What are the 3 things we evaluate FHR for?
Baseline
Variability
Periodic Changes
What are the 4 things we evaluate uterine activity for?
Frequency
Duration
Intensity
Resting Tone
Define acceleration
Abrupt increase in fetal heart rate
- <32 weeks' : >10 BPM above baseline for at least 10 seconds
- >32 weeks' : >15 BPM above baseline for at least 15 seconds
What does a Category I fetal heart tracing strongly predictive of?
Strongly predictive of normal acid-base status at the time of observation
What is the best intervention with this tracing?
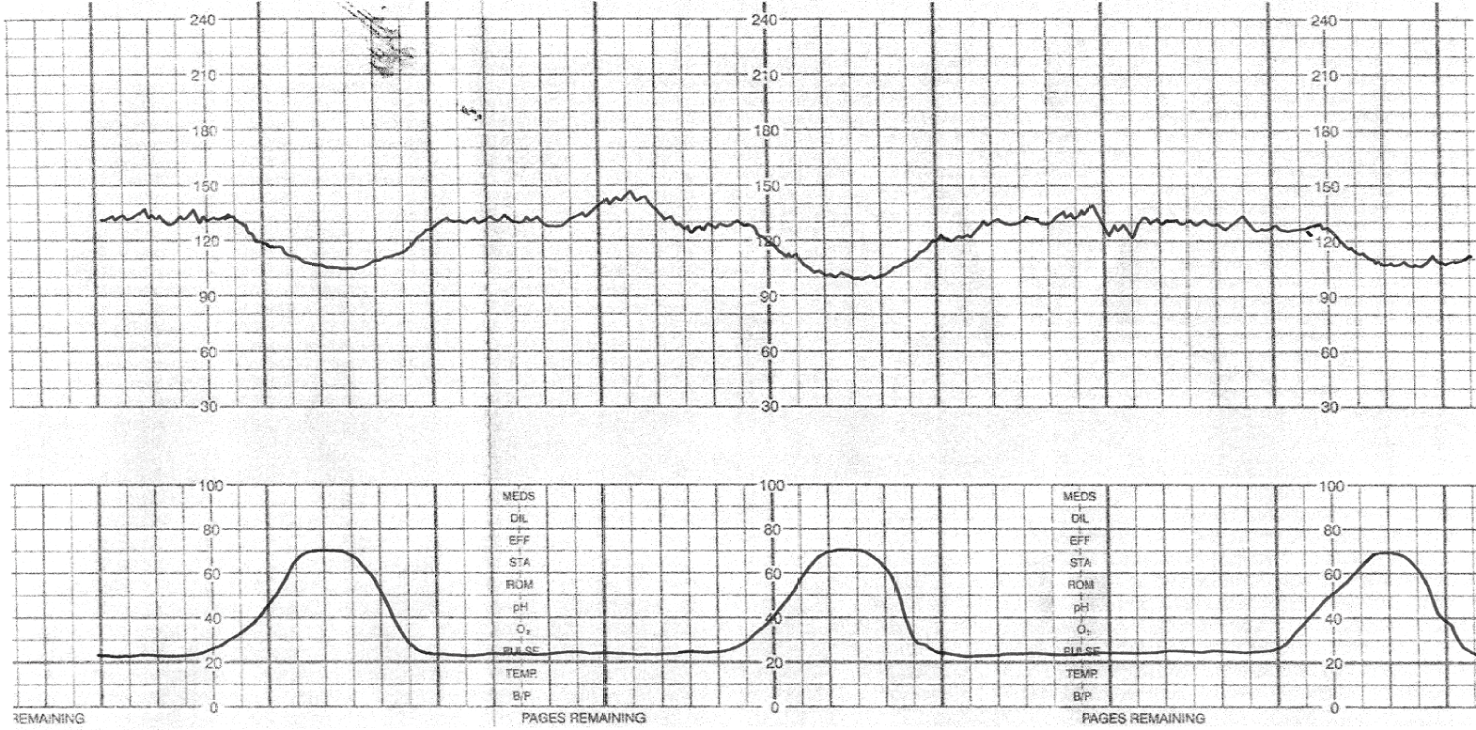
Early decelerations- no intervention
What is the normal FHR baseline?
110-160 bpm
What is the most accurate way to measure uterine intensity?
Intra-Uterine Pressure Cathode (IUPC)
Define early deceleration and cause
Gradual decrease in FHR with onset of deceleration to nadir >30 seconds. The nadir occurs with the peak of a contraction.
Cause: Fetal head compression
What is the difference between prolonged acceleration and baseline change?
Prolonged acceleration are > 2min but less than 10 min
Baseline Change is > 10 min
What would your FIRST intervention?

maternal position change
What are 2 examples of fetal heart tracing periodic changes?
Accelerations and decelerations
What is the uterine resting tone?
Relaxation between contractions
Define variable deceleration and cause
abrupt decrease in FHR with onset to nadir < 30 seconds, > or equal to 15 bpm, lasting > equal to 15 seconds, and < 2 minutes
Cause: Cord Compression
What is the criteria for "Recurrent" decelerations
Occur with more than or equal to 50% of contractions in any 20 minute period
What is the best interventions with this tracing?

Emergent delivery
Name the 4 variability classifications.
Absent
Minimal ( < 5 bpm)
Moderate (6-25 bpm)
Marked (> 25 bpm)
Define Tachysystole
More than 5 contractions in a 10 minute segment averages over a 30 minute period
Define late deceleration and cause
Gradual decrease in FHR with onset of deceleration to nadir >30 seconds. Onset of the decleration occurs after the beginning of the contraction, and the nadir of the contraction occurs after the peak of the contraction.
Cause: Uteroplacental Insufficiency
What is the definition of a category III fetal heart tracing?
Sinusoidal pattern OR
Absent variability with
- recurrent late decelerations,
- recurrent variable decelerations, or
-bradycardia.
Name 4 nursing interventions for intrauterine resuscitation
Position changes
Turn off pitocin
IVF bolus
Oxygen
What 2 patterns are a reliable prediction of the absence of fetal metabolic acidemia?
Moderate variability and/or
presence of accelerations
What serious event could an increased uterine resting tone indicate?
placental abruption
What is the definition of a prolonged deceleration?
A decrease in FHR of > 15 beats per minute measured from the most recently determined baseline rate. The deceleration lasts >= 2 minutes but less than 10 minutes
What are 3 causes of a prolonged deceleration?
- Maternal hypotension
- uterine hyperactivity
- cord prolapse
- cord compression
- abruption
- artifact (maternal heart rate)
- maternal seizure
What could the be the cause of this tracing?

- severe fetal anemia
- fetal hypoxia
- fetal acidosis