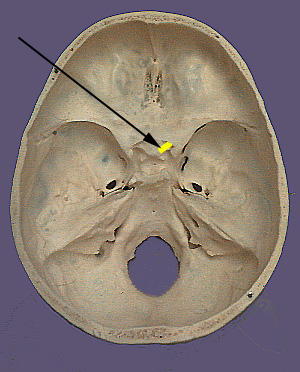
The opening into the orbit that transmits the optic nerve and ophthalmic artery
What is the optic canal?
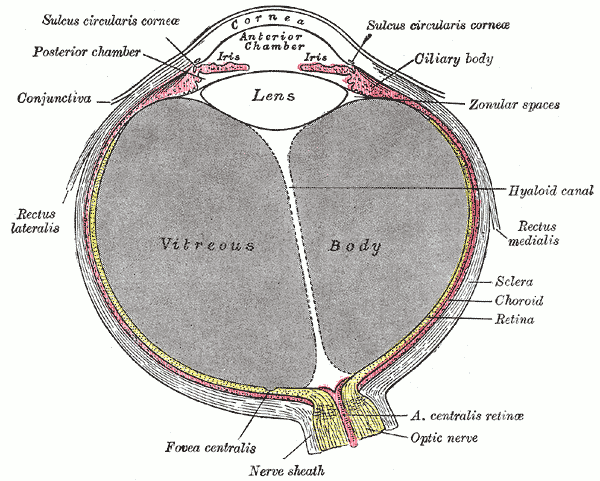
The 3 layers of the Eye
What are the fibrous, muscular/vascular, and sensory layers?
Left eye (Latin)
What is Ocular Sinister?

Glaucoma that occurs at birth
What is congenital glaucoma? 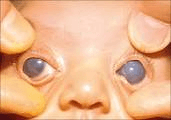
if a baby’s eye cells and tissues don’t grow like they should before birth, they can have trouble with drainage after they are born. But we don’t clearly understand most causes at this time. Some cases are inherited, while others aren’t.
The axons of retinal ganglion cells bundle together to form this structure
What is the optic nerve?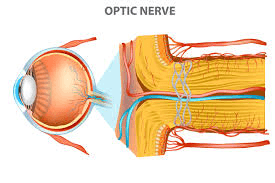
Modified sebaceous glands that secrete an oily substance to increase the viscosity of tears and decrease evaporation
What is the meibomian gland?

Two structures making up the fibrous layer
What are the sclera and cornea
A progressive deterioration of the macular tissue of the retina, an area important in the visualization of fine details. Leads to loss of central vision (reading, watching videos, driving).
What is Macular Degeneration

Something else caused this glaucoma
Secondary Glaucoma can come from injury, inflammation tumor or advanced cases of cataracts or diabetes
Fibers that synapse in the lateral geniculate body of the thalamus continue on to the visual cortex by this structure
What is the optic radiation?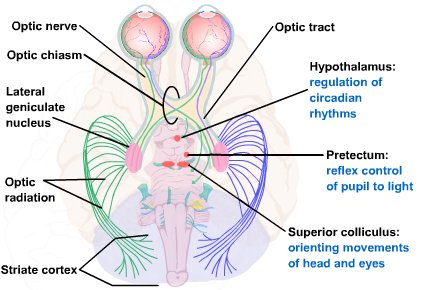
Openings that drain tear fluid from the eye
What are the inferior and superior puncta of the lacrimal apparatus
Parts of the uveal tract
What are the choroid, ciliary body, and the iris
Treatment for closed-angle glaucoma, one of the many types of glaucoma, usually done with a laser .
What is an Iridotomy?
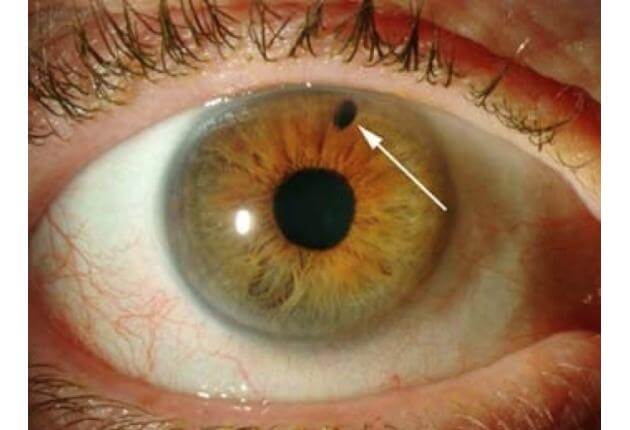 Laser peripheral iridotomy (LPI) is the preferred procedure for treating angle-closure glaucoma caused by relative or absolute pupillary block. LPI eliminates pupillary block by allowing the aqueous to pass directly from the posterior chamber into the anterior chamber, bypassing the pupil.
Laser peripheral iridotomy (LPI) is the preferred procedure for treating angle-closure glaucoma caused by relative or absolute pupillary block. LPI eliminates pupillary block by allowing the aqueous to pass directly from the posterior chamber into the anterior chamber, bypassing the pupil.
Pigmentary glaucoma is caused by this problem
Pigment from the back of the iris, flows toward the trabecular meshwork and clogs the drain
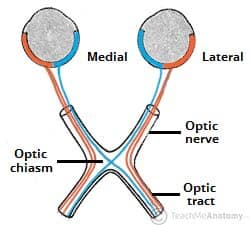
Information from the nasal retina cross over to the contralateral side at this structure.
What is the optic chiasm?
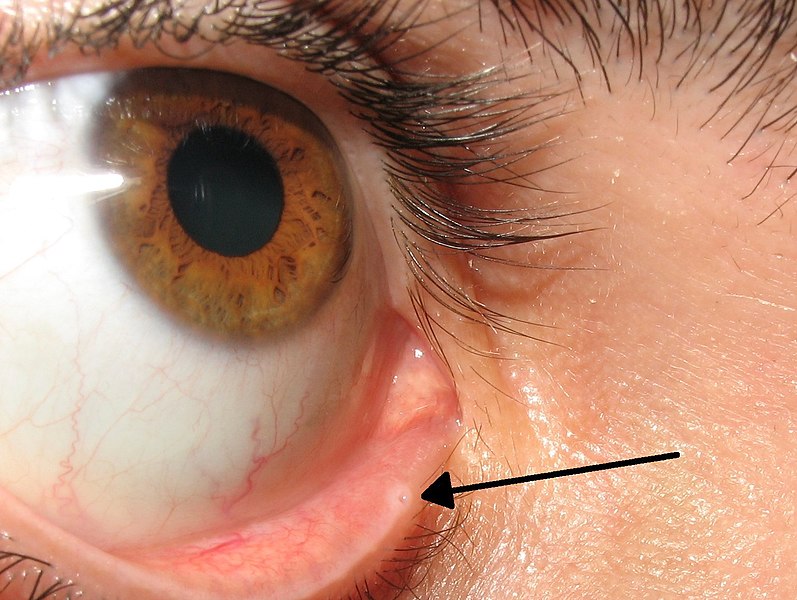
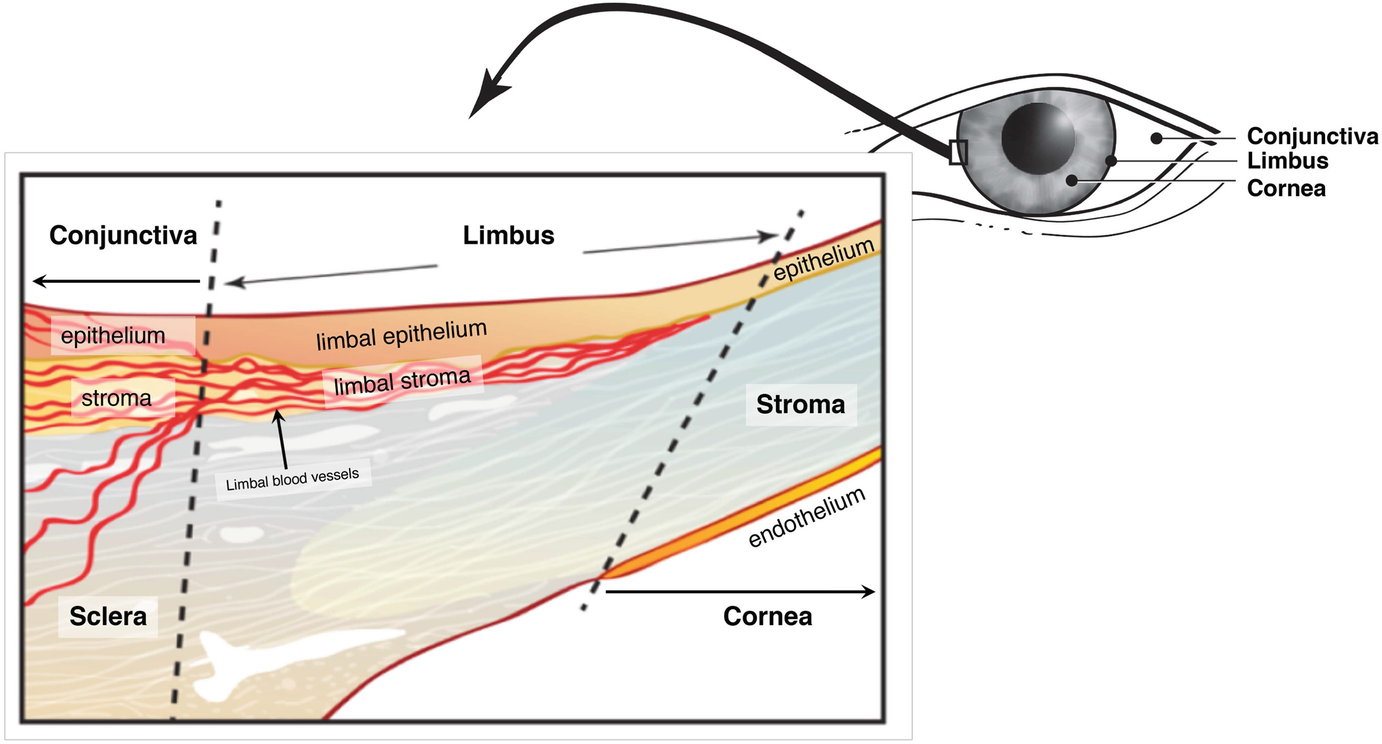
Area where the sclera and cornea come together
What is the limbus?
The function of the fovea centralis
What is responsible for high acuity color vision due to high concentration of cones?
Condition of the eyes in which they have unequal refractive power .
What is Anisometropia
Glaucoma caused by flaky dandruff like material that peels off the outer lay of the lens
What is Pseudoexfoliative Glaucoma?

A lesion at this area along the visual field pathway will cause Contralateral homonymous hemianopia (complete loss of vision in the inner half of one eye and the outer of the other)
What is the optic tract or optic radiation?

Structure that absorbs aqueous humor
What is the Canal of Schlemm aka Scleral Venous Sinus?

Gel like substance responsible for keeping the eye from collapsing
What is the vitreous humor?
Both Eyes (Latin)
Both eyes together (oculi unitas)
Blood Vessels can form this type of Glaucoma
What is Neovascular Glaucoma?
Generally associated with poor visual prognosis. The development of new vessels over the iris and the iridocorneal angle can obstruct aqueous humor outflow and lead to increased intraocular pressure
A lesion in this area of the visual field pathway will cause Bitemporal heteronymous hemianopia (complete loss of vision in the outer half of each eye)
What is the optic chiasm?
