What is scarcity? Relate it to the study of economics.
Scarcity: limited resources in society --> we cannot produce all of the goods and services that people wish to have
Economics: the study of how society manages its scarce resources
Identify the market equilibrium price and quantity.
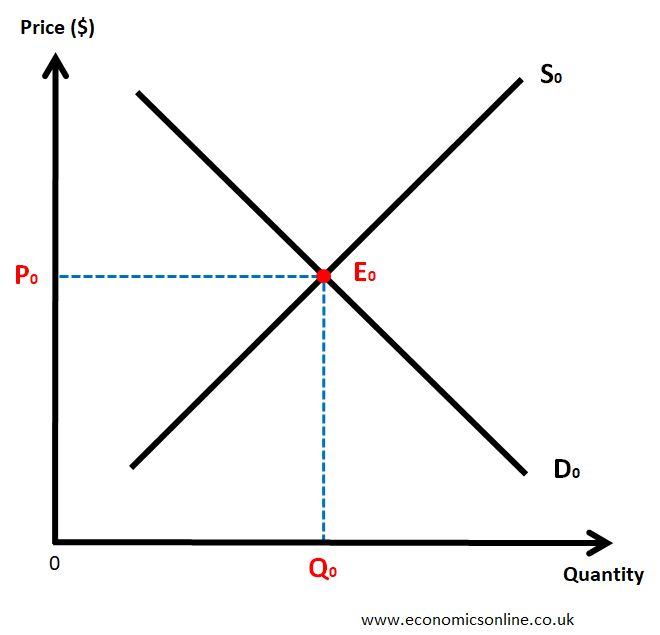
Equilibrium price: P0
Equilibrium quantity: Q0
Name the 4 types of unemployment
frictional, structural, seasonal, cyclical
Name two (or more) types of taxes.
Income, sales, excise, property, carbon
Top 4 countries w/ highest GDP (doesn't have to be in order)
United States: $30.34 trillion
China: $19.53 trillion
Germany: $4.92 trillion
Japan: $4.38 trillion
What is opportunity cost?
The loss of potential gain from alternative choices when one choice is chosen; the cost of the next best alternative
What is this curve called?
The production possibilities frontier / production possibilities curve (PPF / PPC)
What is a bank run?
bank run
What are the liberal and conservative points of view on taxes?
Liberal POV: want more taxes, especially corporate taxes / tax on the rich --> that way we can fund government projects for the public's benefit
Conservative POV: want less taxes, less government intervention
How to calculate GDP
C - consumer spending on goods and services
I - investor spending on business capital goods
G - government spending on public goods and services
Net exports = exports - imports
Name at least 3/5 factors of production.
Labor, human capital/knowledge, land/natural resources, capital, entrepreneurship

as, lras ad
What president enacted the New Deal OR what was its goals?
FDR
regain confidence in economy, create jobs
Name 4 different uses of taxes
education, military, research, etc
Name a limitation of GDP
Excludes work you do in the house (cooking, cleaning, growing vegetables) that you don’t pay someone for, illegal transactions (black market, drug dealing, etc)
- Does not account for income inequality in society, pollution, health, stress
What is the difference between macro and microeconomics?
Macroeconomics: large-scale, includes unemployment, inflation, economic growth, interest rates
Micro: small-scale; to how the individual, and household make decisions to allocate scarce resources,
What is this called OR explain the idea it shows?
Laffer Curve
What was 1 cause and 1 effect of Great Depression?
causes: stock market crash, low demand for goods+services
effects: 25% unemployment, bank runs
What is the difference between a progressive and regressive tax?
A progressive tax taxes the wealthy more, while a regressive tax means the poor pay a larger percent of their income in tax. (They're opposites)
What is a tariff and what is a quota?
tariff: tax on imports
quota: limit to # imported
Are public goods: rival or nonrival AND excludable / nonexcludable
nonrival, nonexcludable
The following is a graph of an international market. Identify the world price, price after tariff, tax revenue rectangle, and quantity imported after a tariff is applied.

World price: P1
Price after tariff: P2
Tax revenue rectangle: middle rectangle made from Q2 and Q3 lines
Quantity imported after tariff: Q3-Q2
Name one famous economist and what they are known for
Adam Smith, Keynes, Karl Marx, David Ricardo, Alfred Marshall, Laffer
Name one of the economic policies Trump has said he will implement as president / has already implemented and its effect
- tariffs (especially on goods from China)
- lower corporate taxes to 15%
- eliminate income taxes
- deportation (leads to labor shortages)
What does the Federal Reserve do?
controls money supply, determines monetary policy, regulates commercial banks, etc
