More than an insulin maker
A _________ profile tests for all varieties of this disease (A through E).
What is a Hepatitis profile?
When assessing the gallbladder for stones, this very common test can be performed at the bedside and requires no prep (per se). It is preferred that the patient be NPO from midnight the night before, but the test can be performed without this stipulation. *This test can also be performed on pregnant women.
What is a gallbladder ultrasound?
For a quick review, please visit this site: https://nurseslabs.com/cholecystitis/
This pancreatic disease has an insidious onset, often with the first symptom being weight loss or painless jaundice.
What is pancreatic cancer?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 46 p. 1495

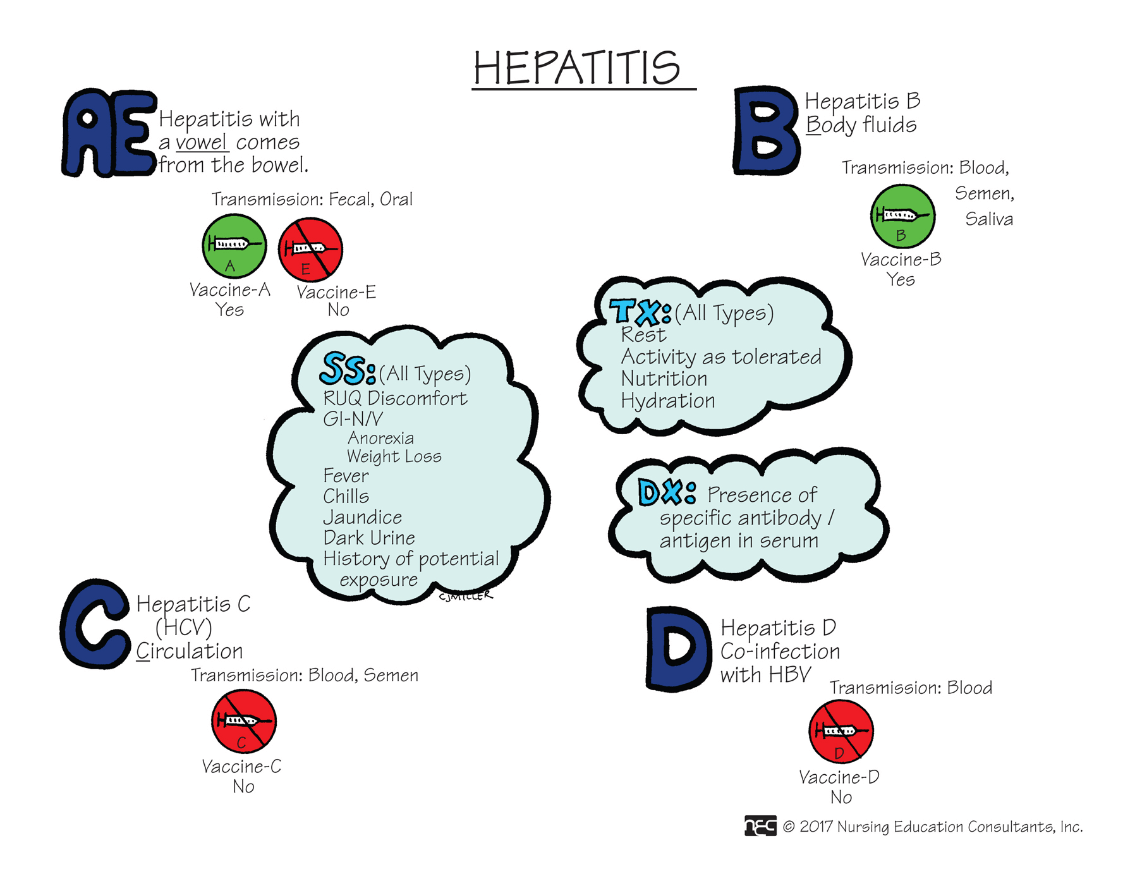
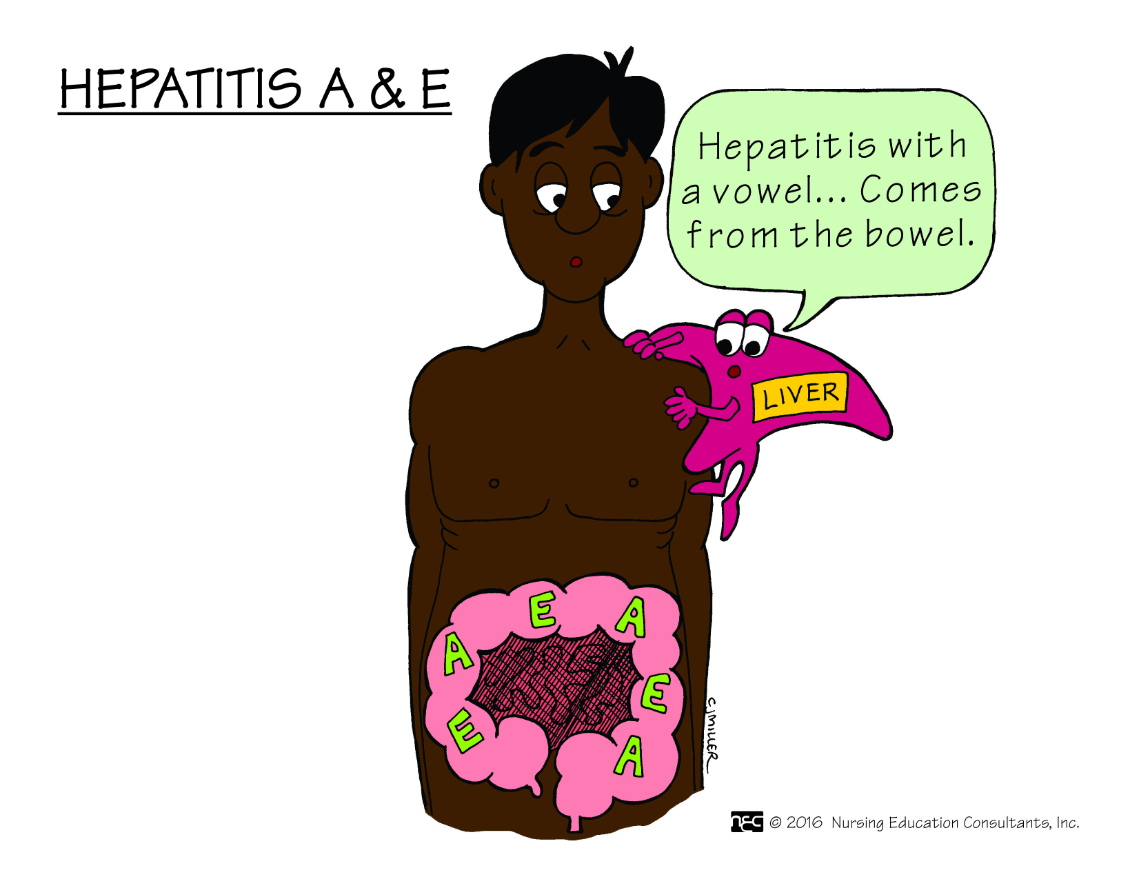
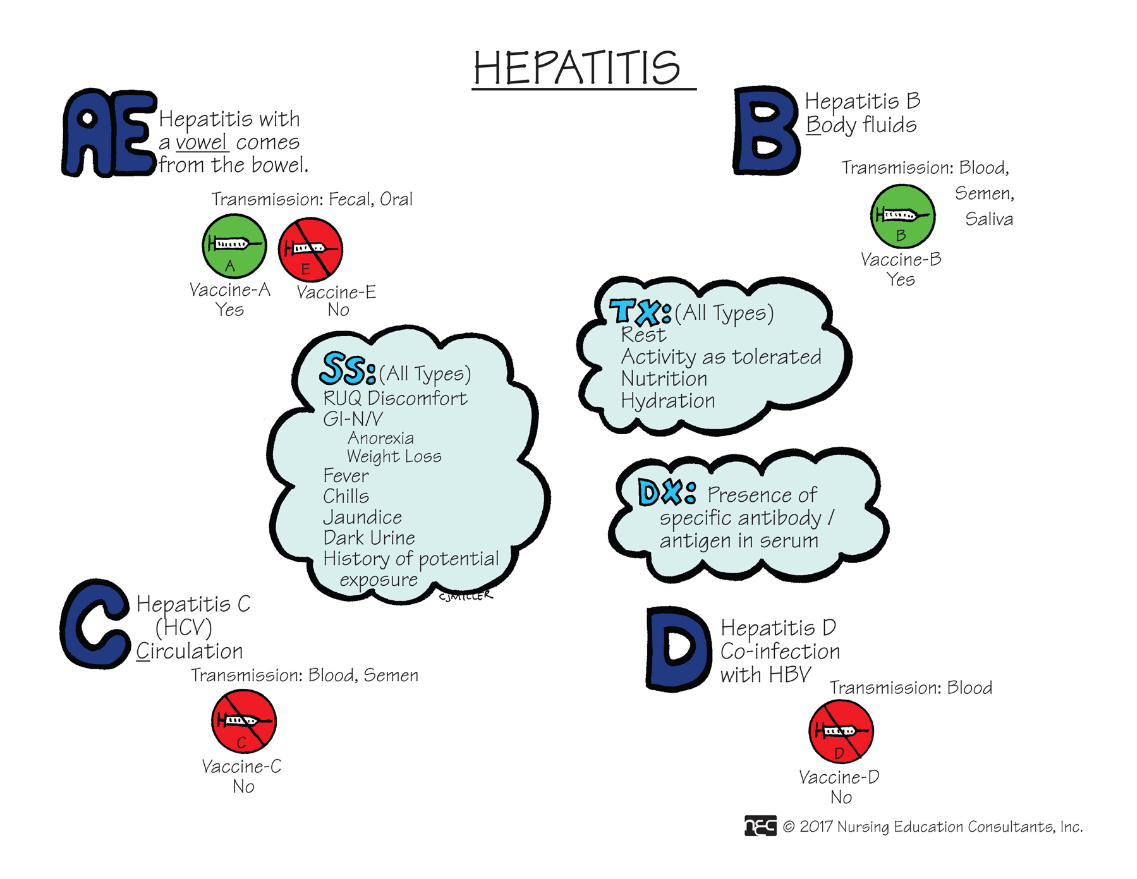
This form of this disease is transmitted through the fecal-oral route.
What is Hepatitis A?
Morphine is not used for gallbladder pain because it causes spasms in this sphincter.
What is the Sphincter of Oddi?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 46 p. 1489
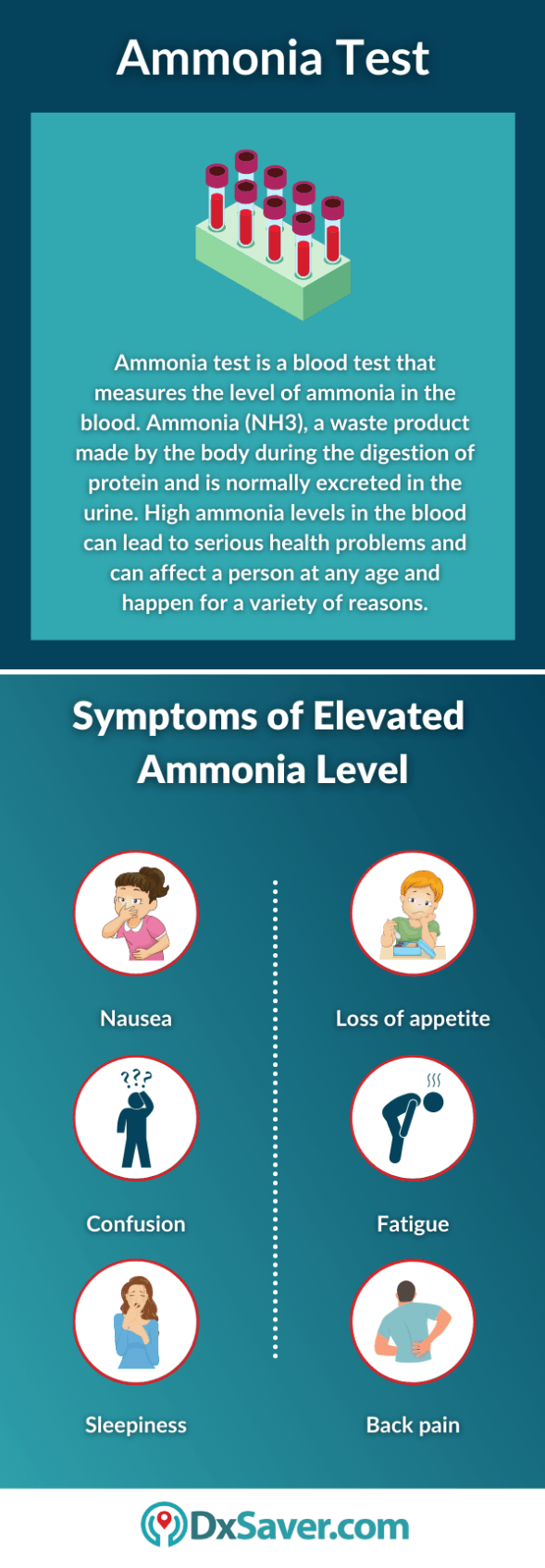
Patients may present with confusion if their ammonia level is higher than ___________.
What is 80 mcg/dL?
The normal range for ammonia is 10-80 mcg/dL
List three critical nursing interventions for the patient undergoing a needle liver biopsy.
1.
2.
3.
What are:
1. Check coagulation studies and PLT count and ensure normalcy prior to procedure.
2. Patient to lie on (R) side to put pressure on RUQ x at least (2) hours following the procedure to help lessen the chance of bleeding.
3. Assess respiratory effort post-procedure to make sure a lung wasn't accidentally punctured.
4. Informed consent signed before the procedure.
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 46 pp. 1472-73
The most common environmental risk factor for pancreatic cancer is ___________.
What is cigarette smoking?
Other risk factors include:
exposure to carcinogens, cirrhosis, chronic pancreatitis, obesity, diets high in red meat & pork
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 46 p. 1494
Multiple stones can inflame this organ which holds bile.
The drainage bag for the __________ if one is used, is placed lower than the level of the common bile duct to facilitate gravity drainage of bile.
What is a T-tube?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 46 p. 1491
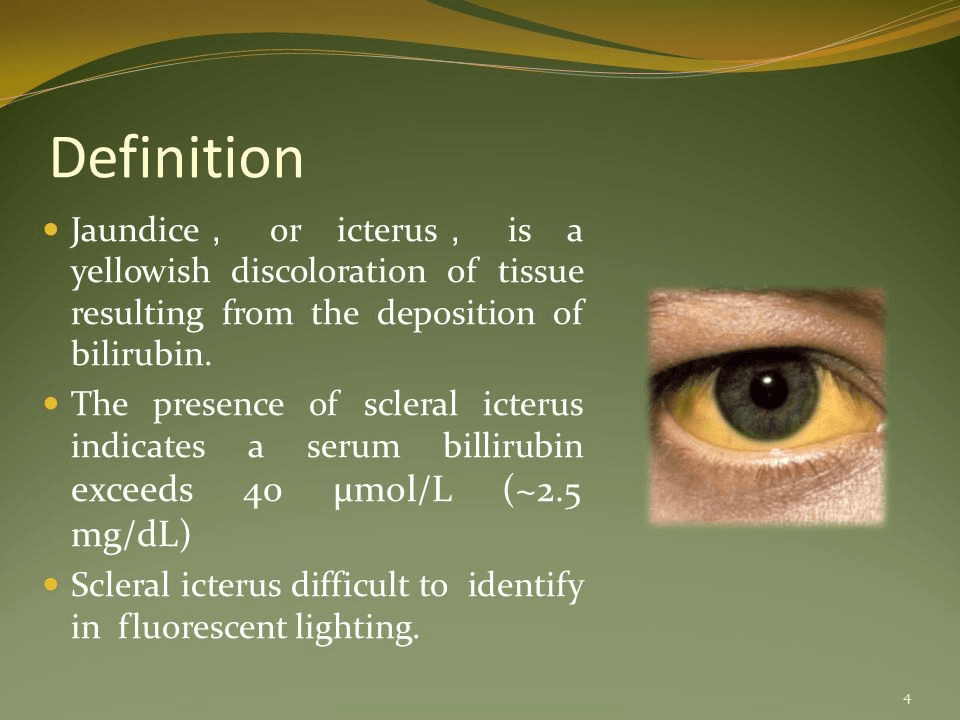
The patient will display jaundice when the serum bilirubin is at ________________.
What is 2.5 mg/dL?
Through the insertion of a flexible duodenoscope, this test is useful in visualizing the biliary system AND the pancreatic duct. Dye is injected directly into the common bile duct and the pancreatic duct. The patient should be NPO x 8 hours prior to this test, and should have an informed consent signed prior to the procedure.
What is endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)?
Pain can follow this procedure as injecting the pancreatic duct can precipitate pancreatitis. This test allows for visualization of the pancreas, where it is hidden in other tests (CT, RUQ U/S).
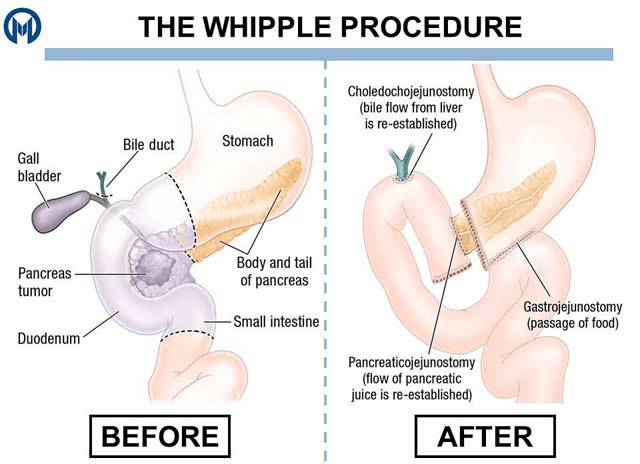
This is the name of the extremely complex surgery performed for patients with pancreatic CA. These patients will be admitted to ICU following this surgery.
What is the Whipple procedure?
It involves resection of the antrum of the stomach, the gallbladder, the duodenum, and varying amounts of the pancreas. Anastomoses are then constructed between the stomach, common bile & pancreatic ducts, and the jejunum.
What is Hepatitis B?
Your patient with cirrhosis should have a diet that is ___________, high in __________ and roughly ___________ calories per day.
What is:
well-balanced
high in protein
2500-3000 calories per day
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 46 p. 1478
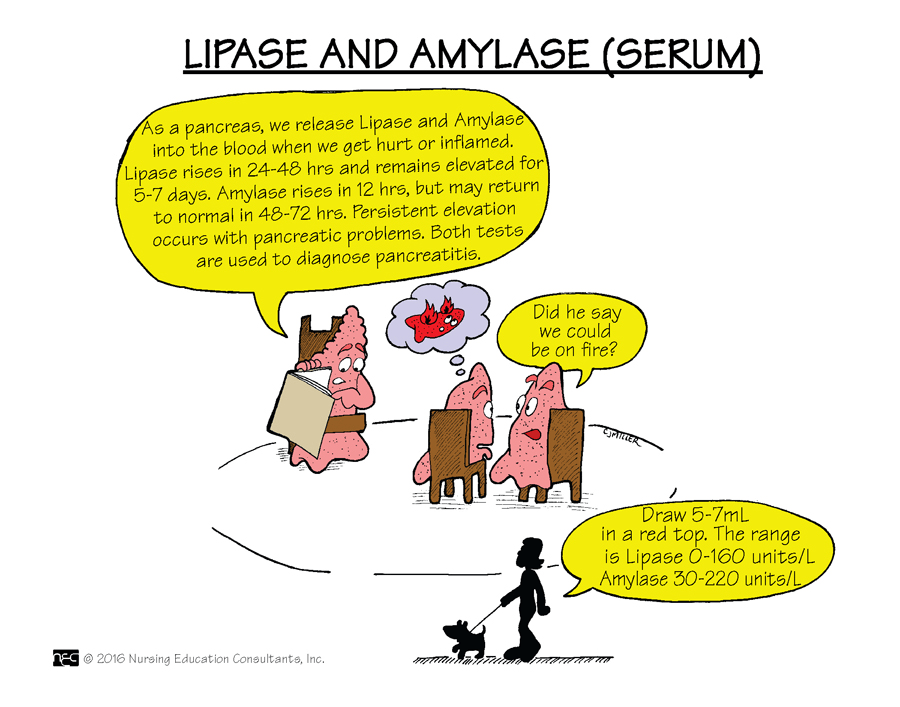
While the amylase and the lipase will be drawn when assessing a patient with symptoms of acute pancreatitis, the _________ level is a little more sensitive because it appears after there has been actual damage to the pancreas, and it remains elevated longer.
What is lipase? Lipase roses in 24-48 hours, but remains higher longer and is more indicative of pancreatic injury.
Lipase: 10-140 units/L Amylase 30-220 units/L
This imaging procedure that shows how well the liver, bile duct, and gallbladder are functioning. It can help diagnose certain conditions, such as cholecystitis, biliary leak and biliary atresia.
This imaging procedure uses an injected chemical called a radioactive tracer (radiotracer) and a scanning camera to evaluate the gallbladder. The scan is performed in the department of nuclear medicine in radiology.
More specifically, this scan tracks the flow of bile from the liver to the small intestine (the biliary system).
What is a HIDA scan? (Hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid)
Great site to review for a HIDA scan overview:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/17099-hida-scan
List three reasons for pancreatitis:
1.
2.
3.
What are:
1. Alcoholism
2. Trauma
3. Infectious disease
4. Following an ERCP
5. Following surgery on the biliary tract, pancreas, stomach, or duodenum.
The surgery for cholelithiasis and cholecystitis is ________________.
What is a cholecystectomy (can be open or laparoscopic)?
This drug is for elevated ammonia levels, and may be given orally, via NG tube, or via enema.
What is lactulose?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 46 Table 46.1 p. 1476
Your patient with liver damage may not be able to process protein, and may have a low total protein. You would know it was low if the total serum protein was less than ________.
What is 6.4 g/dL ?
The range for total protein is 6.4-8.3 g/dL.
Some causes of low protein:
Liver damage (insufficiency), malnutrition, lack of diet rich in protein, renal damage, malabsorption problems
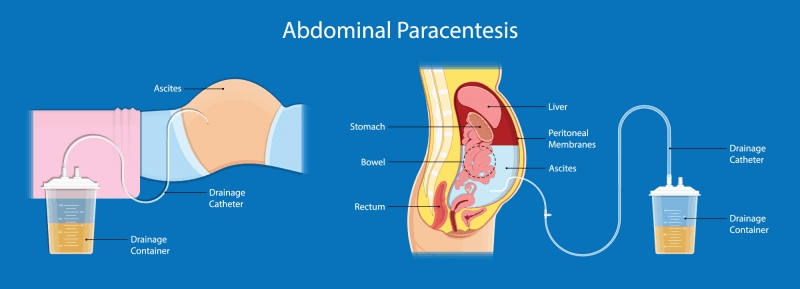
This is a procedure that pulls fluid off of the abdomen distended with ascites. This procedure can be done at bedside, and should have an informed consent obtained prior to the procedure. *The nurse should alert the practitioner when approaching 1 liter removed; at 2 liters, the patient should rest to avoid an unsafe alteration in I & O or BP.
What is a paracentesis?
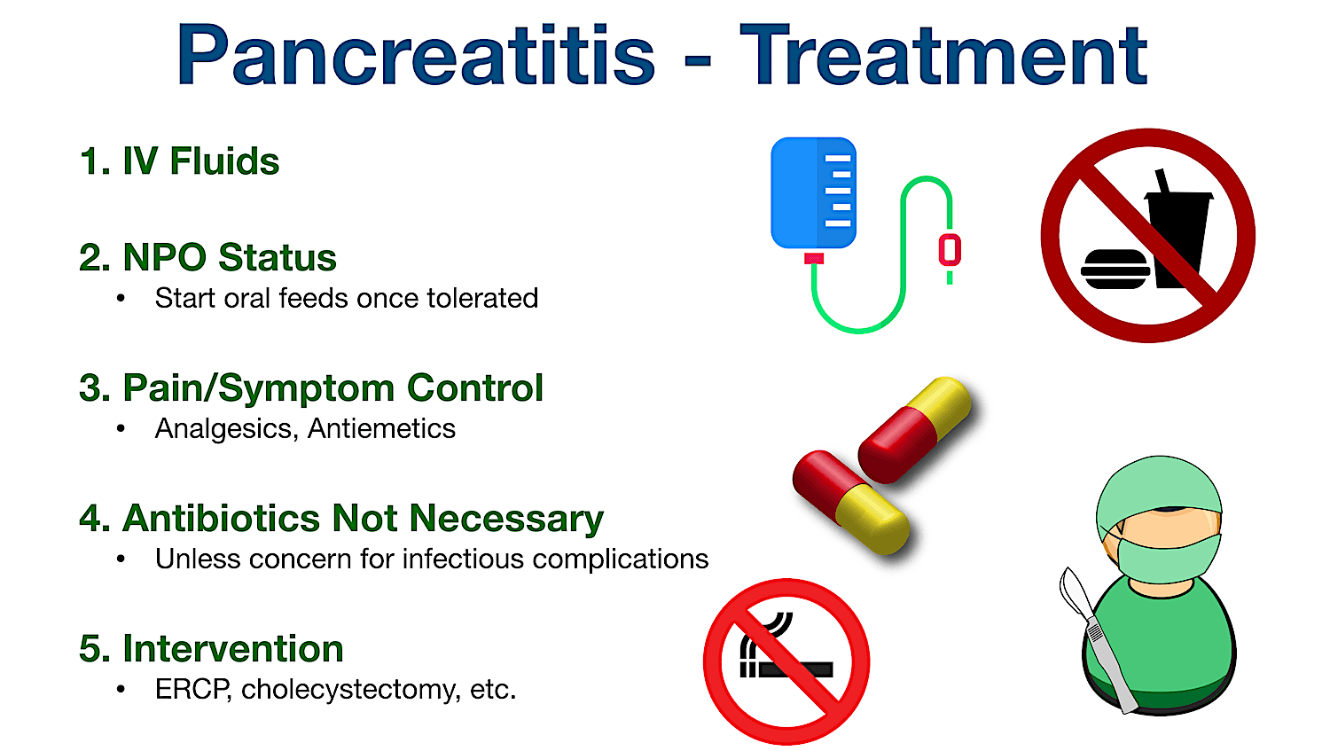
The two most important nursing interventions for pancreatitis are:
1. Pain control
2. Maintain strict NPO status
What are pain control and maintaining strict NPO status?
Retained stones can occur following a cholecystectomy and can cause _______________.
What is pancreatitis?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 46 p. 1492
For the patient with ascites, this diuretic may be administered. Be careful- it may result in hyperkalemia.
What is spironolactone?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 46 Table 46.1