Name the 4 stages of coal formation. Which is combusted for energy production?

Why can't all forms of renewable power be used in all parts of the world? Give 2 examples of renewables and where they make the most sense in the United States.
Based on the natural climate, hydro, wind, solar, and geothermal power sources will vary in intensity and therefore efficiency.
Hydro- areas of significant elevation and river courses; largely west and east coast.
Wind - areas with frequent strong winds; midwest
Solar/photovoltaic - areas low in cloud cover; southwest
Geothermal - areas high in volcanic activity; western United States
Explain "cogeneration" and give an example
Cogeneration involves producing power from a specific fuel source, such as natural gas, biomass, coal, or oil. During fuel combustion, cogeneration captures the excess heat which would have otherwise been wasted.
The captured heat can be used to boil water, create steam, heat buildings, etc. For instance, in the tar sands, steam is required to produce bitumen. By using cogeneration, energy companies can simultaneously produce steam for production and electricity on site.
What is the chemical sequence of events that leads to the formation of ground-level ozone?
Ground-level/Tropospheric Ozone:
1. Nitrous oxides and volatile organic compounds are released by the combustion of petroleum fuels.
2. Nitrogen dioxide decomposes under UV radiation to form nitrogen monoxide and an oxygen atom. VOCs act as a catalyst in this reaction.
3. Oxygen atoms react with oxygen gas molecules to form ozone.
4. Nitrogen monoxide is able to react with ozone to form nitrogen dioxide and oxygen gas, allowing for a positive feedback loop to the formation of more ozone.
OR
1. NOx + VOCs are formed from the combustion of petroleum fuels.
2. NO2 --> NO + O (VOCs + UV catalyze the reaction)
3. O + O2 --> O3
4. NO + O3 --> NO2 + O2
Examine this diagram depicting the Greenhouse Effect

1. Which layer of atmosphere is responsible for keeping the Earth warm?
2. Which layer is responsible for preventing additional radiation from entering?
3. How does increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases contribute to global warming?
1. The troposphere, where greenhouse gases are in their highest density.
2. The stratosphere, where the ozone layer absorbs 97-99% of UV radiation.
3. Too much GHG in the troposphere absorbs outgoing infrared radiation, causing excessive heat to be retained closest to the earth.
What is the process of extracting natural gas called?
Fracking
Daily Double: describe how it is done and 2 of its negative byproducts.
What does it mean to be "carbon neutral"?
The amount of carbon that is released is equal to the amount of carbon that was initially consumed. An example of this is with biofuels, where plants are used to create hydrocarbons, rather than relying on fossil fuel hydrocarbons. Since plants photosynthesize and take in CO2 from the atmosphere, the source of carbon is already in the air, rather than being converted from the source underground.
Give three examples of programs that are designed to improve energy efficiency in municipal areas across the board.
1. Energy Star Appliances - trade in older units that use more energy
2. Innovation of common household items, like lightbulbs
3. Innovation of vehicle fuel efficiency (MPG) to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease per capita fuel cost.
Related to efficiency and having more to do with promotion of renewables:
1. Distributional surcharges
2. Renewable portfolio at state or federal level
3. Green pricing
Which legislation has had the greatest impact in reducing stratospheric ozone depletion? How? What is its greatest known limitation?
The Montreal Protocol, which banned the use of CFCs internationally. It is limited by its delayed effectiveness, due to the resilience of the chlorine atoms already formed from previously released CFCs.
Why is it expected that climate change will increase the spread of infectious diseases?
Disease-carrying insects such as mosquitoes have a specific range of tolerance for warm, humid climates. As climate change increases the latitudes that exhibit these types of climatic conditions, the land area that the insects are able to thrive in will also increase, allowing them to infect more people.
Give 2 advantages and 2 disadvantages of nuclear power
Advantages
- emits only steam
- generates significantly more power than coal per kg
- less use of fuel overall (transport, building, running, etc.)
Disadvantages
- accidents have larger consequences
- if there is an accident, effects are much more long lasting
- requires highly educated workforce
- more expensive to start and maintain
- spent fuel rods are radioactive and must be disposed of far from municipal areas without contaminating soil or water
Give an example of an active solar heating system and a passive solar heating system

The average laptop draws 60 W while plugged in. You spend 4 hours working on an essay for school. If the current cost per kWh is $0.15, how much did the energy cost?
= $0.036
Why are polar regions warming more quickly than other regions of the world?
Despite the extremely cold temperatures associated with the polar regions, the loss of albedo (reflectivity) from melting ice and snow causes a faster rate of warming, especially in the summer months when the axis of the earth tilts polar regions more towards direct sunlight.
Explain what the present-day countries with the greatest coal deposits had in common during the Carboniferous Era?
North America, Northern Europe, and Asia line up with the largest carboniferous swamps, where large quantities of biotic material was buried.
3 advantages of hydrokinetic power
-close to 1:1 cost to coal
-renewable
-no emissions
-recreation
-tourism
Daily Double!
3 disadvantages of hydrokinetic
-disruption of ecosystems on both sides of dam
-disruption of migration
-flooding upstream
-loss of nutrients downstream
-loss of homes in flooded area and/or near floodplain
Noticing the sink full of dishes, you place them in the dishwasher and let it run for an hour and a half (including the drying cycle). The dishwasher uses 2000 watts per hour. How many kWh have been used?
1.5 hr x (2000 W / hr) x (1 kW / 1000) = 3 kWh
Give 2 negative impacts of noise pollution and 2 negative impacts of light pollution.
Noise: disruption of mating calls, migration patterns, echolocation, circadian rhythms, and hunting.
Light: disruption of migration patterns, light-based movement away or towards light, circadian rhythms, night-vision and nocturnal activity.

What causes the oscillating "cycle" of CO2 levels in the atmosphere during the year? (Yes it's related to seasonal variation but what factor about the changing seasons specifically results in these shifts?)
Starting in the autumn months, trees begin to diminish in photosynthetic ability, resulting in more CO2 remaining in the atmosphere. As those trees' leaves fall, net photosynthesis drops and CO2 levels rise. In the spring, as leaves begin to regrow, more CO2 can be taken in from the atmosphere, leading to a decline in overall CO2 in the atmosphere.