The projecting portion of the external ear whose primary purpose is to catch sound and funnel it into the canal.
Pinna
The amount of energy required to cause a fracture or a broken bone
Failure Point
If the AT notices a space between the teeth that was not previously there, discoloration under the tongue, or teeth not lining up properly after contact to the face, the AT should suspect a __________________.
Jaw Fracture (maxilla or mandible)
With a detached retina, one unique symptom the athlete will experience aside from pain, and blurred vision would be seeing ________________________ that are not actually present.
light/ sparks or streaks of light
There are a total of how many bones in the face?
18
In severe head injuries, ________________ may drain from an opening in the skull, the nose, or the ear and needs to be allowed to flow freely.
Cerebrospinal fluid
A ________________ occurs when a significant force displaces bones so that the two bone ends in the same joint no longer line up.
Dislocation
Epistaxis
Color
The lower jaw bone is known as the __________?
Mandible
With a tooth dislocation, if a designated saline tooth container is not available, the tooth can be temporarily stored in __________ to keep the tooth alive for reimplantation.
Milk
If a bone never heals, the fracture is referred to as a ___________.
Nonunion fracture
What is the medical terminology for cauliflower ear?
hematoma auris
A ____________ abrasion can occur when an athlete wears contacts for too long. Diagnosis involves a fluorescein dye and light test.
Cornea(l)
The most commonly injured facial bone in athletics is/are the ________________.
Nasal
The _________ is responsible for focusing the entering light rays on the retina.
Lens
A fracture that travels across and perpendicular to the bone is known as a ________________ fracture
Transverse
An athlete presents in the training room with a significant eye injury. You notice a lack of roundness to the eye, and the inner fluids of the eye are leaking out. The athlete has sustained a __________________.
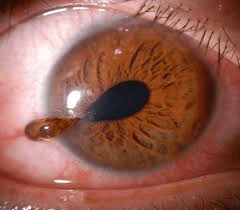
Ruptured Globe
An athlete was poked in the eye during a game. They have no pain or no visual impairments but their eye looks like the image below. What injury have they sustained?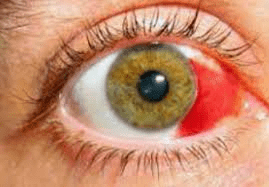
subconjunctival hemorrhage
The "socket" that the eye sits in is known as the ___________________ (two words)
Orbital foramen
The "traditional" eye exam chart, typically performed at sports physicals is called the _____________ chart.
Snellen
A complete tear or rupture of a ligament would be a grade ______ sprain.
3
An athlete that was elbowed in the nose is being evaluated for a nasal injury. The AT notices a "shift" of their nose. This shift is known as a _____________.
Deviated septum
A blow to the eye can force the eyeball backward into the socket. The thin bones beneath the eye absorb the sudden increase in pressure and can fracture. This is known as a
Blowout fracture
A violent blow to the chin can cause a dislocation of the jaw. The appropriate term for a jaw dislocation is a __________________________ dislocation.
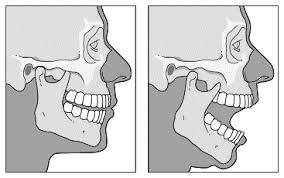
Temporomandibular
