
A) longer and stronger
B) longer and weaker
C) shorter and stronger
D) shorter and weaker
C; shorter and stronger
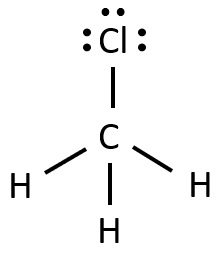
Draw CH3Cl. What are its angles? Be specific!
< 109.5°
Which atoms can have an expanded octet?
S and P
Which atom is more electronegative:
Sn or As
As
How does lattice energy change with an increase in charge on the ions? i.e. does it increase or decrease and why?
Lattice energy increases as charge on the ions increases due to Coulomb's Law. *extra info: Charge effects lattice energy more than size does
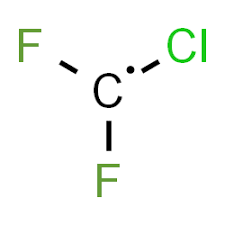
Draw CClF2. What kind of molecule is this?
Free Radical!
What are the oxidation numbers of each of the atoms in ClO3-1?
Cl= +5
O=-2
Which one represents electron affinity:
M(g)-> M+ (g) + e-
or
X(g)+ e- -> X- (g)
Name an atom with a higher electron affinity than Silicon
X(g)+ e- -> X- (g)
Name and describe the three types of bonding.
Covalent: sharing of electrons
Ionic: transfer of electrons
Metallic: electron pooling
How many electron regions does the molecule sulfur tetrafluoride have? What is its electron geometry and its molecular geometry?
SF4:
13 lone pairs and 4 single bonds = 17 electron regions
Electron geometry: Trigonal bipyramidal
Molecular geometry: Seesaw
Draw the resonance structures for phosphate (PO43-).

As atomic size increases the lattice energy:
increases/ or decreases
decreases
The electronegativity of carbon is 2.5 and that of fluorine is 4.0. How would you best characterize this bond?
A) ionice bond
B) metallic bond
C) non-polar covalent bond
D) polar covalent bond
D
What are the electron and molecular geometries for both central atoms in the molecule ClONO2?
Central O:
Electron geometry: Tetrahedral
Molecular geometry: Bent
Central N:
Electron geometry: Trigonal Planar
Molecular geometry: Trigonal Planar
Draw the Lewis structure for CO2. Show the bond dipoles using arrows. What is the bond polarity and what is the polarity of the overall molecule?
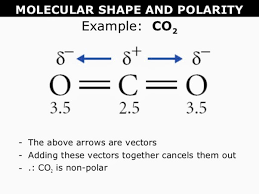
Bonds= Polar
Molecule= Non-polar
Knowing that size increases when going down a column, bond length (increases/ or decreases) going down a column?
*think about Zeff
Increases
Does CH2Cl2 have a net dipole? Why or why not?
Yes. 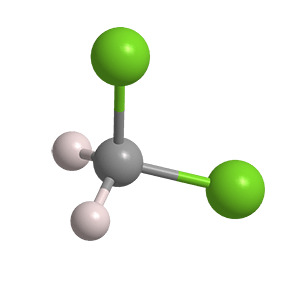
How many resonance structures are there for H2SO4?
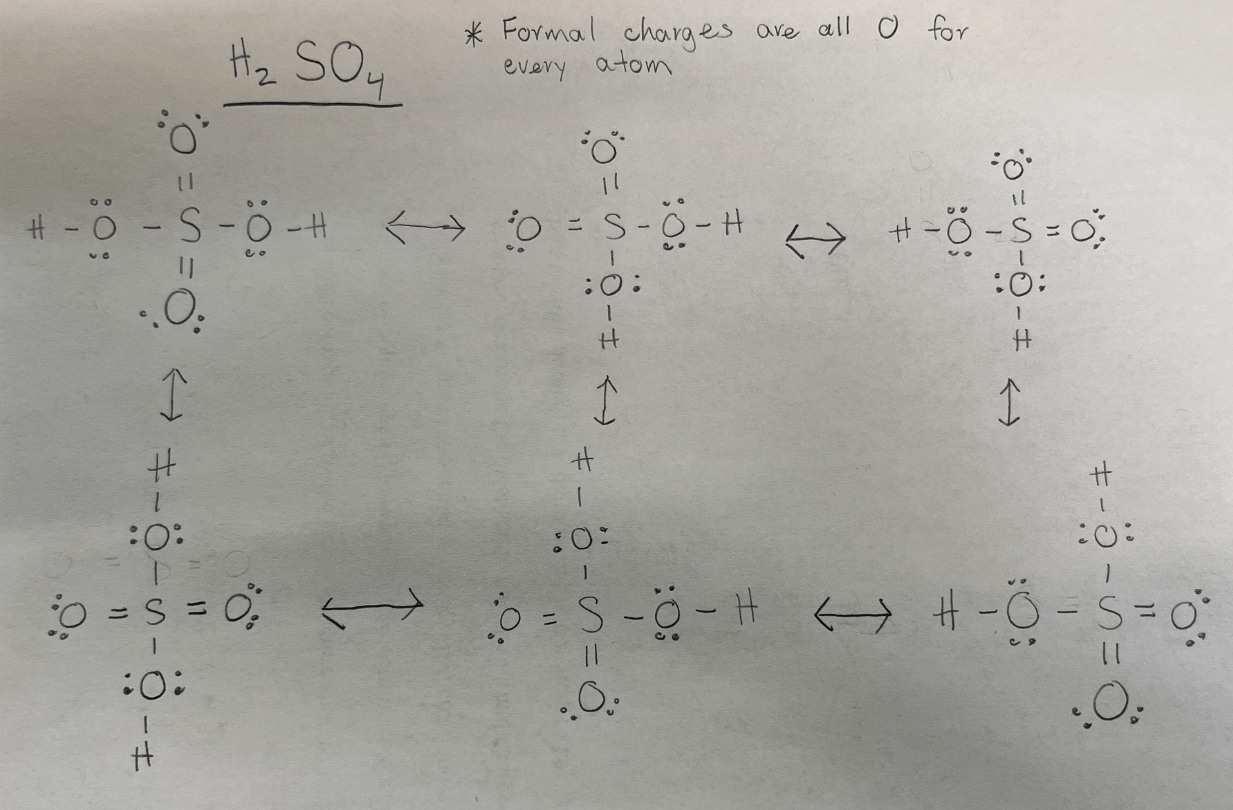
Draw the resonance structures of cyanide (CN-1) and then draw the hybrid. Calculate the formal charges of each atom and the oxidation state of each atom in both structures.

Left:
FC: C= -1, N=0
Oxi: C= +2, N= -3
Right:
FC: C= 0, N= -1
Oxi: C= +2, N=-3
Which of the following elements has the higher electron affinity: chlorine or fluorine? Explain your reasoning based on their positions in the periodic table and any relevant trends.
Fluorine has a higher electron affinity than chlorine. This is because, as we move from left to right across a period in the periodic table, the atomic radius generally decreases, and the effective nuclear charge experienced by the valence electrons increases. As a result, the attraction between the nucleus and an added electron becomes stronger, and the electron affinity increases. Fluorine is located to the right of chlorine in period 2 of the periodic table, and therefore has a smaller atomic radius and a higher effective nuclear charge. These factors contribute to its higher electron affinity compared to chlorine.