Identify the FHR Deceleration or Pattern on this strip.

What is Early Deceleration
Identify the FHR Deceleration or Pattern on this strip.
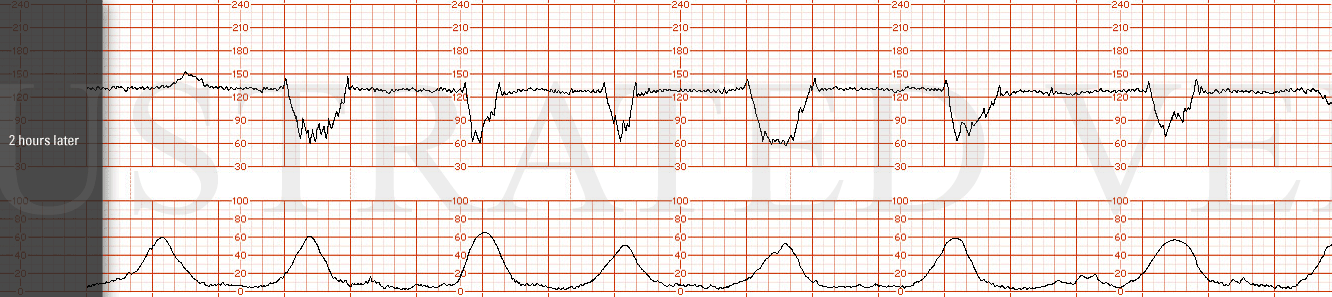
What is Variable Deceleration.
Identify the FHR Deceleration or Pattern on this strip.
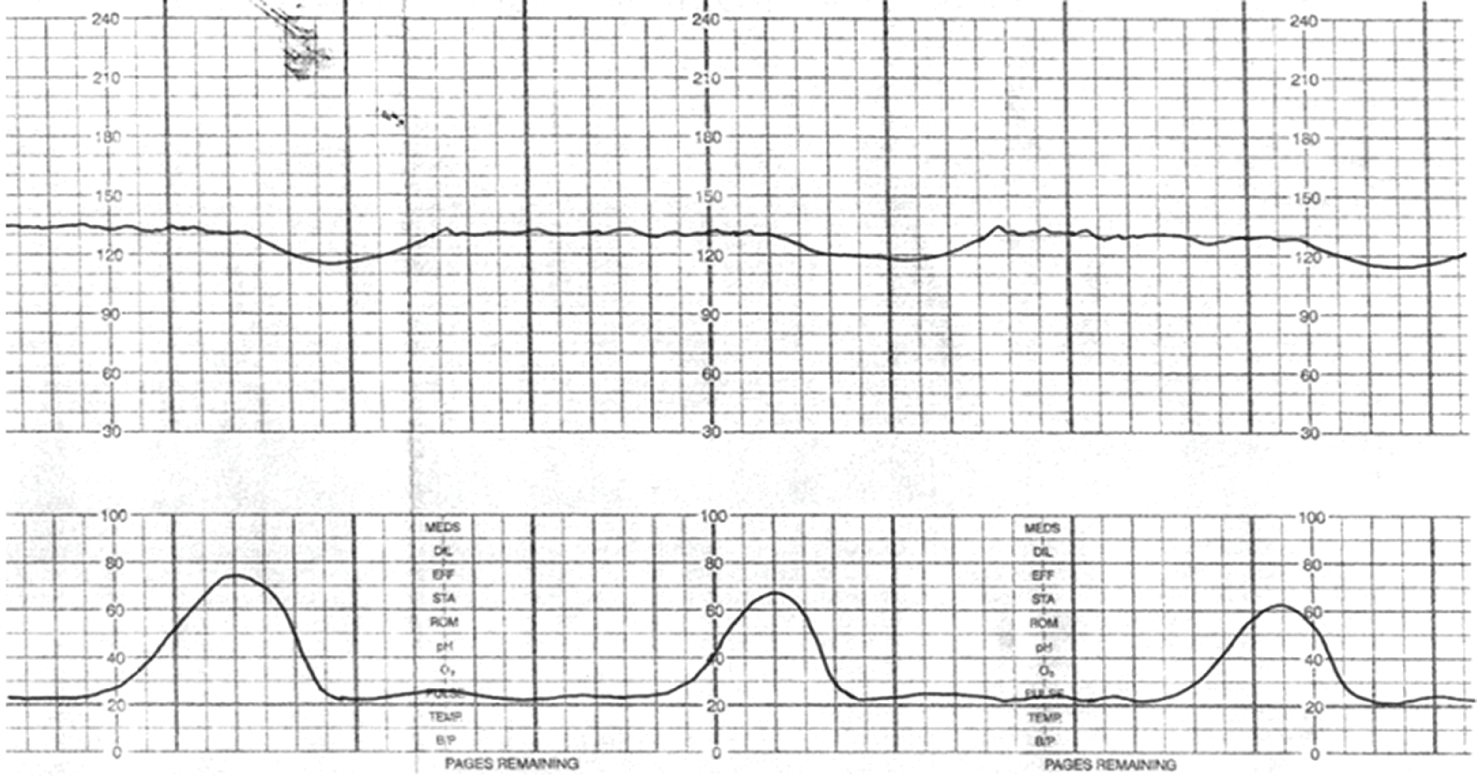
What is Late Deceleration.
The primary intervention to improve a fetal monitor strip showing repetitive variable decelerations.
What is change maternal position to L or R lateral.
Identify the FHR Deceleration or Pattern on this strip.

What is Prolonged Deceleration.
List 5 interventions that should always be initiated when visualizing repetitive late decelerations with a patient on Pitocin.
What is maternal position change to L or R lateral, D/C pitocin, 500 ml IV fluid bolus of NS or LR, O2 at 10 L by NRB, Notify Physician
Identify the FHR Deceleration or Pattern on this strip.
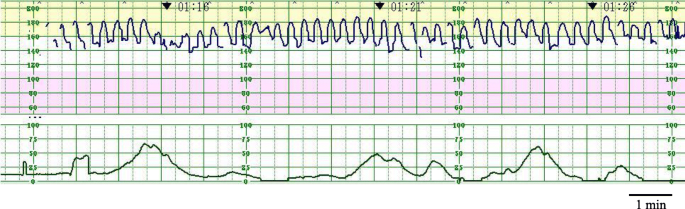
What is Undulating Pattern (or Sinusoidal).