The fundamental unit of life
A cell
Cannot be broken down or transformed into other substances.
An element
What type of chemical bonds are shown here?
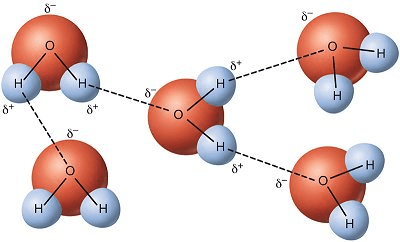
Hydrogen bonds
Carbohydrate monomers are called ___________.
Monosaccharides
Protein polymers are called __________.
Polypeptides
Homeostasis makes up this property of life.
Regulation
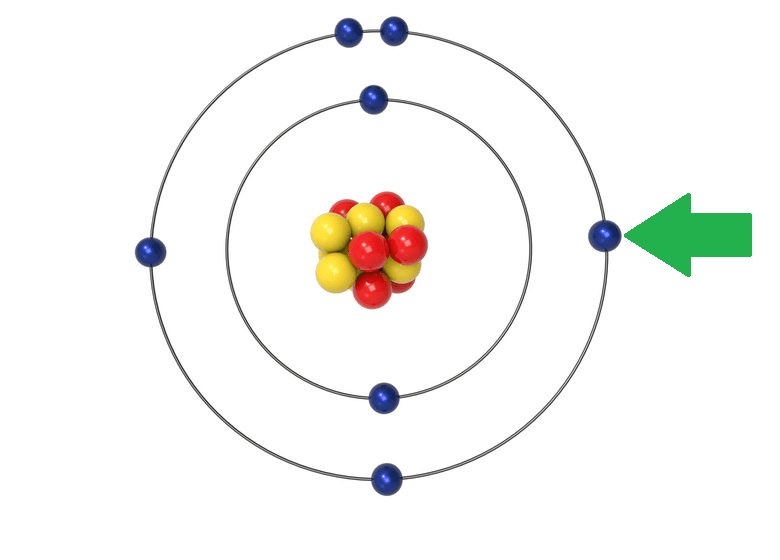
What is the charge of this particle?
Negative
Which functional group is nonpolar and acts as a marker?
Methyl
What type of reaction is seen below?
glucose + glucose → maltose + water
Dehydration reaction
The presence of uracil is found in which nucleic acid?
RNA
Bacteria and Archaea are types of __________ cells.
Prokaryotic
The interaction between these two atoms results in the formation of _____________.
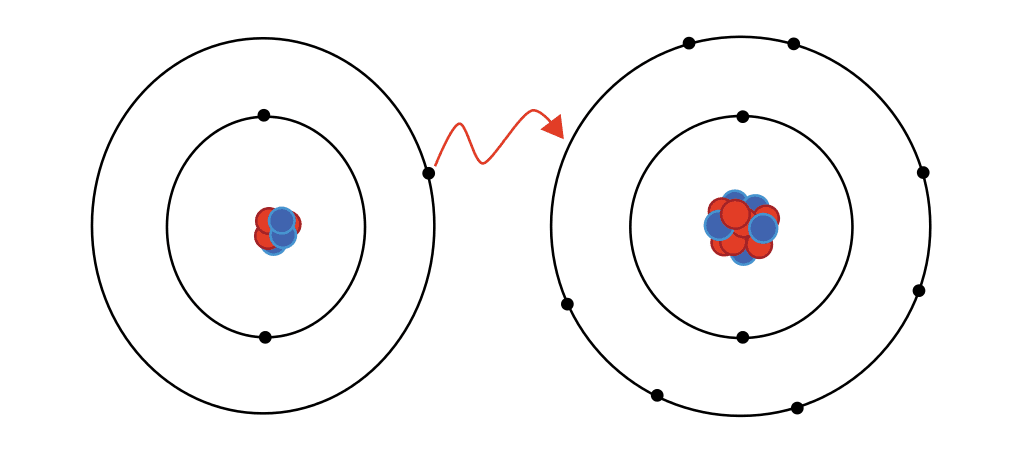
An ionic bond
Water resists temperature it has a high __________.
Specific heat
The presence of mostly hydrocarbons makes lipids __________.
Hydrophobic
There are 20 amino acids. Their properties are determined by differences in the ____________.
Sides Chains/R Groups
________ are eukaryotic organisms that are not found in a kingdom.
Protists
Carbon-13 and Carbon-14 are __________ ; differing in the number of ________.
Isotopes; neutrons
A basic solution will have more _______ ions than ______ ions.
Hydroxide (OH-) ions; hydrogen ions
Name the macromolecule.
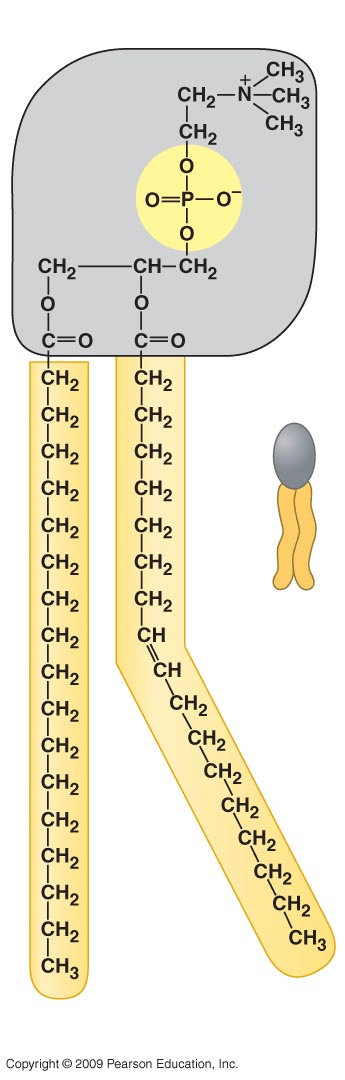
Phospholipid
The structure seen below is seen in which level of protein structure?
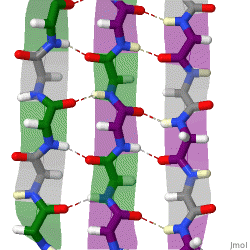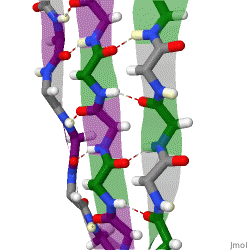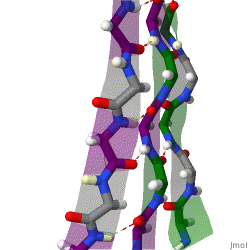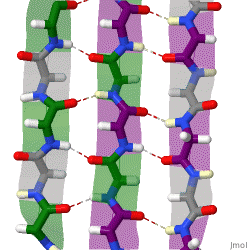
Secondary structure
Each has organism has a two part name: the _____ and the __________.
Genus and specific epithet
An uncharged atom of argon has an atomic number of 18 and an atomic mass of 40. This atom has _____ protons, _____ neutrons, and _____ electrons.
18; 22; 18
The molecules seen below represent _________ isomers.
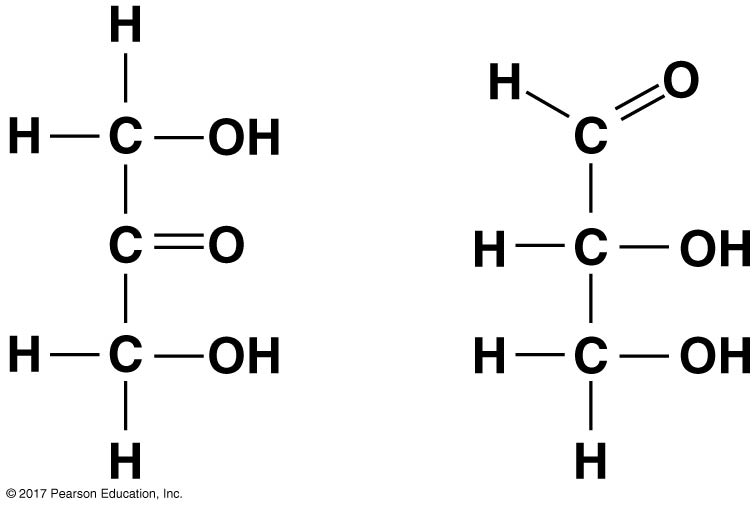
Structural isomers
Major component of insoluble fiber.
Cellulose
Nucleotides are composed of a pentose sugar, a ____________, and one or more ____________.
Nitrogenous base; Phosphate groups
What makes an ecosystem different from a community?
Community only corresponds to the living things (biotic) in a specific area. Ecosystem involves the interaction between living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) things.
Explain how polar and nonpolar covalent bonds form.
Nonpolar = atoms have similar electronegativity values; equal sharing of electrons; no charge
Polar = atoms have different electronegativity values; unequal sharing of electrons; partial charges result
Why does ice float?
Stable hydrogen bonds keep water molecules of ice farther apart than water molecules of liquid water.
Explain the difference between unsaturated and saturated fatty acids.
Saturated fatty acids have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible and no double bonds.
Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds, resulting in a bend.
Why are the nucleic acids called Deoxyribonucleic acid and Ribonucleic acid?
The naming is based on the differences within the pentose sugar of the nucleotides. Deoxyribonucleic acid sees one oxygen missing from the pentose structure, making it deoxyribose sugar. Ribose sugar contains the oxygen in the place where it is missing in deoxyribose sugar.