Three things have to happen to air before it gets to your lungs. What are these 3 things?
1._____________
2._____________
3._____________
What are
1. filtering
2. warming
3. moistening
Did you know? The mucous membranes of the nose secrete about 1 liter of moisture every day, and the receptors for the sense of smell are located there.
Caused by fluid, mucus, or pus in the small airways and alveoli, this sound sounds like bubbling. It is a brief sound, not continuous, and more common on inspiration. *Mrs. Johnson placed a link on D2L for you to listen to this sound :)
What are crackles (rales)?
*Watch the video on D2L for breath sounds, as instructed on your time management sheet.
*Review Table 49.1 on p. 1625
Watch the video below, beginning around the 1;55 mark:
This type of test can literally be performed on any type of body cell. When performed on pleural fluid, it is specifically looking for cancer or other abnormal cells. What type of test/ study is this?
What is cytology?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 49 p. 1627
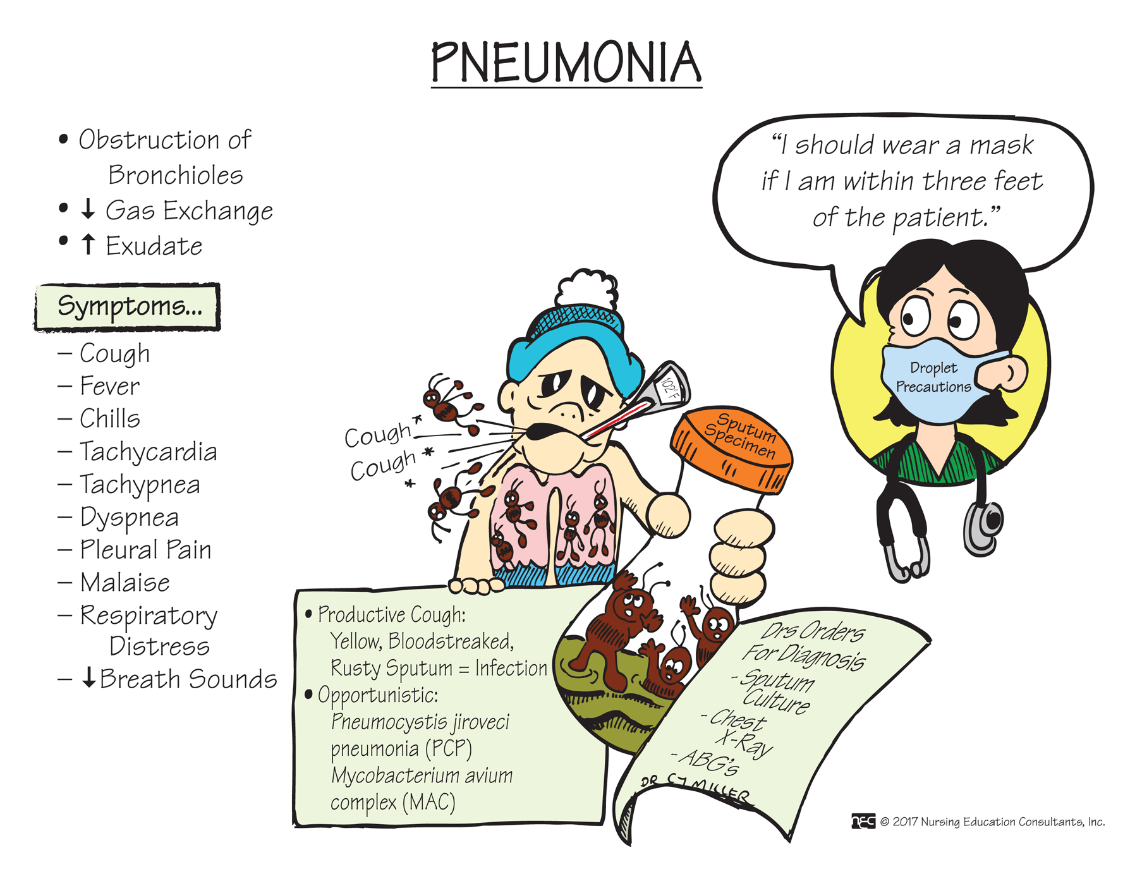
This respiratory disorder can be bacterial, viral, fungal, or from chemical irritation. Typical signs & symptoms include fever, chills, and a painful, productive cough. This disorder is _____________.
What is pneumonia?
*Get those blood cultures STAT if you think you're going to start antibiotics!
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 49 pp. 1650-51
This O2 delivery appliance is easy to apply and usually well-tolerated. It can deliver O2 at a rate from 1-6 Liters per minute or 24-44% FiO2. What appliance is this?
What is a nasal cannula?
*Reference ATI SM O2 therapy
*Reference ATI M/S book Ch. 16
Review from FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 14, Table 14.1 p. 343
The trachea lies __________ to the esophagus.
What is anterior?
These sounds are caused by air moving through narrowed or constricted airways. Your book discusses two distinct types. As a nurse, you should recognize these sounds when you hear them, and search for the cause. *Mrs. Johnson placed a link on D2L for you to listen to this sound :)
What is wheezing?
*Watch the video on D2L for breath sounds, as instructed on your time management sheet.
*Review Table 49.1 on p. 1625
On the video below, begin at the :43 second mark to hear wheezing.
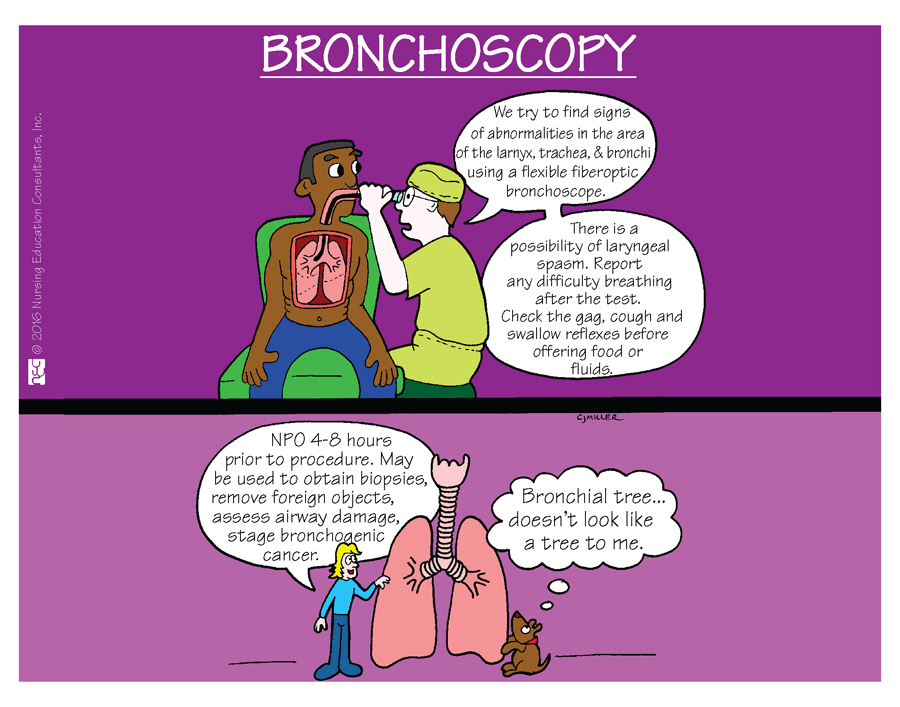
Diagnostics from this type of test are investigating for abnormalities; taking a tissue biopsy; and/or taking a collection of secretions or washings to look for cell or bacteriologic contamination (or for cytology). What type of test is this?
What is a bronchoscopy?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 49 p. 1627
Collapse of the alveoli results in this condition, which often results in hypoventilation.
What is atelectasis?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 49 p. 1657
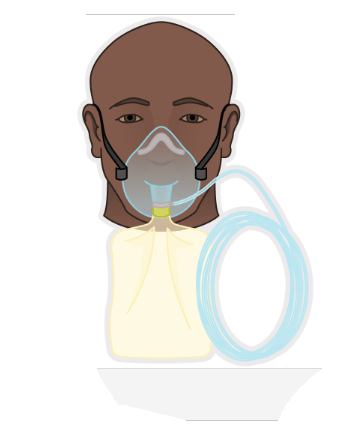
This O2 appliance delivers the highest O2 concentration possible outside of tracheal intubation. The flow rate is from 10-15 liters/minute, for an FiO2 of 80-95%. What is it?
What is a non-rebreather mask?
Reference FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 14 p. 343 Table 14.1
Reference ATI Ch. 16 * use ATI's liters per minute numbers
The centermost area of the thoracic cavity is called the _________.
What is mediastinum?
The mediastinum is where the heart and great vessels are in the chest.
This is the term for abnormal, superimposed breath sounds. You are auscultating the patient to make sure you don't hear these.
What are adventitious breath sounds?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 49 p. 1625
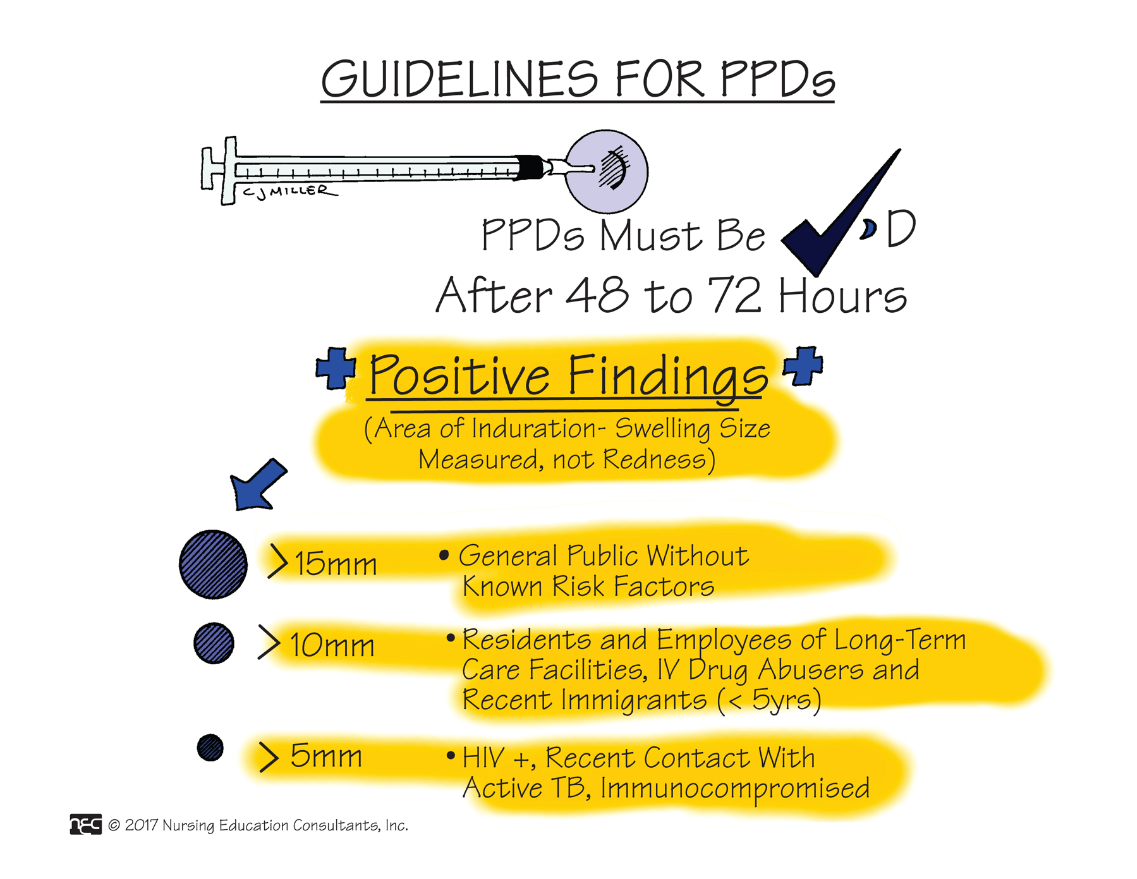
Diagnostic testing for TB includes a PPD skin test. This test is considered positive if _________, not redness, is present. This is measured with a ruler in cm. > 15 mm is considered + or > 10 mm if the person recently immigrated from a country with a dense population of TB patients.
What is induration?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 49 p. 1646
If there is no induration, it is charted "0 mm induration".
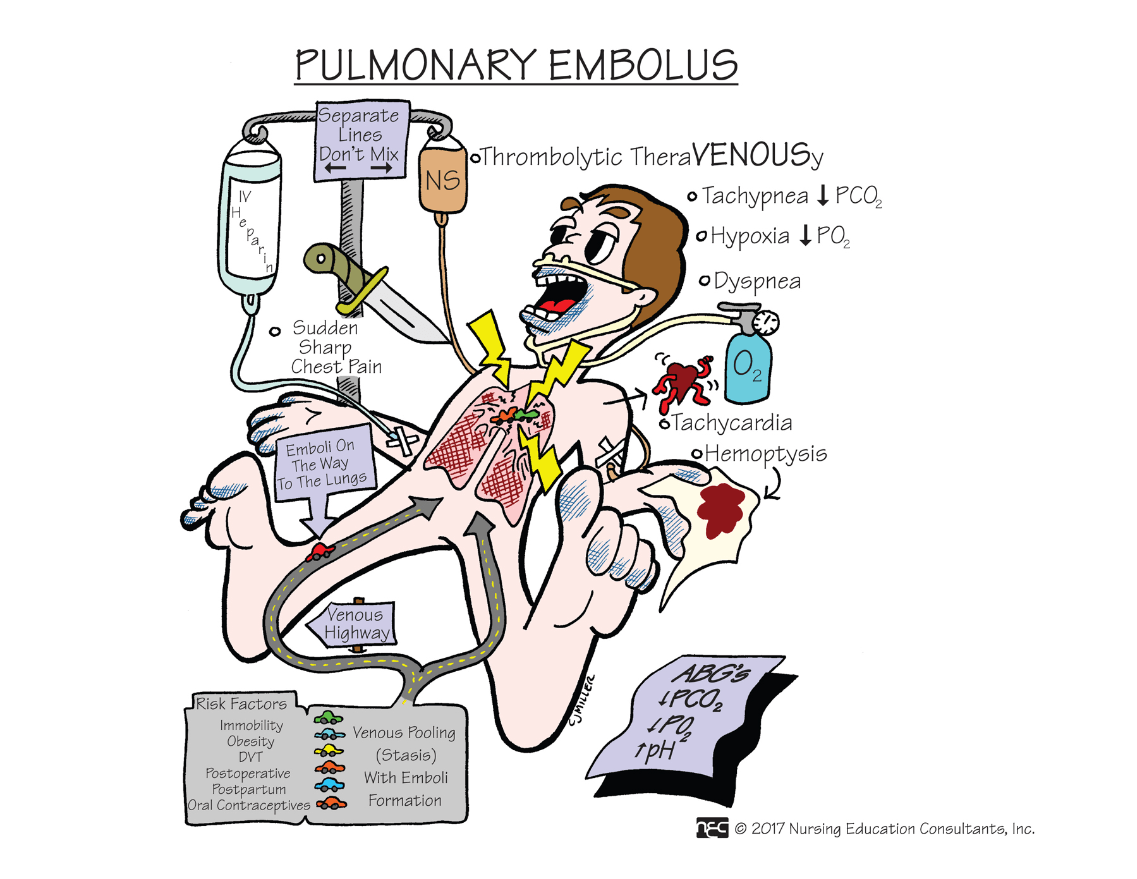
This condition is the result of a foreign body (blood clot, fat, air, tumor tissue, or amniotic fluid) becoming trapped in the pulmonary artery or it's branches blocking blood supply to lung tissue with subsequent collapse. High risk patients are those who have recently given birth or recently had surgical procedures.
What is a Pulmonary Embolus?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 49 p. 1663
This O2 appliance is also easy to apply and can be more comfortable than a nasal cannula. The flow rate for it is from 5-8 liters per minute, for an FiO2 of 40-60%. What is this appliance?
What is a simple face mask?
Reference: ATI SM O2 therapy
Reference: FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 14 p. 343 Table 14.1
Inhaled air contains about 21% oxygen. This oxygen crosses into the blood cells and CO2 comes out through a process known as __________.
What is diffusion?
This sound is a constant pitch with a continuous crowing sound. It is caused by a partially obstructed airway. Airways can be obstructed due to trauma, swelling or foreign bodies.
What is stridor?
Review from Ch. 18 F&E, stridor was discussed as a consequence of hypocalcemia.
In the video below, begin around the 3:30 mark:
This type of radiologic test is more sensitive than an x-ray, typically showing the smaller layers of pulmonary tissue. Dye is sometimes injected in order to perform this test, so you must check the patient's allergies as well as their creatinine level. What is this test?
What is a CT scan? *Pulmonary angiogram also accepted
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 49 p. 1626
A severe, unrelenting, life-threatening type of this attack that fails to respond to usual treatments placing patients at risk for respiratory failure is called __________ _________.
What is status asthmaticus?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 49 p. 1672
A nurse is caring for a patient who has a new prescription for O2 therapy of 4 L/min using a Nasal Cannula. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
a. Provide humidification.
b. Remove the cannula during meal times.
c. Establish an alternate means of communication.
d. Lubricate the nares with 0.9% sodium chloride.
a. Provide humidification.
Humidification should be provided for O2 flowrates of 3L/min or greater.
The air in the lungs is at atmospheric pressure and the the pressure of the pleural cavity is lower than atmospheric pressure. This creates _________ pressure to keep the lungs inflated.
Daily double!: An agent that decreases tension between two surfaces found in the lung and produced by the Alveolar-II cells of the lung is called ____________.
What is negative pressure?
Daily double! Answer:
What is surfactant?
This is a harsh, dry, creaking, grating, low-pitched sound heard during both inspiration and expiration. It will be best auscultated over the anterior chest. *Mrs. Johnson placed a link on your D2L page for you to listen to this sound.
What is a pleural friction rub?
This sound is created by inflammation. *Ask the patient to hold their breath when you auscultate. If you still hear the sound, it is a pericardial friction rub and not a pleural friction rub.
*Watch the video on D2L for breath sounds, as instructed on your time management sheet.
*Review Table 49.1 on p. 1625
**Listen to this video at the 7 minute mark:
This is the blood test performed when a Pulmonary Embolus is suspected.
What is a D-dimer?
The result will be elevated or high when a PE is present.
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 49 p. 1664
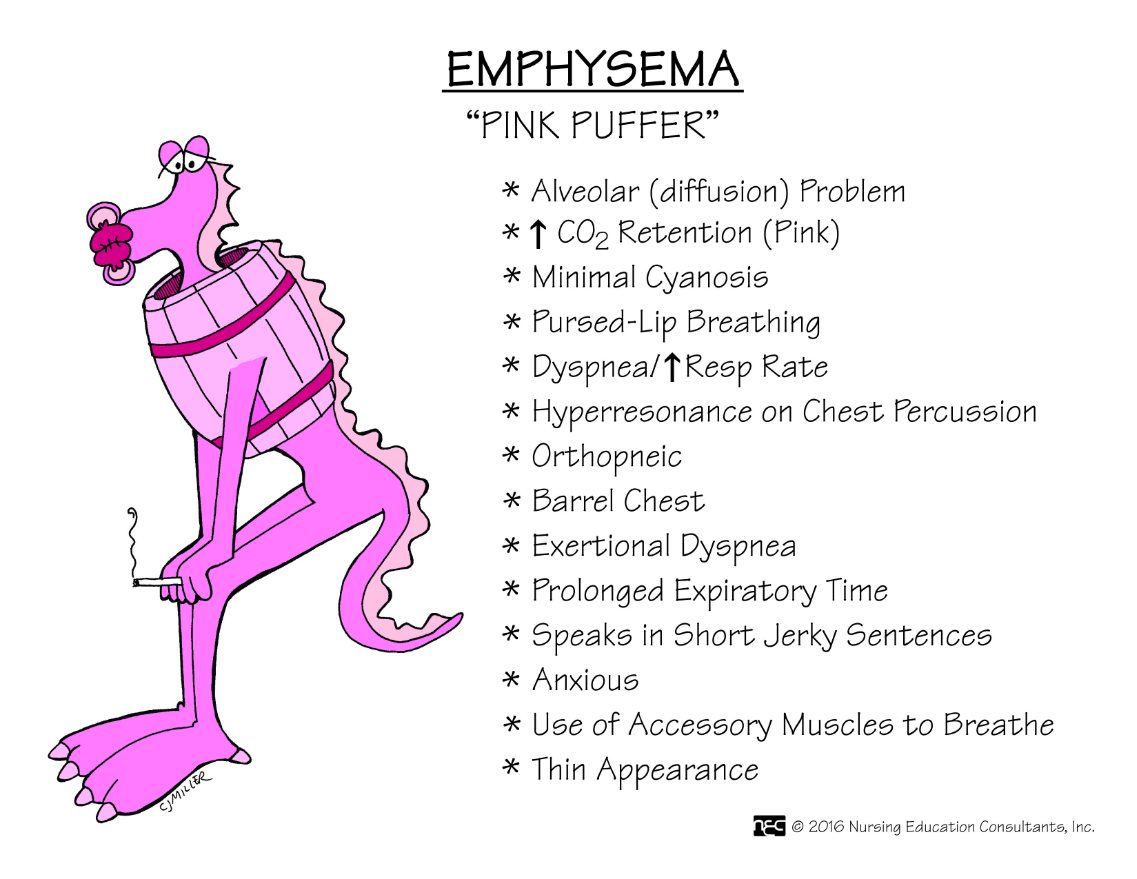
This disease is primarily an alveolar disease, with permanent enlargement of the alveoli distal to the terminal bronchioles. Chronic inflammation also accompanies this disorder, and most cases are caused by smoking.
What is emphysema?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 49 p. 1667
What is 15 seconds?
Reference: FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 14 p. 360