This mountain range runs along the western U.S. and Canada.
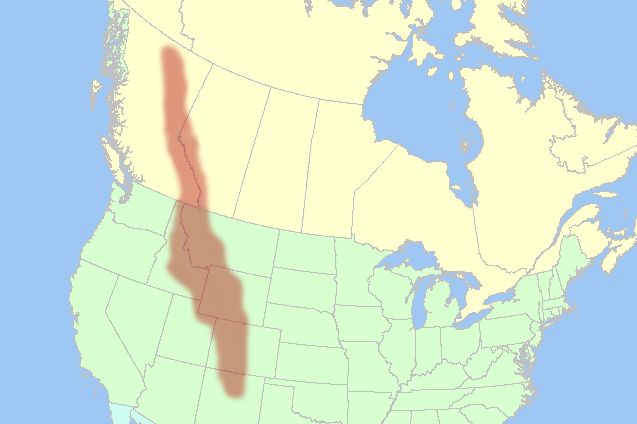
Rocky Mountains
This narrow landform connects North America and South America.
A) Peninsula
B) Strait
C) Isthmus of Panama
D) Archipelago
C: Isthmus of Panama

This is the longest mountain range in the world.
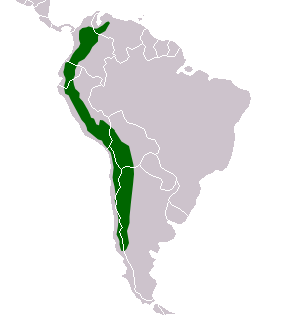
Andes Mountains
This ocean current helps keep Western Europe warmer than other places at similar latitudes.
A) Gulf of Mexico Current
B) California Current
C) North Atlantic Drift
D) Labrador Current
C) North Atlantic Drift
This geographic theme explains how people adapt to, depend on, and modify the environment.
A) Movement
B) Human–Environment Interaction
C) Region
D) Location
B) Human–Environment Interaction
This landform region contains the Mississippi River Basin.
A) Rocky Mountains
B) Canadian Shield
C) Great Plains
D) Appalachian Highlands
C: Great Plains
This man-made waterway increased world trade (Located in Central America)
Panama Canal

This river basin contains the world’s largest rainforest.
Amazon Basin
This fertile landform stretches across several nations and supports large-scale farming.
A) Iberian Plateau
B) Scandinavian Shield
C) Northern European Plain
D) Balkan Peninsula
C) Northern European Plain
This term describes the spread of ideas, culture, and traditions from one place to another.
A) Cultural Diffusion
B) Globalization
C) Nationalism
D) Isolationism
A) Cultural Diffusion
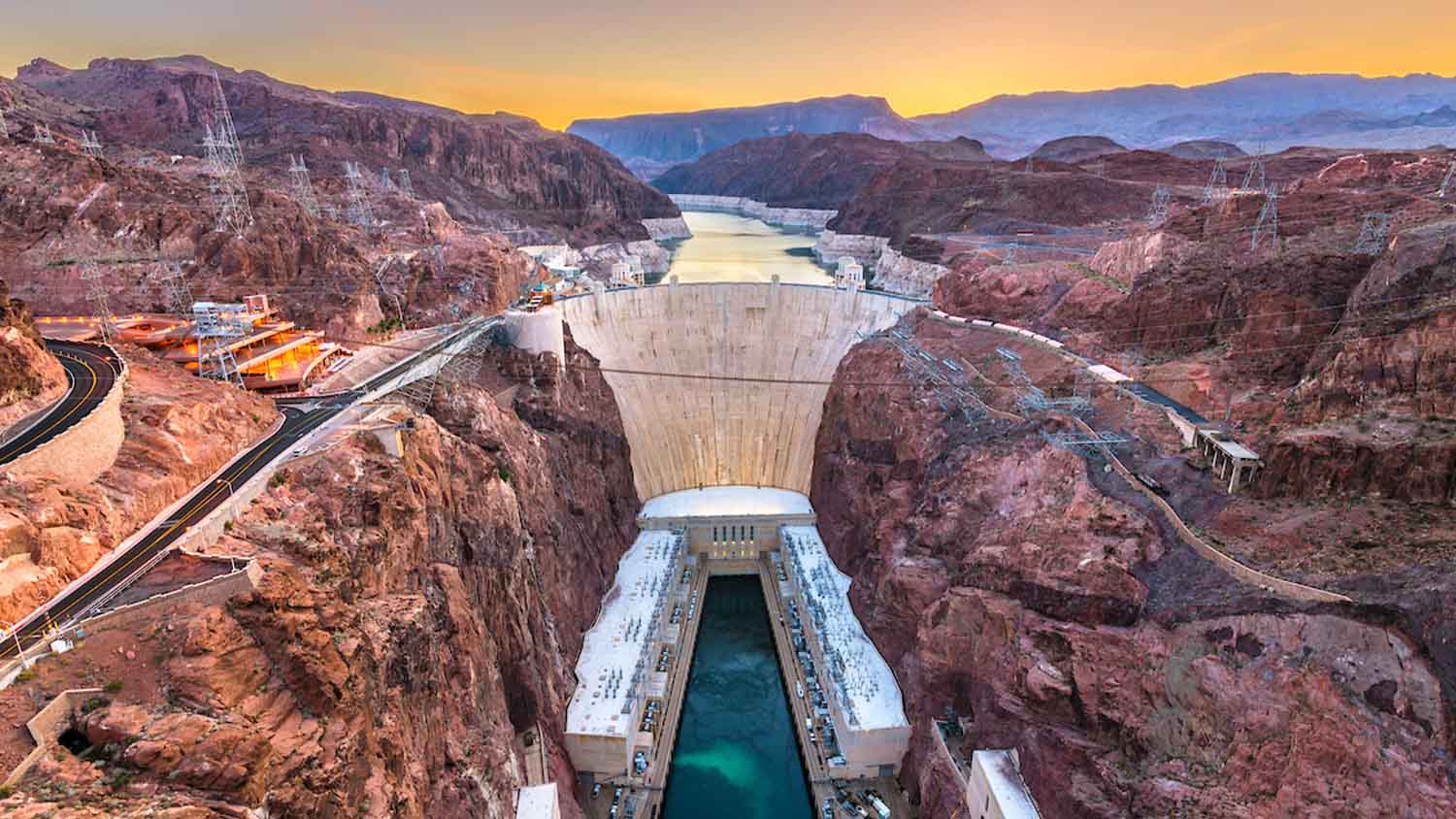
This man-made structure provides water and electricity along the Colorado River.
A) Panama Canal
B) Hoover Dam
C) Golden Gate Bridge
D) Erie Canal
B: Hoover Dam

These natural hazards form where tectonic plates meet.
Volcano and Earthquakes
Farming on mountain steps built by the Inca is called:
Terrance Farming
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/__opt__aboutcom__coeus__resources__content_migration__mnn__images__2015__12__terrace-tea-458bc43b2100494daf2413310fea36e7.jpg)
This structure became a symbol of political division during the Cold War.
A) Hadrian’s Wall
B) Great Wall of China
C) Iron Curtain Fence
D) Berlin Wall
D: Berlin Wall
Which factor is most likely to attract people to coastal cities?
A) Extreme climates
B) Access to trade and transportation
C) Limited economic opportunities
D) High elevation landforms
B) Access to trade and transportation
This environmental problem occurs when cities expand outward into surrounding areas.
A) Desertification
B) Deforestation
C) Urban Sprawl
D) Coastal Erosion
C: Urban Sprawl
This major industry supports many island economies.
Tourism
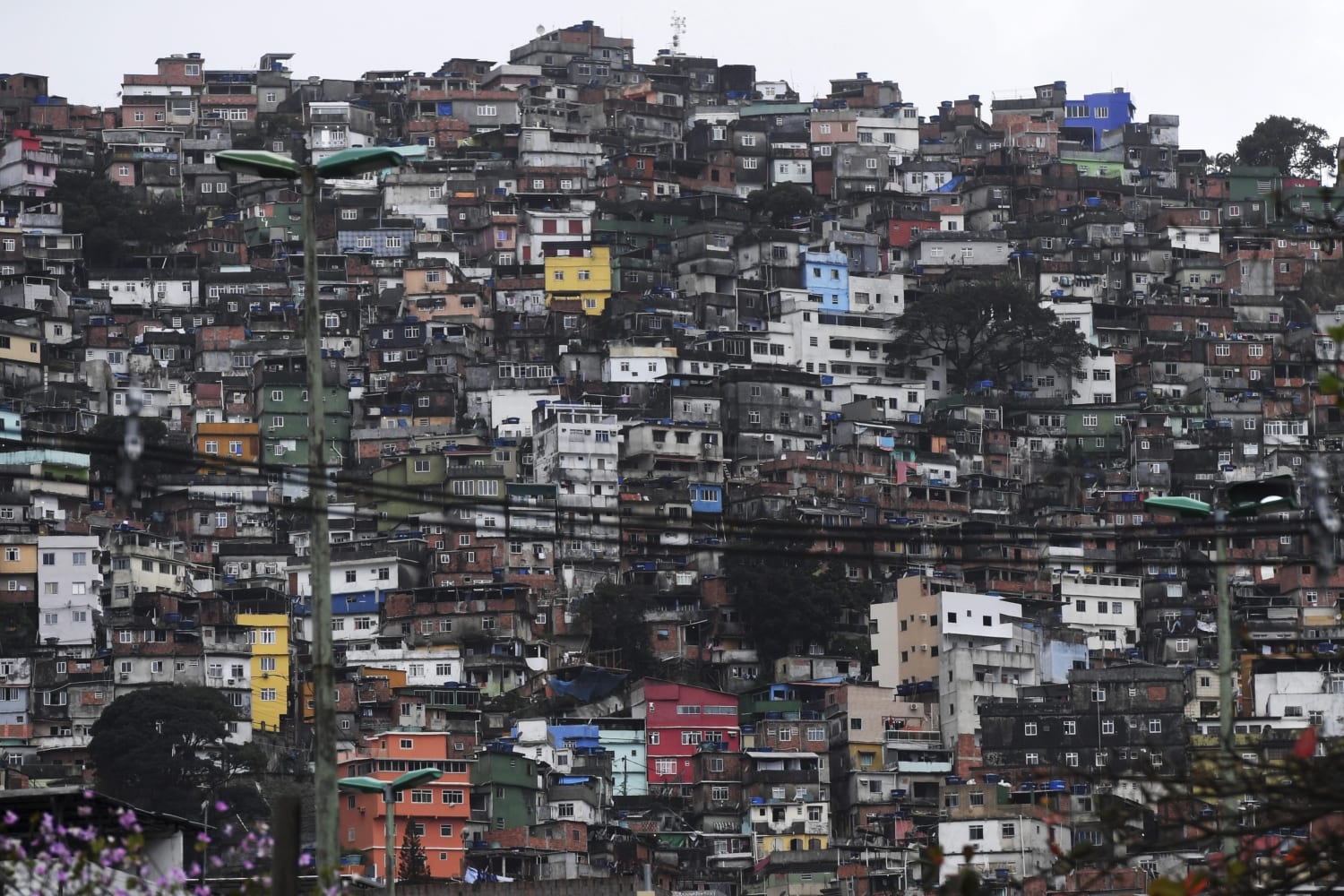
Informal, self-built communities in Brazil that developed as a result of rapid urbanization and rural-to-urban migration are called:
A) Barrios
B) Villas Miseria
C) Colonias
D) Favelas
Favelas

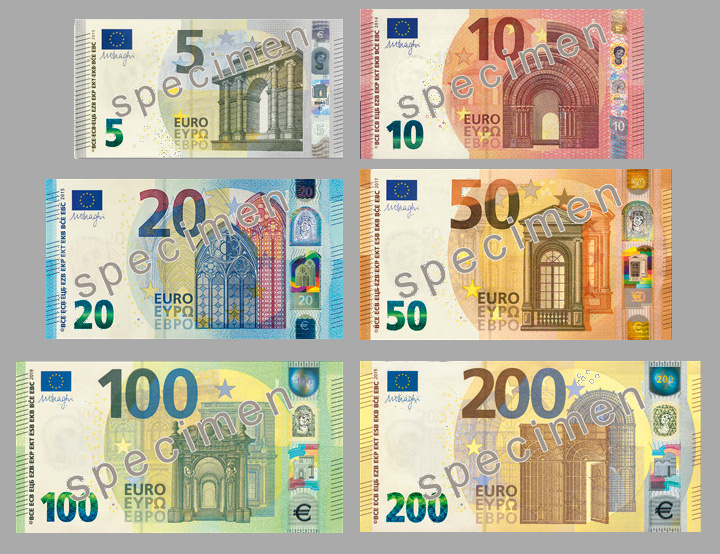
Many European countries use this common currency.
Euro

A country whose economy relies mainly on farming, mining, and raw materials is primarily in which sector?
A) Primary Sector
B) Secondary Sector
C) Tertiary Sector
D) Quaternary Sector
A) Primary Sector
This agreement increased trade among the U.S., Mexico, and Canada.
NAFTA
Cutting down forests faster than they regrow is called:
Deforestation / Unsustainable forestry
The Pampas grasslands of Argentina and Uruguay primarily support which major industry?
A) Mining
B) Commercial Cattle Ranching and Agriculture
C) Oil Production
D) Commercial Fishing
B) Commercial Cattle Ranching and Agriculture
Western Europe’s dominant economic sector is:
A) Primary Sector (Farming, Mining, Logging)
B) Secondary Sector (Manufacturing & Industry)
C) Quaternary Sector (Research & Technology)
D) Tertiary / Service Sector
D) Tertiary / Service Sector
A large city and its surrounding suburbs and connected urban areas are called a:
A) Nation-State
B) Megalopolis
C) Province
D) Metropolitan Island
B) Megalopolis
