True or False
How does transferring charge by contact work?
A. Electrons move from the object that holds them more loosely to the object that holds them more tightly.
B. A charged object repels electrons in a conductor.
C. Electrons move from the object that holds them more tightly to the object that holds them more loosely.
D. Electrons flow between two conductors until both have an equal charge.
A. Electrons move from the object that holds them more loosely to the object that holds them more tightly.
When you use a hair brush, strands of hair become electrically charged when ___________ transfer from the brush to your hair.
A. protons
B. electrons
C. neutrons
D. ions
B. electrons
What happens if an object accumulates negative charges?
A. The object becomes negatively charged
B. The object becomes positively charged
C. The object tends to lose positive charges
D. The object becomes attracted to other objects that accumulate negative charges
A. The object becomes negatively charged
What are electrically charged atoms called?
A. Molecules
B. Neutrons
C. Atoms
D. Ions
D. Ions
How can you demagnetize a permanent magnet?
A. By running a permanent magnet over it in different directions
B. By running a permanent magnet over it in the same direction
C. By heating, hammering or dropping it
D. By freezing it
C. By heating, hammering or dropping it
Which term refers to a region in a magnetic material in which the magnetic fields of the atoms all point in the same direction?
A. magnetic pole
B. magnetic domain
C. ferromagnetic element
D. magnetic field line
B. magnetic domain
What happens to the strength of magnetic field as you move away from the magnet?
A. The strength of the magnetic field decreases
B. The strength of the magnetic field increases
C. The strength of the magnetic field doesn’t change
D. none of these things happen
A. The strength of the magnetic field decreases
What is a magnetic material?
A. A material that produces a magnetic force
B. A material that is attracted to or repelled by a magnet
C. A material that becomes positively charged when a magnet is brought near it
D. A material that becomes negatively charged when a magnet is brought near it
B. A material that is attracted to or repelled by a magnet
The strength of an electric field increases as the distance between the two objects ____________.
A. increases
B. decreases
C. slow down
D. remains the same
B. decreases
Electrons move around the PROTONS of an atom.
False
Electrons move around the NUCLEUS of an atom.
Magnets can attract ALL metals.
False.
Magnets can attract SOME metals.
What is the area surrounding a charged object called?
A. A polarized area.
B. An electric field
C. An electrically charged zone
D. A negative Field
B. An electric field
What is static charge?
A. An unbalanced charge
B. A balanced charge
C. A type of electric current
D. A charge that moves freely
A. An unbalanced charge
A positively charged proton and a negatively charged electron will ______ each other.
A. repel
B. cancel each other out
C. do nothing
D. attract
D. attract
What are atoms made of?
A. Protons, neutrons, and electrons
B. Neutrons and electrons only
C. Only protons and neutrons
D. Only electrons
A. Protons, neutrons, and electrons
What is magnetic force?
A. A force exerted by a magnet only when it physically touches an object
B. A force exerted by magnets that can be felt by objects around or near a magnet
C. A force exerted by electrically charged particles
D. A force exerted by magnets that makes an object become electrically charged
B. A force exerted by magnets that can be felt by objects around or near a magnet
When two magnets are brought together, the magnetic fields of the magnets ___________.
A. combine and form one new field.
B. overlap.
C. disappear.
D. do not interact with one another.
A. combine and form one new field.
Any material that is strongly attracted to a magnet is a ______________.
A. magnetic material
B. electrically charged material
C. copper metal
D. non-magnetic material
A. magnetic material
What is an electromagnet?
A. A magnet that causes an electric current to move through a wire
B. A magnet that resists current flowing through a circuit
C. A magnet that reduces resistances in a circuit
D. A magnet created by an electric current
D. A magnet created by an electric current
Aluminum and copper are great examples of electrical _____________.
A. conductors
B. insulators
C. polarizers
D. magnets
A. conductors
Electrons have an electric charge, but NEUTRONS do not.
False.
Electrons have an electric charge, but NEUTRONS do not.
Magnetic forces get STRONGER the further you move them away from each other.
False.
Magnetic forces get WEAKER the further you move them away from each other.
What is an electric field?
A. A region surrounding a charged object
B. A space with no charge
C. A type of electric current
D. A field of energy
A. A region surrounding a charged object
Lightning is a powerful example of:
A. Accumulating electricity
B. Electric discharge
C. Magnetic discharge
D. Positive charges repelling negative charges
B. Electric discharge
When electrons concentrate at one end of an object, the object is ___________.
A. ionic
B. charged
C. discharged
D. polarized
D. polarized
What happens when an atom loses one or more electrons?
A. It becomes negatively charged.
B. It becomes cancelled.
C. It becomes positively charged.
D. All of these answers.
C. It becomes positively charged.
What are two ways that the strength of an electric force is affected?
A. The amount of charge on the objects and the distance between them.
B. The speed and direction of the moving electrons
C. The type of material and the color of the objects.
D. The strength of the magnetic attraction and repulsion.
A. The amount of charge on the objects and the distance between them.
Which surrounds all magnets, and allows magnets to repel or attract each other even when they are not touching?
A. magnetic field
B. magnetic north
C. magnetic pole
D. magnetic domain
A. magnetic field
How can you make a magnetic material into a temporary magnet?
A. If you run a permanent magnet over a magnetic material in the same direction several times, you can convert that magnetic material into a temporary magnet by aligning all of the domains.
B. If you run a metal object over another metal object in the same direction you can change both objects into temporary magnets.
C. By heating a magnetic material you can force the domains into alignment to create a temporary magnet.
D. You can't turn magnetic material into a temporary magnet.
A. If you run a permanent magnet over a magnetic material in the same direction several times, you can convert that magnetic material into a temporary magnet by aligning all of the domains.
What is a magnet?
A. An object that causes objects to become positively charged
B. An object that causes objects to become negatively charged
C. An object that attracts nonmetallic objects towards it
D. An object that produces magnetic force
D. An object that produces magnetic force
A material in which electrons cannot easily move is a(n)
A. electric conductor
B. electric insulator
C. electric polarizer
D. magnetic insulator
B. electric insulator
An electron has a negative charge.
True.
Magnetic forces and electric forces are NONCONTACT forces, meaning they can have an effect on other objects without touching them.
What are the two types of electric charge?
A. Positive and negative
B. Positive and neutral
C. Negative and neutral
D. none of these choices
A. Positive and negative
What is the name of a material in which electrons can easily move?
A. An electric insulator
B. A polarized object
C. An electric conductor
D. both conductors and insulators
C. An electric conductor
What do electrically neutral objects have?
A. More positive charge than negative charge
B. Equal amounts of positive and negative charge
C. More negative charge than positive charge
D. A large amount of charge
B. Equal amounts of positive and negative charge
What happens to an atom when it gains electrons?
A. It becomes positively charged
B. It becomes neutral
C. It becomes negatively charged
D. It loses its mass
C. It becomes negatively charged
What type of particle exerts an electric force?
A. A positively charged particle
B. A negatively charged particle
C. A neutral particle
D. A positively and negatively charged particle
D. A positively and negatively charged particle
The field lines on a magnet move in what direction?
A. Field lines come out the north side of the magnet, around the side of the magnet, go back into the south side of the magnet.
B. Field lines come out the south side of the magnet, around the side of the magnet, go back into the north side of the magnet.
C. Field lines come out both the south and north side of the magnet, around the side of the magnet, go back into both the north and south side of the magnet.
D. Field lines do not have a specific direction.
A. Field lines come out the north side of the magnet, around the side of the magnet, go back into the south side of the magnet.
What happens if you cut a magnet in half?
A. You will get one half that is the North and the other half that is the South, they no longer function as a magnet with both a north south side.
B. The domains will no longer be in alignment and the magnet is no longer a permanent magnet.
C. You will get two smaller magnets – you do not separate the North and South Pole.
D. All of these situations can happen depending on how you cut the magnet.
C. You will get two smaller magnets – you do not separate the North and South Pole.
Which is the term for a magnet that quickly loses its magnetic field after being removed from a magnetic field?
A. ferromagnetic element
B. permanent magnet
C. temporary magnet
D. electromagnet
C. temporary magnet
_________________ are elements, including iron, nickel, and cobalt, that have an especially strong attraction to magnets.
A. ferromagnetic elements
B. ferromagnetic metals
C. ferromagnetic magnets
D. magnetic elements
A. ferromagnetic elements
When an atom has more electrons than protons or more protons than electrons it is considered unbalanced. This is called INTENSE charge.
False.
When an atom has more electrons than protons or more protons than electrons it is considered unbalanced. This is called STATIC charge.
A PERMANENT magnet loses its magnetism easily.
A TEMPORARY magnet loses its magnetism easily.
Which particles do not have the property of electric charge?
A. protons
B. electrons
C. neutrons
D. none of these choices, they all have an electric charge.
When a balloon comes in contact with a sweater, electrons from the surface of the sweater transfer to the surface of the balloon. Because the sweater lost electrons, it has an unbalanced ___________ charge.
A. negative
B. positive
C. neutral
D. magnetic
B. positive
How do oppositely charged particles interact?
A. They attract each other
B. They repel each other
C. They have no effect on each other
D. They explode
A. They attract each other
Electrically charged atoms are called ______.
A. polars
B. isotopes
C. ions
D. protons
C. ions
Magnets can repel or attract each other even when they are not touching. This is because an invisible _____________ surrounds all magnets.
A. electric field
B. magnetic repulsion
C. magnetic attraction
D. magnetic field
D. magnetic field
Which properly explains what happens to a compass needle when the compass is placed near a magnet?
A. The needle points in random directions.
B. The needle points directly toward Earth's geographic north pole.
C. The needle aligns with the magnet's magnetic field lines.
D. The needle points directly toward the magnet's south pole.
C. The needle aligns with the magnet's magnetic field lines.
Which of the following is NOT a way to demagnetize a permanent magnet?
A. Heat the magnet
B. Freeze the magnet
C. Drop the magnet
D. Hit the magnet with a hammer
B. Freeze the magnet
A magnet that remains a magnet after being removed from another magnetic field is a ________________.
A. temporary magnet
B. permanent magnet
C. electromagnet
D. ferromagnetic element
B. permanent magnet
Which is the process of an unbalanced electric charge becoming balanced?
A. electric discharge
B. electric resistance
C. polarization
D. grounding
A. electric discharge
An object that loses enough electrons leaving it with more protons than electrons, the object is NEGATIVELY charged.
False.
An object that loses enough electrons leaving it with more protons than electrons, the object is POSITIVELY charged.
True or False: This is an image of a magnet. How do you know?

True. I know this is a magnet because there are domains and they are all aligned (facing the same direction).
What is the process of an unbalanced electric charge becoming balanced called?
A. Polarization
B. Electric recharge
C. Electric discharge
D. Grounding
C. Electric discharge
When a balloon comes in contact with a sweater, electrons from the surface of the sweater transfer to the surface of the balloon. Because the balloon gains electrons, it has an unbalanced ________ charge.
A. negative
B. positive
C. neutral
D. magnetic
A. negative
Many scientists think that lightning is related to the _____________ that separate within storm clouds.
A. electrons
B. neutrons
C. protons
D. electric charges
D. electric charges
Which particles in atoms have a positive charge?
A. Neutrons
B. Electrons
C. Protons
D. None of these answer choices
Which term refers to a force of attraction or repulsion between the poles of two magnets?
A. ferromagnetic force
B. polar force
C. magnetic domain
D. magnetic force
D. magnetic force
Which is the cause of the Earth having a magnetic field?
A. molten copper and iron in the inner core of the Earth
B. charged particles from the Sun
C. molten iron and nickel in the outer core of the Earth
D. iron in the inner core of the Earth
C. molten iron and nickel in the outer core of the Earth
A temporary magnet that is made by coiling wire around an iron core and running electricity through the wire is called a(n)
A. permanent magnet
B. static electric magnet
C. electromagnet
D. double magnet
C. electromagnet
For an object to be a magnet, its magnetic ___________ must align. This causes their magnetic fields to combine, forming a single magnetic field around the entire material.
A. domains
B. polarizations
C. ions
D. charges
A. domains
NUCLEAR energy, sound energy, and thermal energy are the three types of energy that comes from lightning.
LIGHT energy, sound energy, and thermal energy are the three types of energy that comes from lightning.
True or False: This is an image of a magnet. How do you know?

False: This is a magnetic material, I know it isn't a magnet because the domains are not aligned (all facing the same direction). I know it is magnetic material because it has domains.
An electric field gets stronger as you ____.
a. get closer
b. get farther away
c. add electrons to a positively charged object
d. remove electrons from a negatively charged object
a. get closer
When objects made of different materials touch, electrons tend to collect on the object that _____.
A. is a better conductor.
B. holds electrons more tightly.
C. holds electrons more loosely.
D. has less electrons.
B. holds electrons more tightly.
Which of the following statements about the forces between charged objects is NOT true?
a. As the distance between charged objects decreases, the electric force between them decreases.
b. If one object is positively charged and another is negatively charged, the objects will attract each other.
c. Two negatively charged objects will repel each other.
d. Two positively charged objects will repel each other.
a. As the distance between charged objects decreases, the electric force between them decreases.
Normally, atoms are electrically neutral because they have ____.
a. more protons than electrons
b. more electrons than protons
c. equal numbers of protons and neutrons
d. equal numbers of protons and electrons
d. equal numbers of protons and electrons
Which answer choice describes the relationship between electric force and electric field?
A. An electric field, which is an invisible region that surrounds every charged object, applies a force to other charged objects, even when the objects are not touching. This force is known as an electric force.
B. Electric fields only exist when two charged objects are touching, and the force they apply is called electric force.
C. Electric force creates electric fields, and these fields only exist around neutral objects.
D. Electric fields are visible regions around charged objects, and the force they apply is known as magnetic force.
A. An electric field, which is an invisible region that surrounds every charged object, applies a force to other charged objects, even when the objects are not touching. This force is known as an electric force.
What two things happen to an object’s electric field if it gains more and more electrons?
A. The object’s positive charge increases, and the electric field becomes weaker.
B. The object’s negative charge decreases, and the electric field disappears.
C. The object’s charge remains neutral, but the electric field extends farther into space.
D. The object’s negative charge increases and the electric field around the object becomes more and more intense (stronger).
D. The object’s negative charge increases and the electric field around the object becomes more and more intense (stronger).
The south pole of a magnet ____.
a. attracts another magnet’s south pole
b. repels a paper clip
c. attracts another magnet’s north pole
d. repels another magnet’s north pole
c. attracts another magnet’s north pole
Complete the statement. When an object that is not a magnet, but is made of magnetic material, comes in contact with a magnet_______.
a. all of its magnetic domains align and it begins to REPEL other objects made of magnetic material because it becomes a temporary magnet.
b. all of its magnetic domains align and it begins to ATTRACT other objects made of magnetic material because it becomes a temporary magnet.
c. its magnetic domains are now all out of alignment and it begins to ATTRACT other objects made of nonmagnetic material because it is no longer a magnet.
d. its magnetic domains fall out of alignment and it begins to REPEL other objects made of magnetic material because it is no longer a magnet.
b. all of its magnetic domains align and it begins to ATTRACT other objects made of magnetic material because it becomes a temporary magnet.
Which answer choice below best explains the relationship between a conductor and an insulator?
A. Conductors and insulators both help electrons flow freely to other materials.
B. Conductors and insulators are opposites. A conductor is a material in which electrons can flow through easily, while an insulator is a material in which electrons do not flow easily.
C. Both conductors and insulators prevent electrons from flowing through wires.
D. Conductors and insulators are opposites. An insulator is a material in which electrons can flow through easily, while a conductor is a material in which electrons do not flow easily.
B. Conductors and insulators are opposites. A conductor is a material in which electrons can flow through easily, while an insulator is a material in which electrons do not flow easily.
Objects become electrically charged when they gain or GROW electrons.
False.
Objects become electrically charged when they gain or LOSE electrons.
True or False: This is an image of a non-magnetic material. How do you know?

True. I know this is non-magnetic material because there are no domains.
Lightning is an example of _____.
a. charging by contact
b. conduction
c. electric discharge
d. static charge
c. electric discharge
When an object has more negative charge than positive charge or more positive charge than negative charge, the result is called a _____.
a. electric discharge
b. positive charge
c. series charge
d. static charge
d. static charge
When does a neutrally charged object become electrically charged?
A. When the neutrally charged object is heated or cooled.
B. When the neutrally charged object gains or loses protons.
C. When the neutrally charged object loses or gains electrons.
D. When the neutrally charged object comes into contact with a magnetic field.
C. When the neutrally charged object loses or gains electrons.
An atom with a neutral charge has equal numbers of protons and ___.
a. charges
b. neutrons
c. nuclei
d. electrons
d. electrons
Which two variables determine the strength of electric force between charged objects?
A. The size of the objects and the type of material they are made from.
B. The amount of electric charge the objects have and the distance between the two objects.
C. The speed of the objects and the type of charge they carry.
D. The temperature of the environment and the objects’ masses.
B. The amount of electric charge the objects have and the distance between the two objects.
The region around a magnet where the magnetic forces act is called the ____.
a. electromagnetic pole
b. magnetic domain
c. magnetic field
d. magnetic pole
c. magnetic field
Which statement explains why the Earth has its own magnetic field?
A. Earth has a magnetic field because its surface is covered with magnetic rocks.
B. Earth has a magnetic field due to the molten iron and nickel in the Earth’s outer core.
C. Earth has a magnetic field because of its atmosphere, which generates magnetic forces.
D. Earth has a magnetic field because it spins, creating friction with the Sun’s magnetic field.
B. Earth has a magnetic field due to the molten iron and nickel in the Earth’s outer core.
When you break a bar magnet into two pieces, you get ____.
a. one piece that contains only a north pole and another piece that contains only a south pole
b. two magnets, each piece containing both a north pole and a south pole
c. two very strong magnets
d. a piece of metal that is no longer magnetic
b. two magnets, each piece containing both a north pole and a south pole
Which answer choice describes the relationship between electric discharge and grounding?
A. Grounding prevents all electric discharge by blocking the flow of electrons.
B. Electric discharge occurs when an object is grounded, causing electrons to stop moving entirely.
C. Electric discharge happens only in wires, so grounding is not involved in natural events like lightning.
D. An example of electric discharge is lightning. When lightning discharges electrons to a lightning rod, the rod grounds the lightning by providing a path for the electric charge to flow safely into the ground.
D. An example of electric discharge is lightning. When lightning discharges electrons to a lightning rod, the rod grounds the lightning by providing a path for the electric charge to flow safely into the ground.
DRAW
A magnet with a north and south pole and it's magnetic field lines. Include arrows.
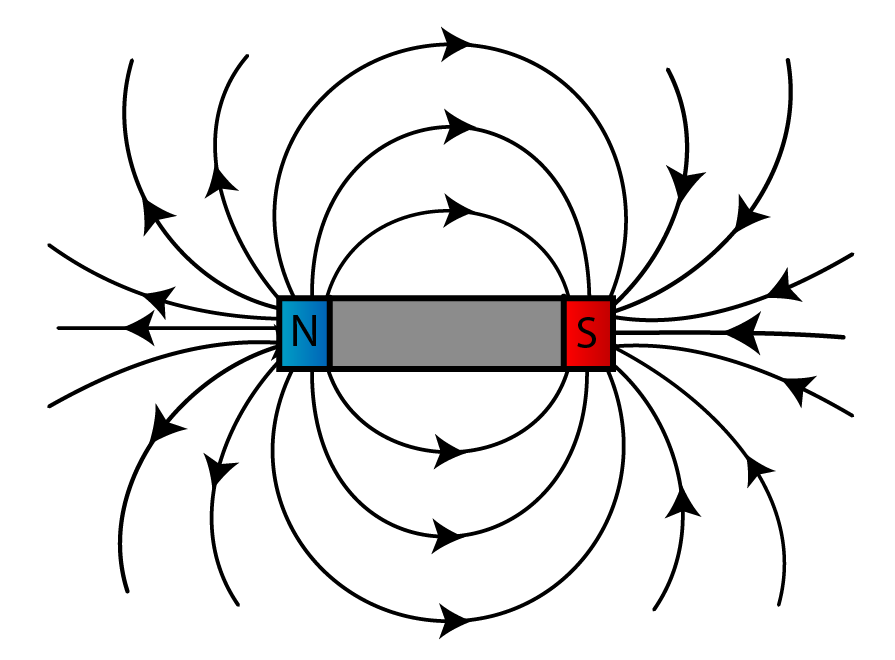
Where is the strongest force on a magnet?
a. center of the magnet
b. magnetic domains
c. magnetic fields
d. magnetic poles
d. magnetic poles
Shimmering sheets of light called auroras form due to Earth’s magnetic field. Which statement explains why this happens?
A. Charged particles emitted from the Sun travel along Earth’s magnetic field lines and concentrate near the magnetic poles. The particles collide with atoms of gas in the atmosphere, causing the atmosphere to glow as auroras.
B. The Sun’s light reflects off Earth’s magnetic field, creating glowing sheets of light called auroras near the poles.
C. Earth’s magnetic field traps heat from the Sun, which makes the atmosphere near the poles glow as auroras.
D. Earth’s magnetic poles absorb sunlight and release it as glowing light at night.
A. Charged particles emitted from the Sun travel along Earth’s magnetic field lines and concentrate near the magnetic poles. The particles collide with atoms of gas in the atmosphere, causing the atmosphere to glow as auroras.
Which of the following best explains why two magnets can attract or repel each other without touching?
A. Magnets are only active when in contact.
B. Magnetic fields exist around magnets and exert forces over a distance.
C. The air between the magnets carries magnetic charges.
D. Magnets lose their force when separated.
B. Magnetic fields exist around magnets and exert forces over a distance.
Groups of atoms with aligned magnetic poles are called ______.
A. poles
B. contacts
C. atoms
D. domains
D. domains
Which answer choice describes the relationship between electrons and something that is polarized?
A. Polarization occurs when electrons stop moving and are evenly distributed throughout the object.
B. An object is polarized when electrons are concentrated at one end of the object.
C. An object is polarized when it loses all its electrons and becomes neutral.
D. Polarization happens when protons move to one side of the object, leaving electrons behind.
B. An object is polarized when electrons are concentrated at one end of the object.