Name this graph:
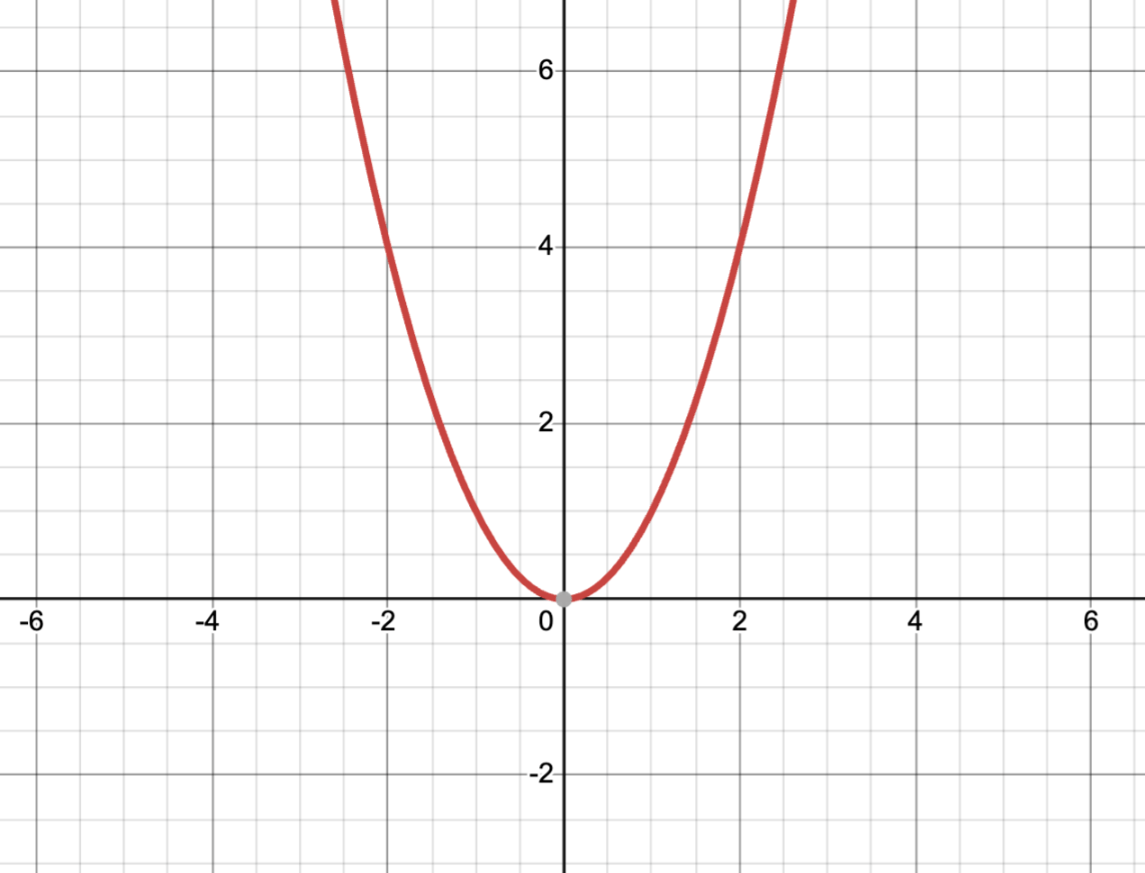
Parabola (or Quadratic)
A variable that influences both the explanatory variable and response variable, interfering with experimental results and causing a spurious (false) association.
Confounding Variable (or lurking)
Measures an outcome, or the expected effect, of a experiment.
Response Variable
Name both:
The entire group of individuals or items we want information about.
A subset of the entire group of individuals or items we want information about.
Population & Sample
The CNHS guidance counselor.
Ms. Deirdre
Identify the coordinates of the vertex:
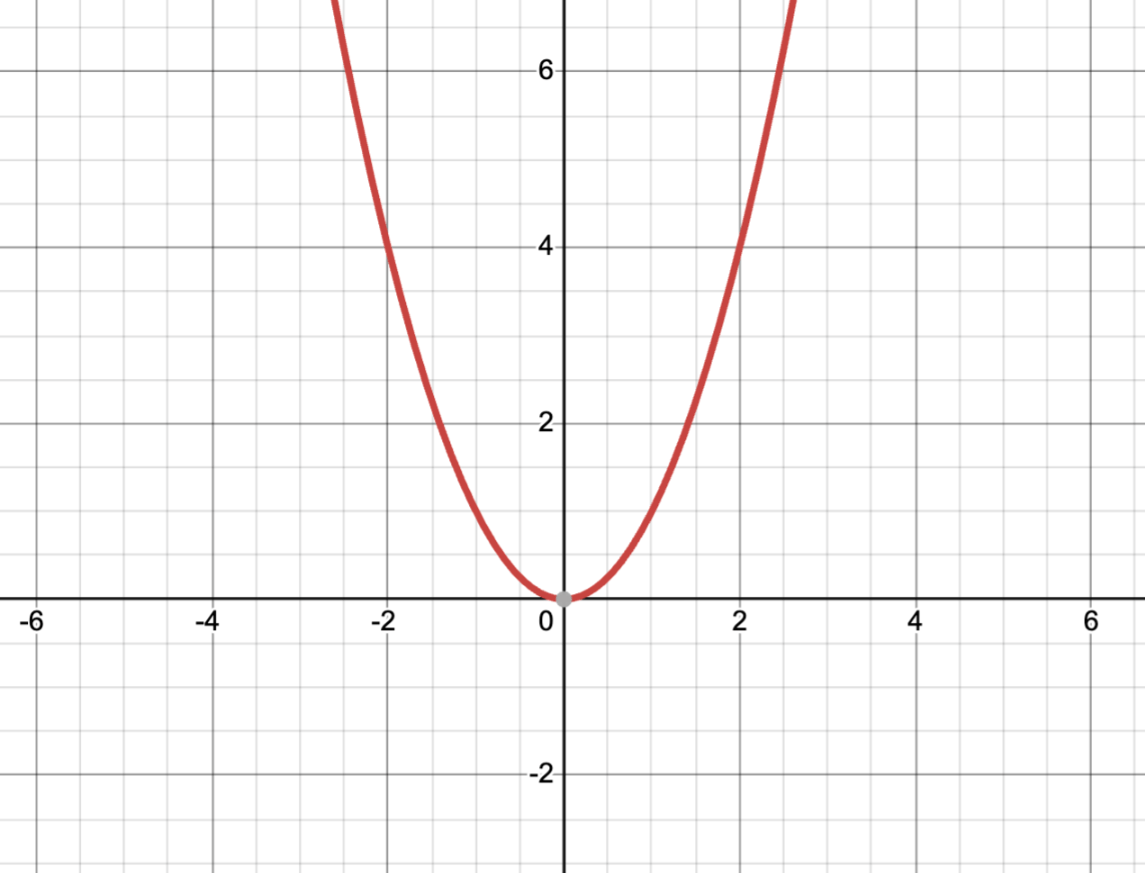
(0,0) or the origin
Mr. Turner is trying out a new facial hair ointment to make his beard grow faster for No Shave November. At the end of November, his beard is 3 inches long. He concludes since his beard grew 3 inches, the ointment must work. What is wrong with his reasoning?
There is no comparison being made (no control group).
What a statistician can manipulate in an experiment. It may explain changes in the outcome of the experiment.
Explanatory Variable
In order to prevent bias in our samples we want to make sure our samples are__________________.
Random
This video conferencing platform gained popularity in the early 2020s, becoming a generational moniker in the process.
Zoom
15g + 15 = 30
Solve for g:
g = 1
Identify a possible lurking variable:
Those people who tend to carry lighters in their pockets also have a higher risk of cancer.
People who carry lighters tend to smoke. Smoking is the lurking variable.
Observational Study
A process that is unpredictable, where each element has an equal opportunity to be selected is __________.
Random
When a school strives to give students to a deeper understanding of a general subject area while fostering an appreciation for a variety of art forms and the rich connections that all subjects have.
Arts Integration
A stunning prom dress is on sale for 20% off at the Overpriced Prom Dress Store. Originally the dress was $440. How much is the dress after the 20% discount?
$352
Identify a possible lurking variable:
Students who eat dinner with their family often are more likely to have better grades
Students who have time to eat with family also may have time to study, etc. (no job, etc.)
This type of data collection procedure can prove a causal relationship between an explanatory variable and a response variable.
Experiment
Ms. Zahrt wants to find how many guests, on average, seniors plan to bring to graduation. Rather than ask all seniors she assigned a number to each student and used a random number generator to select students for her sample. This is an example of what type of random sample?
SRS (Simple Random Sample)
The process by which plants make their own food.
Photosynthesis
Solve for z:
6x^2+6=30
+-2
Saniya and Ariel wanted to see whether CNHS students preferred chocolate chip cookies or oatmeal raisin cookies. They each made a batch of both cookies and - Saniya tested her cookies with 9th and 10th graders and Ariel tested her cookies with 11th and 12th graders. Why is this not a well-designed experiment?
No control, they are using cookies made by different people.
Something that appears to exoerimental participants to be an active treatment but does not actually contain the active treatment.
Placebo
Mr. Goines wanted to determine how much interest there would be for a CNHS pickleball team. He assumed each grade might have different answers so he chose 10 random students from each grade to ask. This is an example of what type of random sampling?
Stratified random sampling
The largest mammal in the world.
Balaenoptera musculus (Blue Whale)
An individual rose costs $5.00. A dozen roses cost $48.00. What percent discount do you get by purchasing a dozen roses together rather than 12 individual roses?
20%
Name the 4 principles of good experimental design.
Comparison
Random Assignment
Replication
Control
In an experiment, the subjects who do not receive a treatment. They may instead receive a placebo.
Control Group
The thought process that allows you to use a sample statistic value to make judgments about the population parameter value. [to use samples to make claims about the population]
Inference
Blue Crabs are the number one seafood product harvested in Maryland. Name one of the next two seafood products on the list.
Striped Bass or Oysters
Evaluate the following function at x=4:
f(x)=(2x^2)/8
f(x)=4 or (4,4)
Suppose that we have 30 students willing to participate in our experiment to test androids vs. Iphones to complete simple online tasks. We decide to have 15 students use androids and 15 students use Iphones.
Suppose we let students pick which device they wanted to use. Why might this be a problem?
The subjects in an experiment who receive what the researcher is interested in studying.
Treatment Group
Kiyah and Journey wanted to know where CNHS seniors were going for senior week. They sent an email survey to the entire senior class. Students could choose whether or not to fill it out. What type of bias is this most likely to result in?
Voluntary response
This mathematician, who lived c.570 – c. 495 BC, was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher, polymath and political/religious figure taught the "transmigration of souls", which holds that every soul is immortal and, upon death, enters into a new body. He also has a geometric theorem named after him.
Pythagoras