this structure lines the sclera of the eyeball
What is the bulbar conjunctiva?
hyphema typically result from this type of injury
What is vascular injury with a direct, hard blow (i.e. getting hit in the eye with a baseball)?
this is th part of the retina where the optic nerve exits, creating a blind spot
What is the optic disk?
this structure can be described as the halo around the fovea
these are the sensory and motor legs of the pupillary light reflex
sensory = CN II (seeing light)
motor = CN III (reacting to light)
these two structures lie within the fibrous layer of the eye
What are the sclera and the cornea?
this structure of the eye is completely avascular and rather receives nourishment from lacrimal fluid and aqueous humor
What is the cornea?
bonus: what layer is the cornea in?
relaxation of the ciliary body of the lens results in this type of vision
What is far vision?
this is the difference between rods and cones
rods = low light, B&W
cones = day vision, color
this is the definition of presbyopia
What is age related thickening/stiffening that results in worsening vision?
the amount of this substance in the iris determines eye color
What is melanin?
These are the afferent and efferent limbs of the corneal reflex
afferent = V1 (to spinal trigeminal nucleus)
efferent = VII (to obicularis oculi)
What is an astigmatism?
the dilator pupillae muscles are controlled by the _________ nervous system whereas the sphincter pupillae are controlled by the ___________ nervous system
sympathetic, parasympathetic
the sclera is composed of this substance?
What are collagen fibrils?
the iris is within this layer of the eyeball
What is the vascular layer?
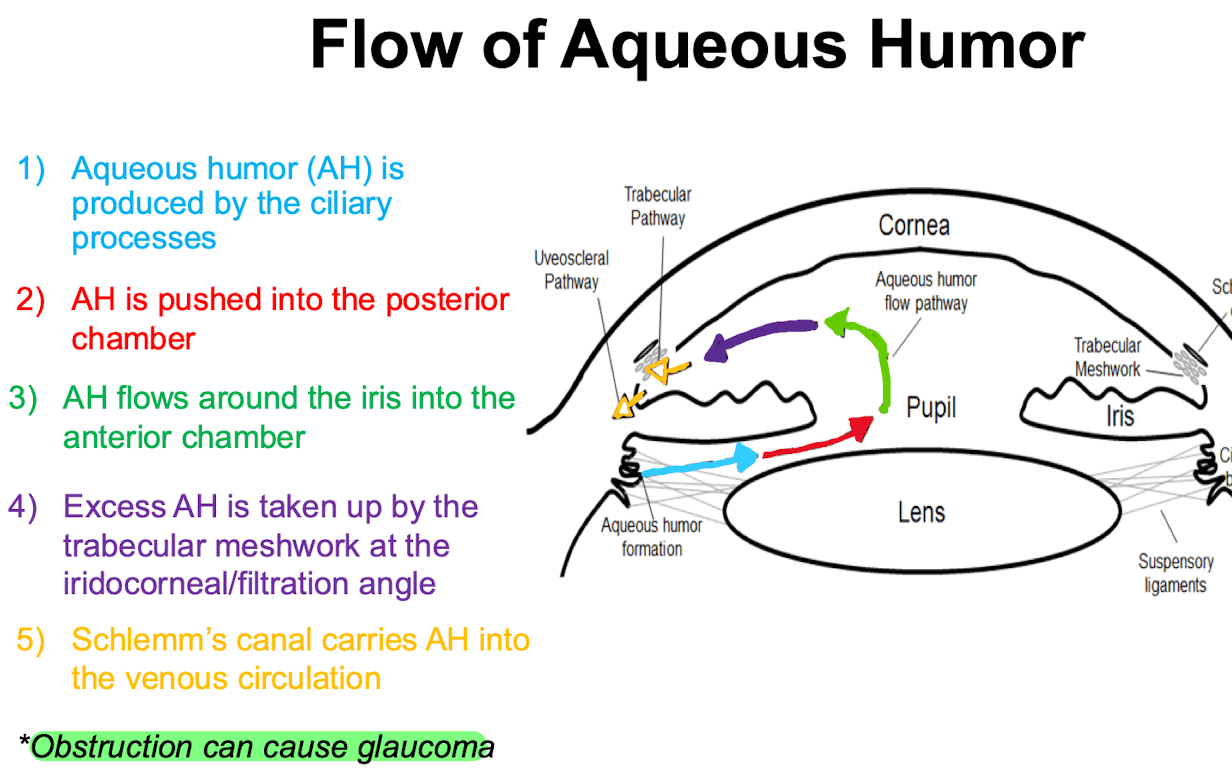
these structures produce aqueous humor
What are ciliary processes?
this is the name of the angle between the sclera and cornea
What is the limbus?
this lines the innermost layer of the eyelids
What is the palpebral conjunctiva?
place of 'most perfect vision' due to the high concentration of rods and cones
What is the fovea?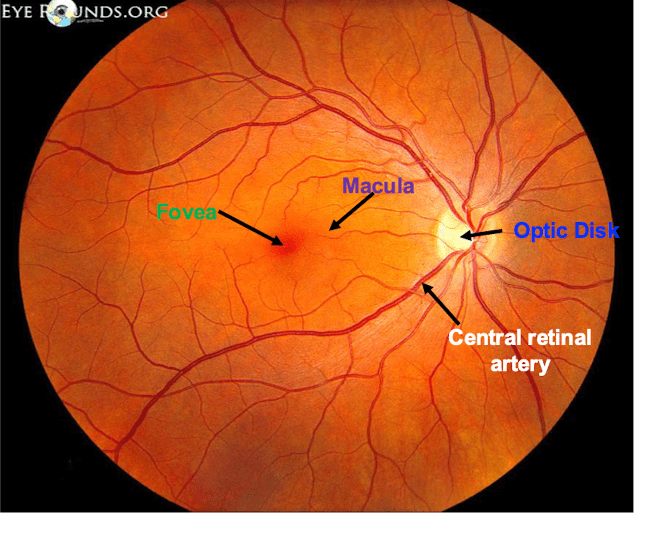
This structure is the main vascular supply to the eye
What is the choroid?
this is the function of bipolar cells of the nuclear layer of the retina
transmit cells from the photoreceptor cells to ganglion cells?
symptoms of this pathology include blurred, cloudy vision, glare, and poor night vision
What are cataracts?
in near vision, the ciliary body constrictions and these fibers relax allowing the lens to become "bunched"
What are zonular fibers?
this is the sequential flow of aqueous humor