This man used attentuation to develop vaccines for anthrax, rabies, and chicken cholera.
Who is "Louis Pasteur"?
Who discovered lymphocytes that participate in cellular and humoral immunity (B cells and their antibodies)?
Who is Bruce Glick
Innate immunity consists of the ____________ lines of defense.
What are "first and second"?
This specific lab technique is used to determine protein-protein interactions.
What is co-immunoprecipitation?
Name at least one possible outcome of the complement systems.
What is cell lysis, chemotaxis, inflammation, opsonization & clearance of immune complexes, or aids in adaptive immunity?
Two methods of attenuation used by Louis Pasteur are:
Oxidizing agents, Serial infection
When finding HSCs, this type of selection is at play when using antibodies that detect Lin+ markers on cells.
What is negative selection?
Name the antimicrobial peptide that punctures the bacterial cell membrane and can be found in neutrophil granules
What are defensins?
An indirect ELISA is used to detect the presence of ______ in a sample
What are antibodies
This inhibitor protein is known to degrade C3b and C4b.
What is factor I?
What early form of vaccination had a relatively high infection/death rate?
What is "variolation"? (associated with Onesimus and Lady Mary Wortley Montagu)
The spleen is divided into three main regions. The marginal zone separates the white pulp and red pulp. The region that is immunologically active is known as __________
What is "white pulp"?
These are the 3 ways that neutrophils can kill a pathogen.
What are phagocytosis, degranulation, and NETosis?
Which technique is being utilized in this figure?
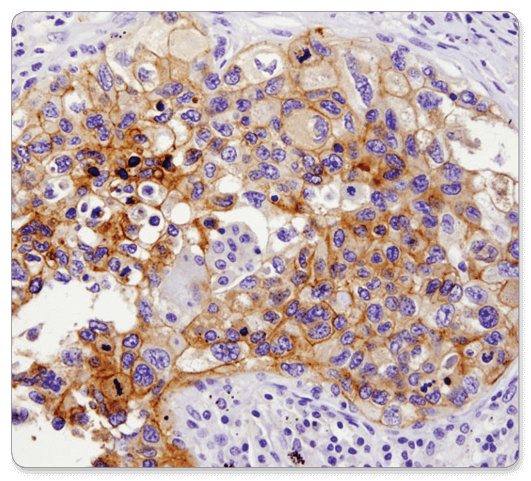
What is immunohistochemistry
What components form the membrane attack complex (MAC)
What are C5b, C6, C7, C8, and a bunch of C9
Describe 3 effects that cytokines can induce
Chemotaxis, Activate adaptive immunity, Vasodilation, Phagocytosis, Cell differentiation and division, Promotion of more cytokine release
M cells are specialized epithelial cells that endocytose antigen and present them to immune cells. Where are they located?
What is MALT
What is the effector enzyme activated after a PAMP binds to an NLR?
What is "caspase-1"? (cleaves pro-IL-1 into active form)
An ELISA specializes in detecting ______ proteins, while a western blot specializes in detecting ______ proteins
Secreted, cellular
SLE (lupus) correlates with _____ deficiency. This results in _____ ___________ in tissue without clearance.
C4, chronic inflammation
What are 3 examples of immune system failures?
immunodeficiences, hypersensitivies, allergies, asthma, autoimmunity, organ/tissue transplant failure, cancer
Which three specific types of macrophages do we learn about in BIOL0530?
What are Microglia (brain), Kupffer cells (liver), and Langerhans cells (skin), Osteoclasts (bone)?
These are the two methods NK cells (that we've learned) can use to kill cells?
What are Perforin + Granzyme and FasL/Fas?
What was the purpose of utilizing heat inactivated MHV (mouse hepatitis virus) and CQ (chloroquine) in figure 3 of the paper?
These were used to prove that viral replication and entry are NOT required to activate pro-inflammatory signaling pathways in infected cells.
What are 2 outcomes that may occur when a person has complement deficiencies?
1. Greater frequency of infections by bacteria due to inefficient opsonization and phagocytosis
2. Present with immune complex disorders due to inadequate clearance