What kind of transport is osmosis? and does it go from high to low or low to high?
Osmosis is passive transport and goes from high to low.
a movement of ions and other atomic or molecular substances across cell membranes without need of energy input
What is passive transport
____________is the splitting of the cytoplasm in cell division.
cytokinesis
During which stage in meiosis 1 does crossing over occur?
prophase 1
100 Kcal
the principal molecule for storing and transferring energy in cells
what is ATP
What simple molecules are the basic units of proteins?
What are amino acids
DNA or RNA
What are the products of cellular respiration?
water and carbon dioxide
Name the long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism and what half of that is called too.
What is a chromosome and chromatid
what is in all cells?
cytoplasm and DNA
A biomolecule that serves as a fast source of energy?
What are carbohydrates
What is a nucleus and in what kind of cells is it found in?
A nucleus controls and regulates the activities of the cell and carries the genes. They are found in eukaryotic cells.
Human cells organize DNA into one or more of these that carry genetic material.
What are chromosomes?
This process produces four genetically unique cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as in the parent
meiosis
process by which organisms use oxygen to break down food molecules to get chemical energy for cell functions
What is cellular respiration
This type of reproduction involves two parents and offspring that are not genetically identical to either parent. And name the pros and cons of this reproduction.
sexual reproduction.
Pros: Variation, genetic variation, evolution, adaptions.
Cons: Requires two organisms, requires more energy, takes longer,
Made of mostly phospholipid molecules embedded with proteins, this flexible boundary separates life from nonlife.
What is the plasma membrane (cell membrane)?
What are the light reaction inputs for photosynthesis
Water, sunlight(light), NADP+ and ADP
The differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic Cells? The group with the most amount of differences gets the points.
Prokaryotic: Size is 0.1- 5.0 um, Ribosomes smaller, chlorophyll scattered in the cytoplasm, Flagella, Cell wall chemically complexed, Transcription occurs in the cytoplasm, Examples: Bacteria and Archaea
Eukaryotic: Size is 5-100 um, Nucleus, Membrane-bound Nucleus, Multicellular, Lysosomes, Endoplasmic reticulum, Mitochondria, Cytoskeleton, Ribosomes larger, Golgi apparatus, Chloroplasts (Plants), Vacuoles, Transcription occurs inside the nucleus., Examples: Protists, Fungi, Plants, and Animals
Find the Amino Acids
TAC - AGT - CTC - CCC - GAA - ACC
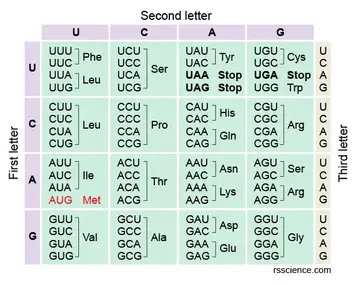
DNA: TAC - AGT - CTC - CCC - GAA - ACT
RNA: AUG - UCA - GAG - GGG - CUU - UGA
Amino Acids: MET - Glu - Gly - Leu - Stop
Sickle cell anemia is a recessive disease. If you cross two parents with the alleles Aa x Aa, what are the chances their children will have sickle cell anemia?
25%