What does it mean for a patient to be complete?
What is dilated to 10cm?
Best from of nutrition for an infant?
What is Breastfeeding?
A patient comes in at 24 weeks gestation 4cm dilated and consistent contractions
Cumulative blood loss of greater than or equal to 1000 mL or blood loss accompanied by signs or symptoms of hypovolemia within 24 hours after the birth process
What is a PPH?
definition according to ACOG 2017
Synthetic form of endogenous oxytocin
What is Pitocin?
A drop in FHR with a contraction? Cause?
Due to head compression of the fetus
In the fetus, an unossified space, or "soft spot", consisting of a strong band of connective tissue lying between the cranial bones of the skull
What is a fontanel?
Persistent high blood pressure greater than 140/90mmHg that develops during pregnancy or the postpartum period. Associated with proteinuria, kidney or lover involvement and puts a patient as risk for seizures
The practice where a baby is dried and laid directly on the mother's bare chest after birth?

What is Skin-to-Skin?
Given IM to infant to stimulate clotting factors by the liver
What is vitamin K injection?
Condition that happens when one or both of an infants shoulders get stuck during vaginal delivery
What is Shoulder Dystocia?
Treatment for Hyperbilirubinemia
What is Phototherapy?
More than 5 contractions in 10 minutes averaged over a 30 minute Fetal Heart Rate Strip, with or without changes in the FHR pattern
What is Tachysystole?
A term used to describe the uterine fundus when it is not firmly contracted after the birth of the baby and in the early post partum period?
What is a boggy uterus?
Given IM at 28 weeks gestation and after delivery to a mother with a negative blood type?
What is Rhogam?
The two layers of the membrane surrounding the developing fetus
What are the Chorion and the Amnion?
Chorion: the layer closest to the intrauterine wall that gives rise to the placenta and continues as the outer membrane surrounding the amnion Amnion: the inner of the two membranes that form the sac containing the fetus and the amniotic fluid
Infants placed on hypoglycemia protocol
What is LGA, SGA, late preterm and infant born to GDM or diabetic mother?
Occurs when the umbilical cord exits the cervical opening before the fetal presenting part
What is an Umbilical Cord Prolapse?
4 T's of PPH
- Tone: Uterine atony
- Trauma: Genital tract trauma
- Tissue: Retained products of conception
- Thrombin: Coagulopathy
Given IM to mom to stimulate fetal lung maturity
What is Betametasone?
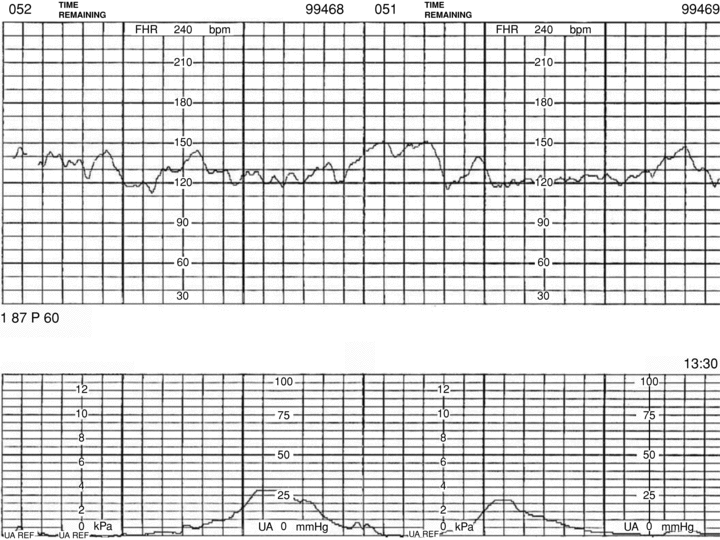
What is a category 1 FHR tracing?
Baseline rate: 110 to 160 bpm
Moderate baseline FHR variability
No late or variable decelerations
Early decelerations may be present or absent
Accelerations may be present or absent
Baby's red blood cells have the mother's antibodies attached to them, putting them at high risk of developing moderate to severe jaundice after birth
What is a coombs positive newborn?
On Palpation using Leopolds manuvers the Nurse feels the hard vertex in the fundus and can perform ballotment of the fetal head independently of the fetal body. The fetal heart tones are auscultated above the umbilicus
What is Breech?
The nurse is assessing a woman who gave birth to a 3260g full term female newborn via normal vaginal delivery 6 hours ago. Where would the nurse expect to palpate the client's fundus?
What is A?
The fundus should be located at or slightly above the level of the umbilicus during the first few hours after birth. On the day of birth, uterus descends from the level of the umbilicus in the first few hours after delivery to the level of 1 fingerbreadth (1cm) at 24 hours postpartum. It continues to descend at a rate of 1 cm per day and is typically not palpable by postpartum day 10, having descended within the true pelvis.
What medication used to control PPH is contraindicated in a patient with a h/o asthma?
What is Hemabate?