Definition of normal baseline rate
What is 110-160 bpm?
Variability is a reflection of fetal oxygenation status and what other influence, of which healthy interplay results in a continual increase and decrease of the heart rate to optimize fetal cardiac output.
What is the autonomic nervous system (sympathetic and parasympathetic modulation)?
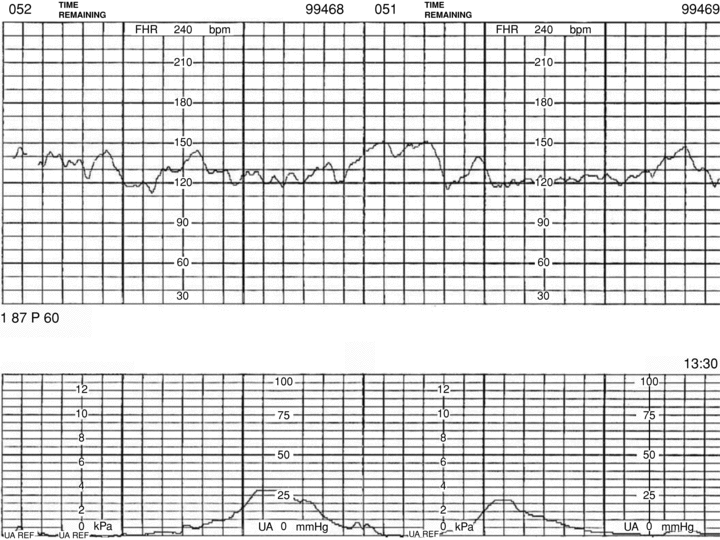
Name any Periodic/Episodic event(s) present in this tracing. If none, say absent.
What are accelerations?
Bonus:
(100pts) What gestational age requires 15x15 accelerations?
What all fetuses experience with uterine contractions.
The purpose of an amnioinfusion.
What is to correct fetal heart rate changes caused by umbilical cord compression?
There must be at least __ minutes of identifiable baseline segments to determine a baseline rate.
What is 2 minutes (not necessarily contiguous)?
The variability depicted in this tracing.
What is moderate?
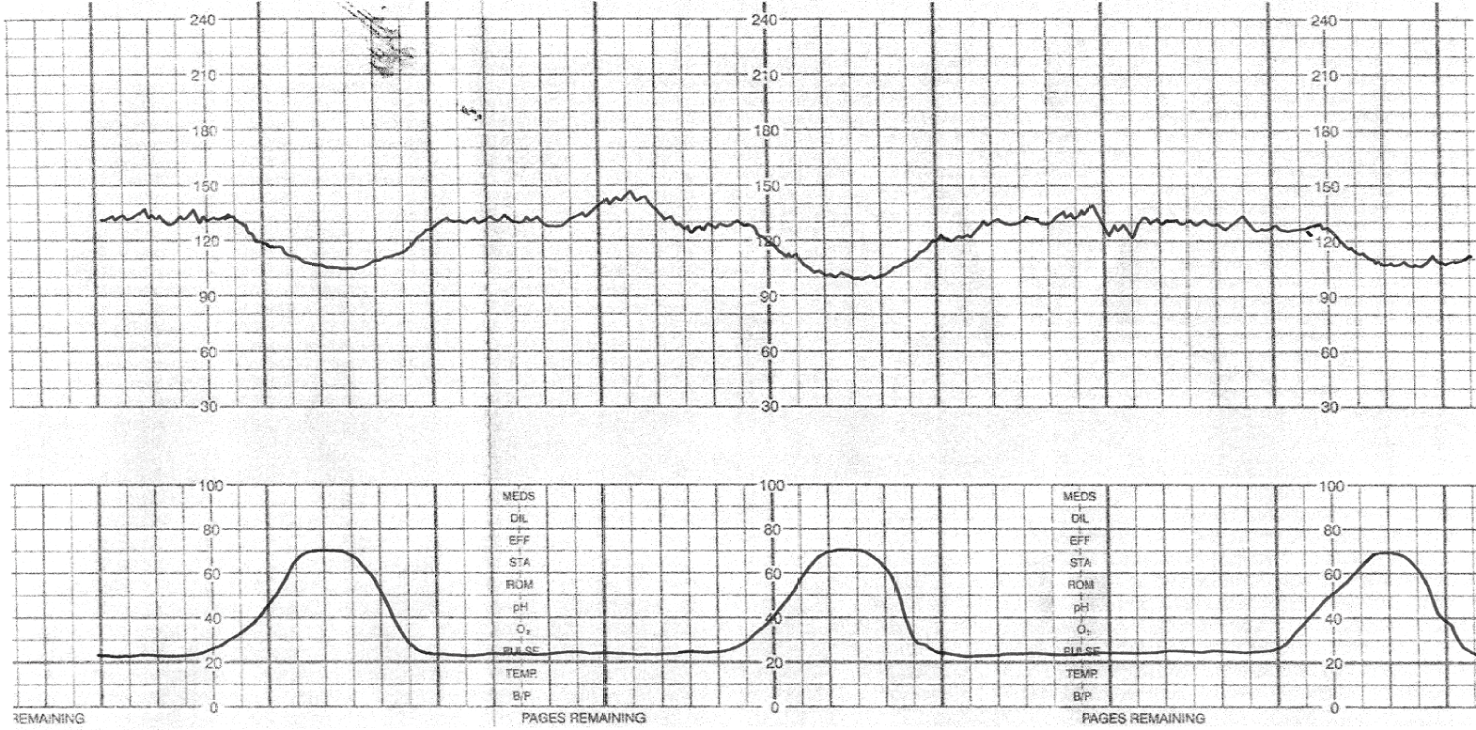 The physiology behind an early deceleration.
The physiology behind an early deceleration.
What is pressure on the fetal head stimulates the vagus nerve and causes the heart rate to decrease?
What is fetal reserve?
Bonus:
(200pts) Name the two components of fetal reserve.
Appropriate positions to facilitate labor progression.
Gestational age plays a big part in the baseline fetal heart rate because of the maturation of this component of the cardio regulatory center (CRC).
What is the parasympathetic tone?
Sympathetic tone is much more mature in the preterm fetus; therefore the baseline FHR is usually at the higher ends of normal.
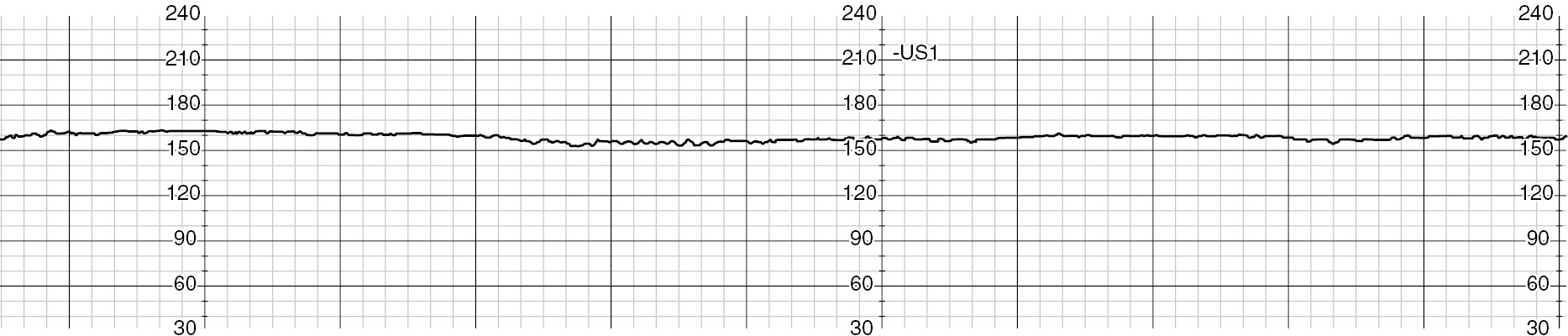
Definition of absent variability.
What is undetectable?
 Periodic/Episodic event(s) present in this tracing.
Periodic/Episodic event(s) present in this tracing.
What is variable decelerations?
The influences that (1) affect blood flow to the fetus and (2) the ability of the fetus to maintain homeostasis.
What are Extrinsic and Intrinsic factors?
Bonus:
(100pts) Name 2 extrinsic factors
(100pts) Name 2 intrinsic factors
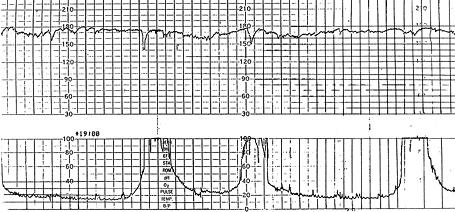
Based on this information alone, name 3 appropriate interventions for this tracing.
What are evaluate maternal vitals, reposition, fluid bolus, and/or cervical exam
Bonus:
(300pts) Explain the rationale behind your interventions.
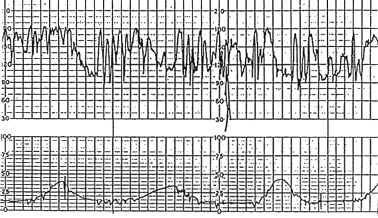 The baseline of this tracing.
The baseline of this tracing.
What is indeterminate?
 Three categories of causes for decreased variability.
Three categories of causes for decreased variability.
What are sleep cycles, sedation/CNS depressant, or neurologic injury/acidosis?
Match the following term with their appropriate definition:
Episodic >50% of time in 20-min
Intermittent Not with contractions
Periodic Occurs with contractions
Recurrent <50% of time in 20-min
Episodic = not with contractions
Periodic = with contractions
Intermittent = <50% of time in 20-min
Recurrent = >50% of time in 20-min
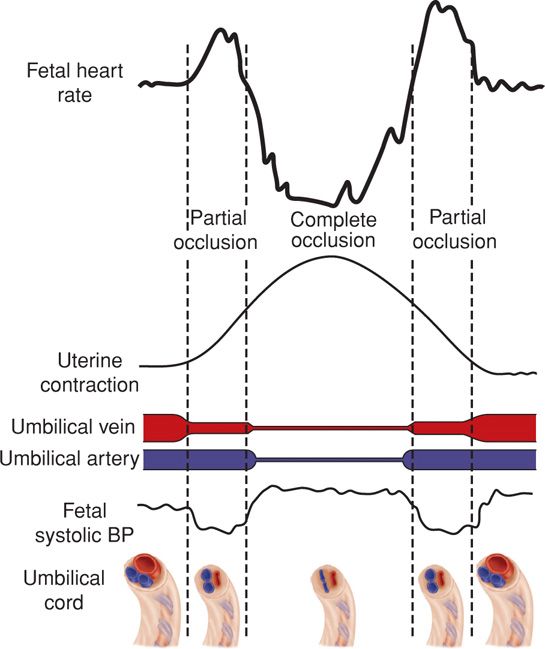 The stimulation of these receptors causes abrupt changes in the FHR as a compensation for fetal blood pressure changes secondary to compression on the umblical vessels.
The stimulation of these receptors causes abrupt changes in the FHR as a compensation for fetal blood pressure changes secondary to compression on the umblical vessels.
What are baroreceptors?
Most ideal positions to increase maternal venous return and cardiac output.
What are left or right lateral or knee chest?
This hemodynamic measure is primarily determined by the fetal heart rate.
What is cardiac output?
Which of the following is true:
A. The absence of moderate variability reliably predicts the presence of metabolic acidosis.
B. The absence of variability is the only definitive indication of acid-base status.
C. The presence of moderate variability reliably predicts the absence of metabolic acidosis.
D. The degree of acidosis correlates with the amount of variability.
What is C?
Caused by compression of maternal blood vessels in the myometrium, reducing maternal perfusion to the intervillous space. This results in reduced diffusion of gasses and a decline in fetal PO2. The fetal response is peripheral vasoconstriction, shunting blood toward vital organs and resulting in increased fetal blood pressure, stimulating a parasympathetic reflex slowing of the fetal heart rate.
What is the mechanism of late decelerations?
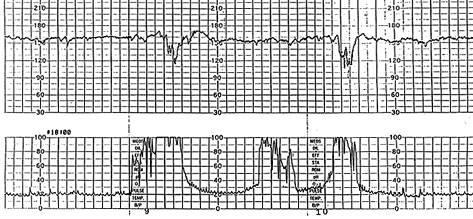
 Your patient is complete and pushing in this tracing. How would you interpret this tracing?
Your patient is complete and pushing in this tracing. How would you interpret this tracing?
What is indeterminate/signal ambiguity?
Bonus:
(500pts) Why is this tracing unusual during second stage?
The time(s) ACOG recommends the use of supplemental Oxygen, according to their practice bulliton January 2022.
What is with maternal hypoxia?