to elevate the meaning/drama of the words
The greatest composer of Renaissance Catholic music
Palestrina
England's most famous Early Baroque composer
Henry Purcell
Rembrandt's artistic brilliance shows mastery of _________ and shadow.
Light
The duplication of a phrase at two or more different pitch levels
Sequence
A melismatic passage in music has __________
multiple notes per syllable
Bach & Handel were very similar in _____ (multiple acceptable answers)
1) age
2) Both were influenced by Italian composers
Philosophy that systematized all intellectual & religious experience according to rigid rules of medieval logic
Scholasticism
The scale patterns of Gregorian Chants are referred to as:
Modes
English Composer who used the English language in settings of the litergy for the Anglican Church
Thomas Tallis
A new notation device that appeared in the Baroque and made a big difference in the composition and performance of music
Bar Lines
In the Renaissance, culture subscribed to this philosophy
Humanism
Music exists in ___________
time
A manner of writing in which a melodic line was supported by a very simple chordal accompaniment is called:
Monody
Famous Greek philosopher/mathematician who led the first investigation of music as a natural phenomena was ________________
Pythagoras
Thomas Morley
The two most famous composers to work at Notre Dame
Leonin & Perotin
This English composer was also known as an organist
Thomas Tallis
The Baroque Era is the "Age of __________"
Renaissance art was transformed due to the invention of:
Oil Paints
Three instruments which read music in the bass clef
trombone, timpani, double bass
What is a fugue?
An imitative contrapuntal form built on 1 or 2 recurring themes?
After Handel's success with _____________, he never wrote another Italian Opera again
Messiah
Double-reed instrument, forerunner of the oboe
Shawm
Characteristics of Gregorian Chant (multiple possible answers)
-Small, stepwise motions
-Lyric-driven (non-metered)
-Modal
-Neumes
-Latin
In the Renaissance, patronage of the arts began to shift from ___ to ___.
The church to the courts
Italian composer who had a great impact on Bach's compositional style
Antonio Vivaldi
The Renaissance brought stability and rationality channeled through the arts, but the Baroque era brought ____ and ____ through the arts.
Passion and emotions
A repeating bass pattern
Ground Bass
The name of the first scale degree (the most important!) of a major scale is called __________
Tonic
Expanded the Big Book of Organum to 3-4 voices
Perotin
Organum is based off ________ and ________
Hint: Intervals
4ths & 5ths
This establishment/organization dominated the history of Western Music for its first 1400 years.
The Catholic Church
The three musical forms included in the Renaissance
Mass, Motet, Madrigal
This many people attended Handel's first performance of Royal Fireworks
More than 10,000
Renaissance art was transformed due to the invention of:
Oil Paints
The Major key with Three Sharps is
A Major
What are two instruments keyed in B flat?
-Clarinet
-Trumpet
who devised the names of "do (ut), re, mi..." for singing the notes of the scale?
Guido of Arezza
The Key of G Minor has:
2 Flats (B flat & E flat)
He "softened" the dissonance by adding thirds and sixths to his organum
Machaut
The Renaissance brought ______and ______channeled through the arts
Stability and Rationality
Handel spent nearly 50 years writing this genre of music in England
Italian Opera
In the Baroque Era, the father of modern philosophy who said "I think, therefore I am."
Rene Descartes
No single feature of music... determines the effect of music more crucially than ____________
Duration and Accent
In a major key, the fifth scale degree (V) is called _______
Dominant
The Composer of the Magnus Liber Organi (The Great Book of Organum) was ________
Leonin
The Greeks' greatest contribution to music was ______
Music Theory
who was the famous Trovere who wrote the secular musical play, "Le Jeu de Robin et de Marion"?
Adam de la Halle
Thick Renaissance polyphony produced a problem, namely:
obscuring of the text
The Greatest Early Baroque Italian Composer was _______
Monteverdi
In Renaissance Art, MANNERISM refers to the idea that ________________
Artists show off their own style
The composite form of vocal music which has soloists, chorus, and orchestra, but NOT costumes, staging, and scenery is called ___________
Oratorio
In a diatonic triad, the bottom note is called the ___________, with the third and the fifth stacked on top
Root
Concerto Grosso
Why were gargoyles displayed on churches in the Gothic era?
To dispel evil
Cultural philosophy of the Medieval age; severe self-discipline and avoidance of all forms of indulgence, typically for religious reasons
Asceticism
The invention of linear perspective refers to ______________ in Renaissance paintings
Naturalism
Three hallmarks of the Baroque Period:
1) New musical forms
2) Development of Opera
3) The major-minor tonal system
Describe the Visual Art (Era, Artist, & 3 Characteristics)
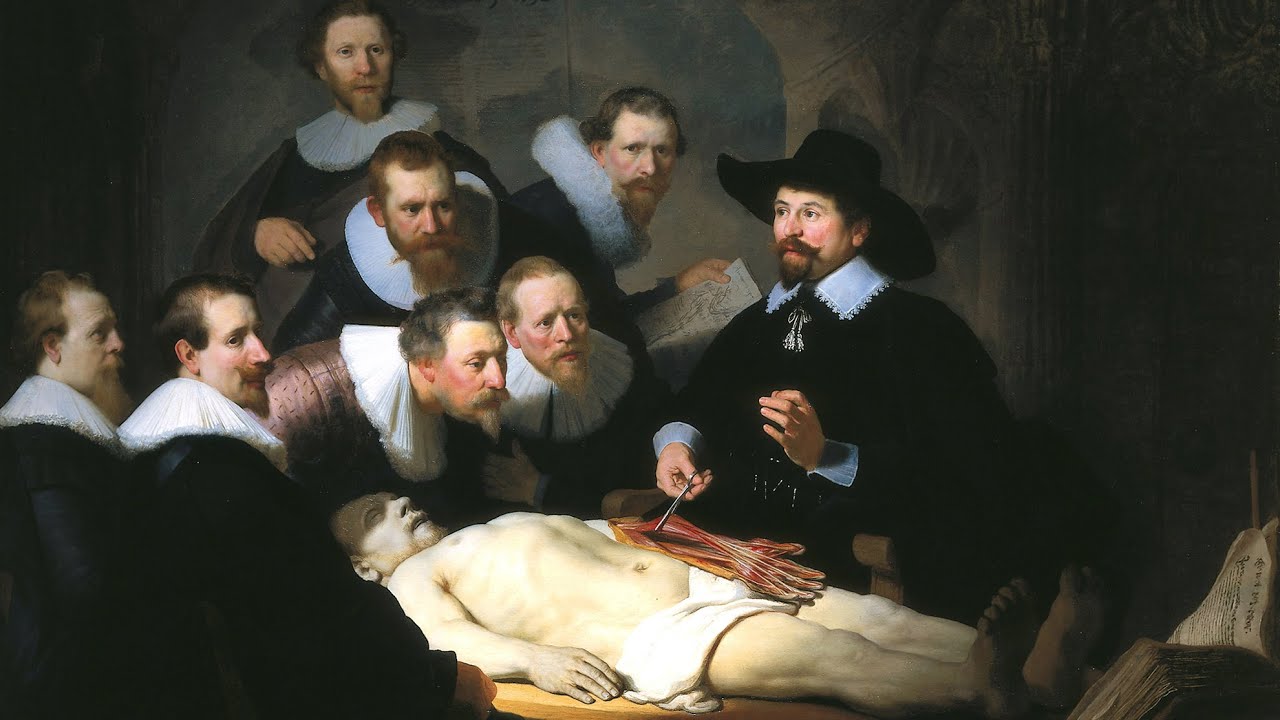
-Baroque
-Rembrandt
-1) Dramatic gestures, 2) vivid expressions, 3) polished finish
The Aeolian Mode is the same scales as the modern...
Natural Minor Scale
The fourth scale degree in a Major key
Sub-Dominant
The Baroque artist and founder of modern violin technique is
Coreli
1) Ionian
2) Dorian
3) Phrygian
4) Lydian
5)Mixolydian
6) Aeolian
7) Locrian