At what week does the fetal bowel normally return to the abdomen after physiological herniation?
What is 12 weeks
What abdominal wall defect occurs to the right of the umbilical cord and has no membrane covering?
What is gastroschisis?
Which syndrome includes omphalocele, macroglossia, and organomegaly?
What is Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome
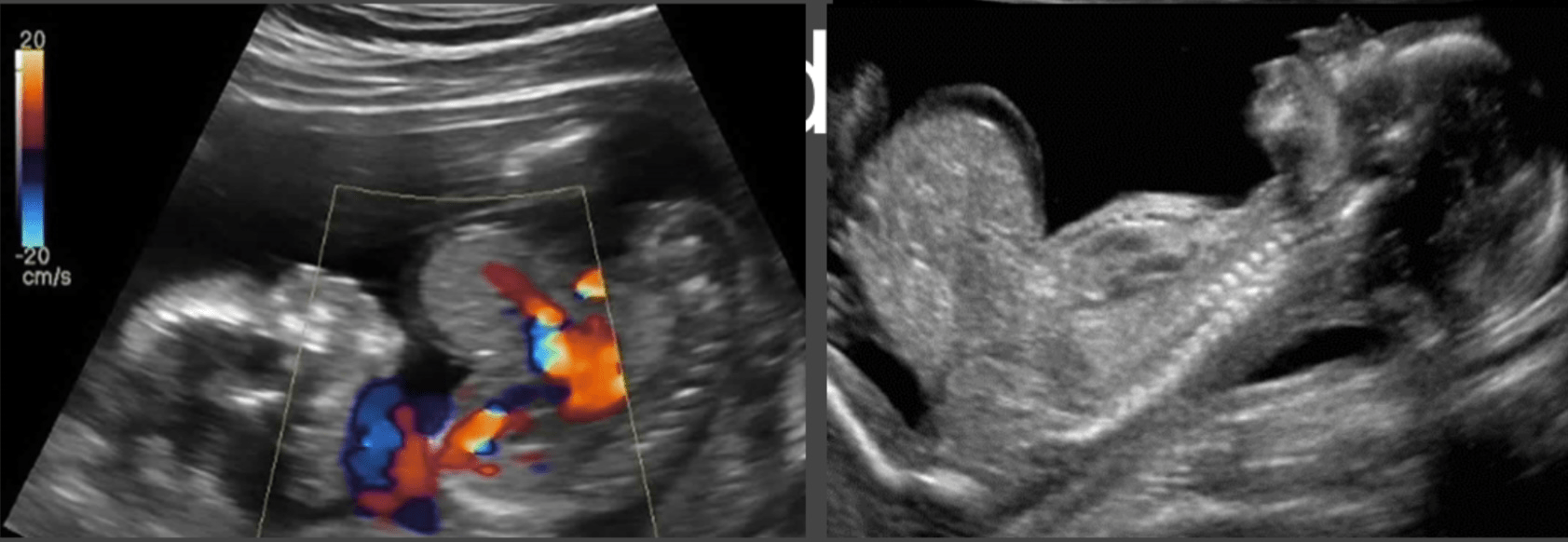
Image shows a midline abdominal wall defect where bowel and possibly liver are herniated into a membrane-covered sac. What is the most likely diagnosis?
What is Omphalocele
Which anterior wall defect features a membrane and may include bowel and liver?
What is omphalocele
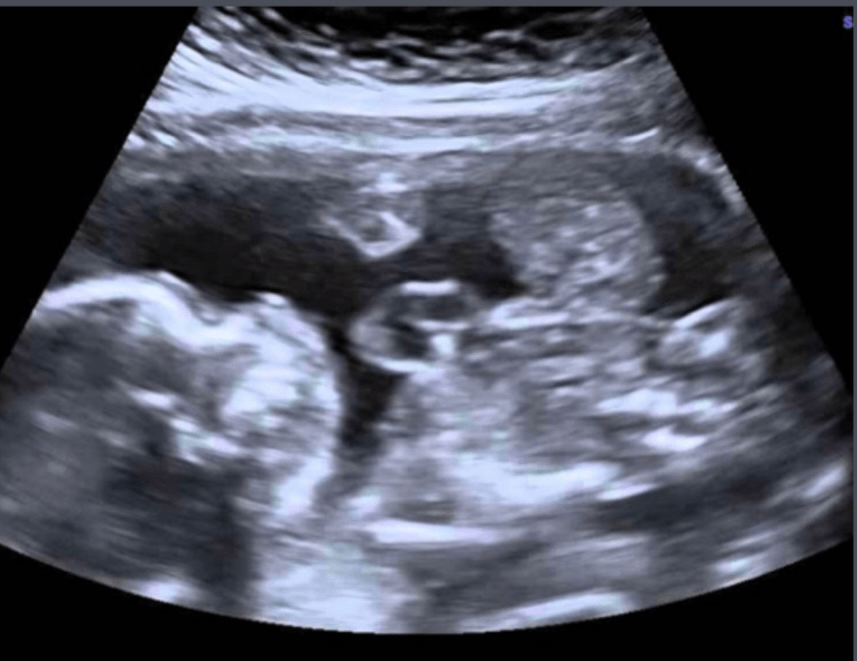
Image demonstrates a large anterior wall defect involving the sternum, diaphragm, pericardium, heart and abdominal wall. What syndrome is shown here?
What is Penalogy of Cantrell
This appearance on ultrasound suggests duodenal atresia.
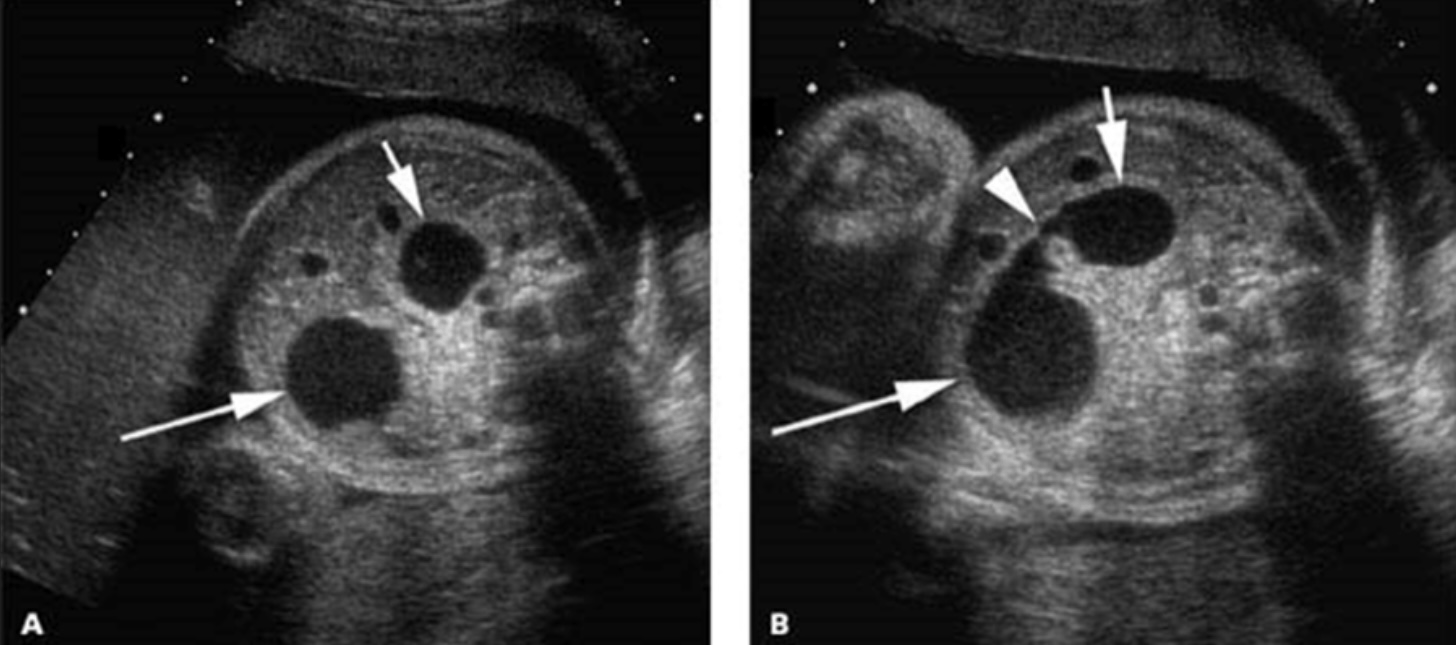
The sonographic image shows two fluid-filled structures in the upper abdomen, known as the "double bubble" sign. What condition does this represent?
What is Duodenal Atresia
What condition is indicated when the fetal stomach is not visualized, but amniotic fluid is increased?
What is esophageal atresia
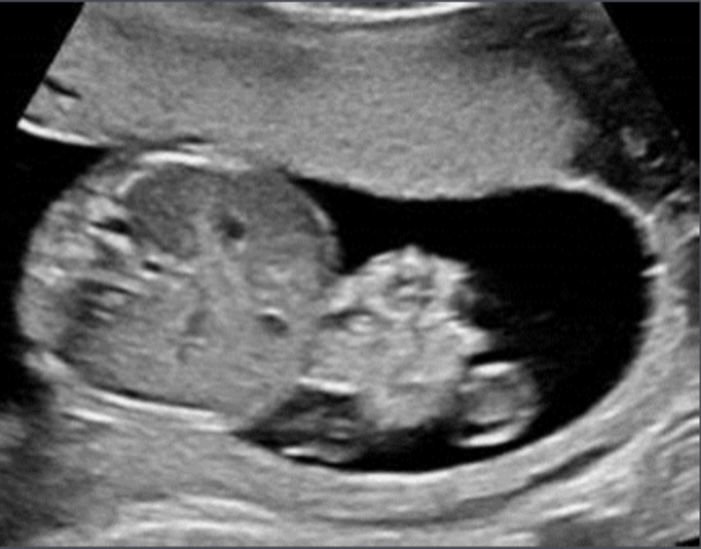
Image reveals free-floating bowel loops to the right of the umbilical cord with no surrounding membrane. What is the diagnosis?
What is Gastroschisis
What is the most common cause of echogenic small bowel in the fetus?
What is cystic fibrosis
What is meconium peritonitis
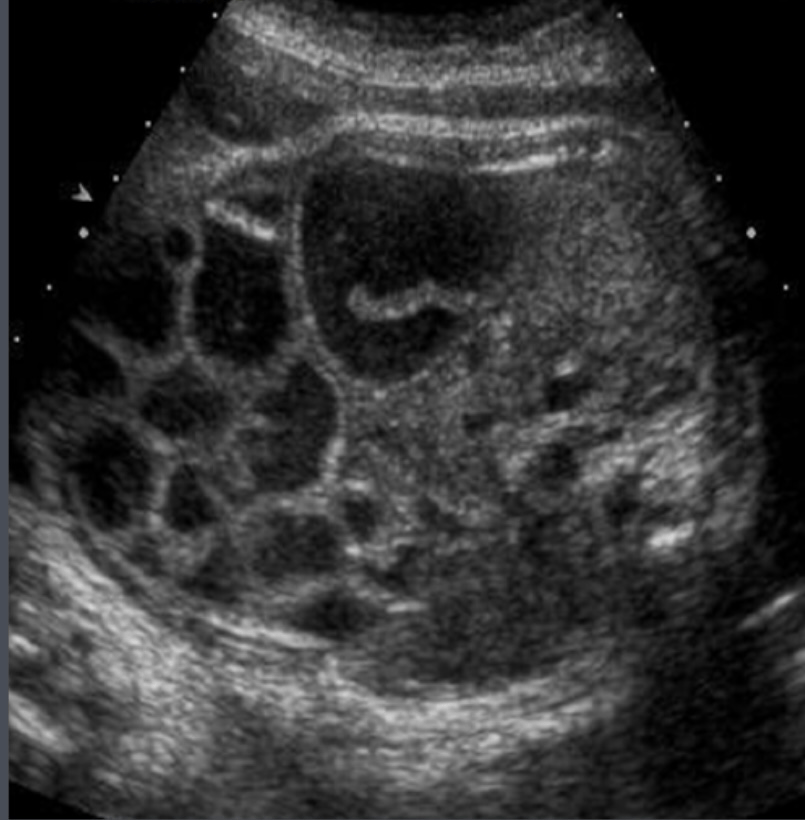
Image displays echogenic bowel in the lower abdomen, consistent with thick meconium. It is often associated with which condition?
What is Meconium Ileus